leetcode基础知识 - 栈和队列
这里写目录标题
- 目录
- STL - 栈(stack)和队列(queue)
- 练习题
- 两个队列模拟栈操作
- 两个栈模拟队列操作 - LC232
- 最小栈- 返回栈中最小的元素 LC155
- 出栈顺序是否合法
- 队列合法的情况
- 顺序不合法过程
- 模拟计算器
- 栈模拟计算
- 栈处理优先级 compute_flag 记录是否可以计算
- 计算过程
- 模拟计算器实现
- 字符串转数字
- 单次计算
- 字符串处理 - 状态机
- 实现
- STL-优先级队列(priority queue) 实现 堆(heap)
- 最大堆最小堆
- 练习题- 堆
- 第k大的数字 -LC215
- 获取中位数
- 过程
- 实现
目录
STL - 栈(stack)和队列(queue)
练习题
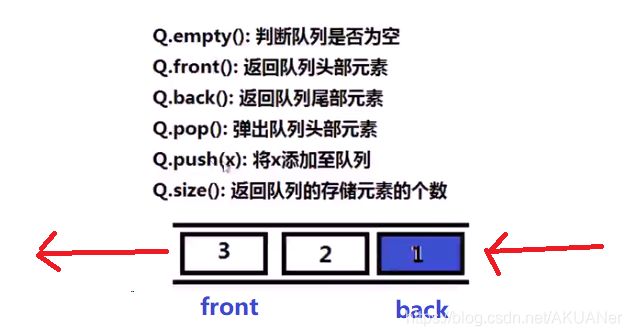
两个队列模拟栈操作
pop - 删除队首
push 插入到队尾
队首que队尾
myque不可能有超过一个元素,
temque是用来存储和调换顺序的
核心思想:
新元素入temque
清空myque
清空temque
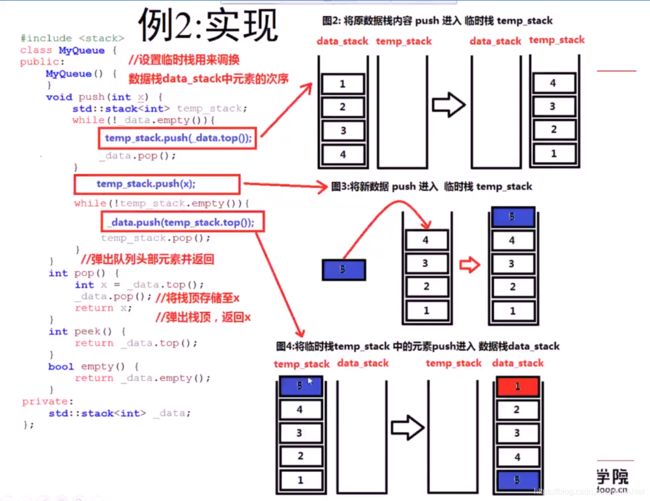
#include 两个栈模拟队列操作 - LC232
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> mystack;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stack<int> temstack;
while (!mystack.empty())
{
temstack.push(mystack.top());
mystack.pop();
}
temstack.push(x);
while (!temstack.empty())
{
mystack.push(temstack.top());
temstack.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int val = mystack.top();
mystack.pop();
return val;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
return mystack.top();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return mystack.empty();
}
};
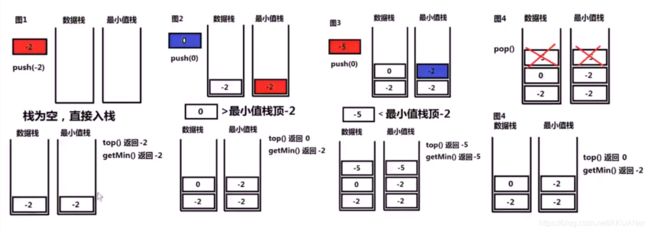
最小栈- 返回栈中最小的元素 LC155
借助一个栈minstack,辅助栈每次压入当前mystack的最小值
就三步
step1: x -> mystack
step2 : if temstack.empt() ?
strp3 : x -> temstack
temstack为空,直接进, 不为空 比较x和temstack.top()的大小
#include 代码优化
if (x > temstack.top())
{
x = temstack.top();
temstack.push(x);
}
else {
temstack.push(x);
}
}
}
优化后
if (x > temstack.top())
{
x = temstack.top();
}
temstack.push(x);
}
}
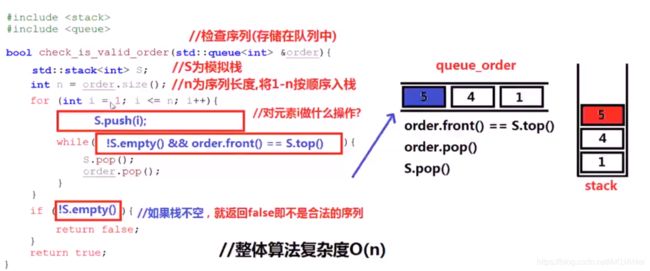
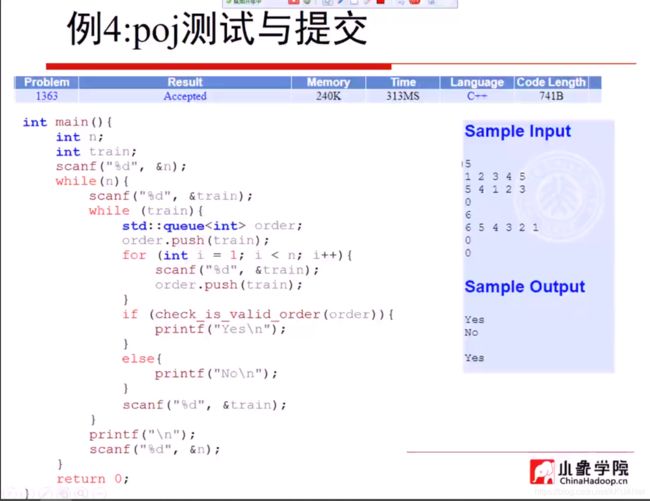
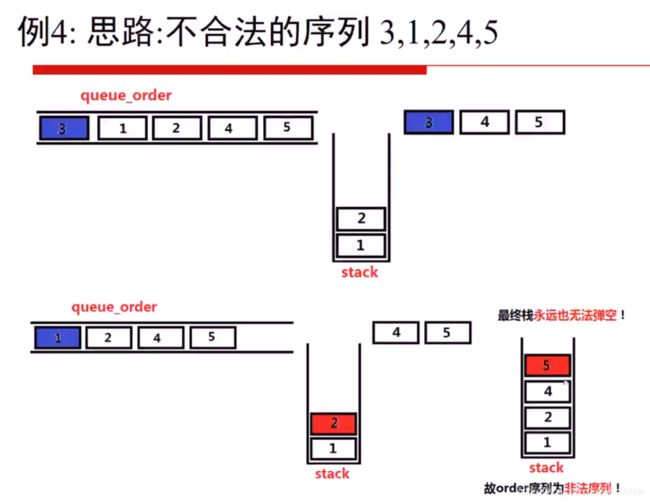
出栈顺序是否合法
输出12345
判断32541的出栈循序是否合法
输出12345,for循环压入栈
32541 队列que存储
用队列首 和 栈顶 比较, 相同就出栈 出队列 ,不同就继续入栈 ,队列不同
队列合法的情况
顺序不合法过程
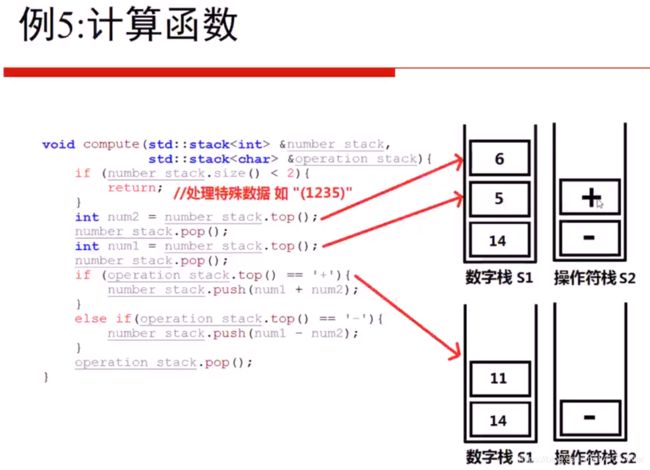
模拟计算器
栈模拟计算
数据放入一个栈, 符号放入另一个栈
调用的时候 就是数据栈的top 和数据栈的top-1 用 符号栈的top 进行运算
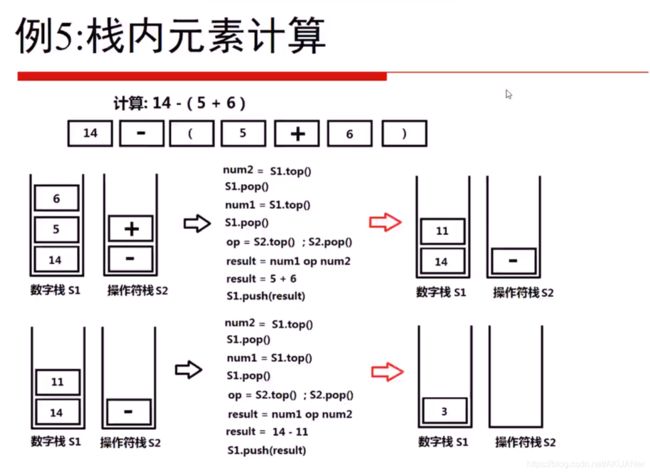
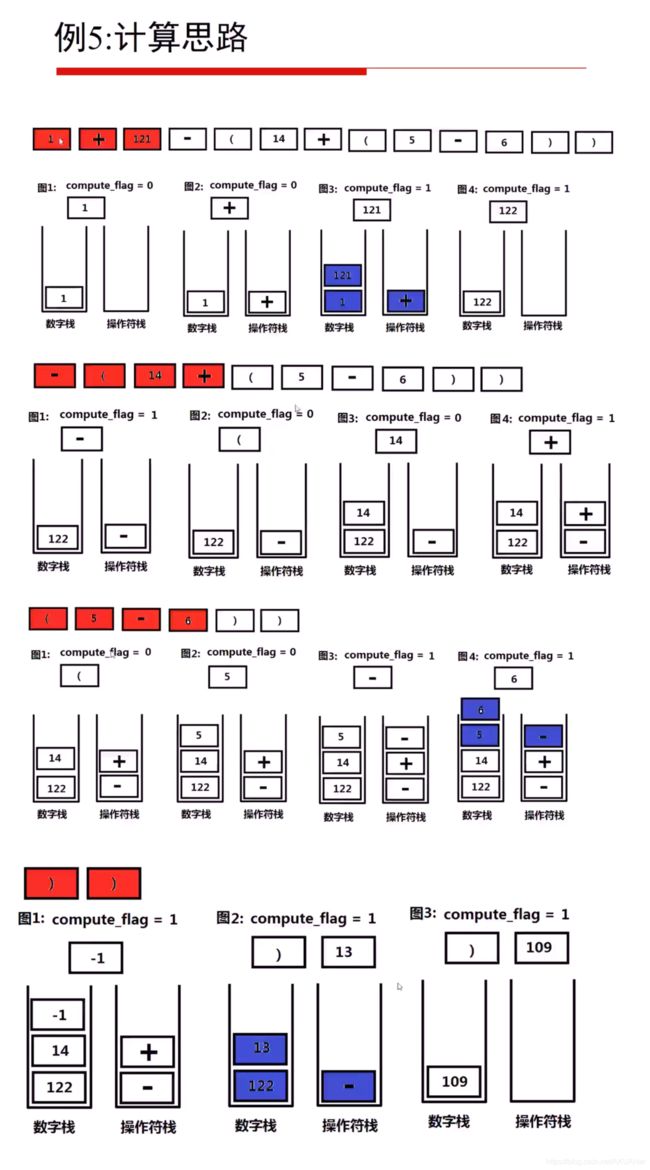
栈处理优先级 compute_flag 记录是否可以计算
计算过程
遇见( compute_flag = 0 ;
即使后面来了数字,也没办法计算
遇见其他运算符+ - flag 变回1
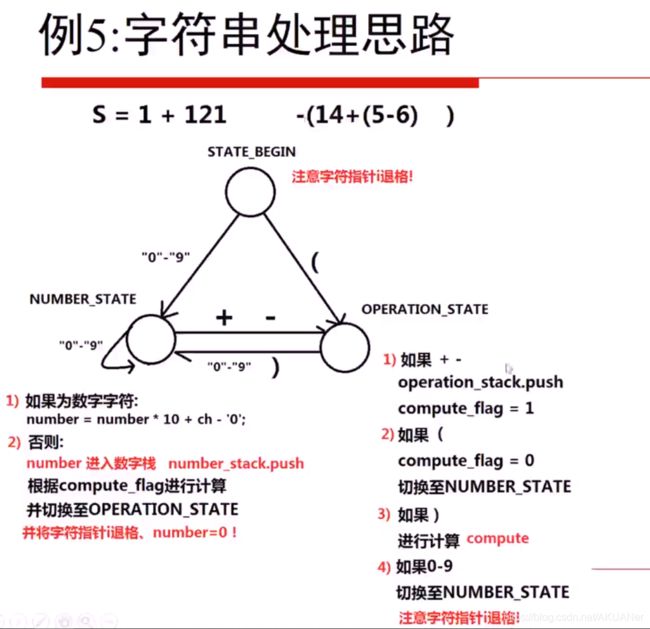
模拟计算器实现
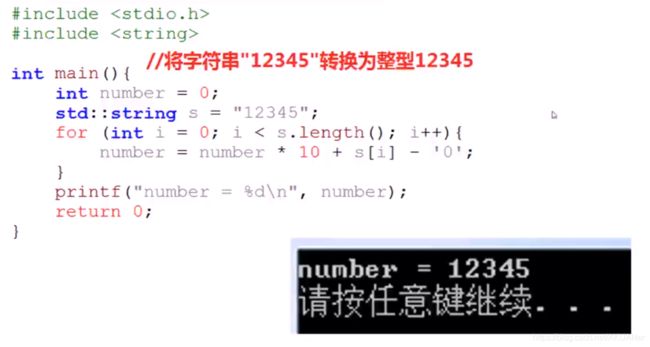
字符串转数字
for循环string str[i]-‘0’ 就转成了对应的数字
number = number * str[i]-‘0’ //是为了转成对应的数字串
单次计算
字符串处理 - 状态机
实现
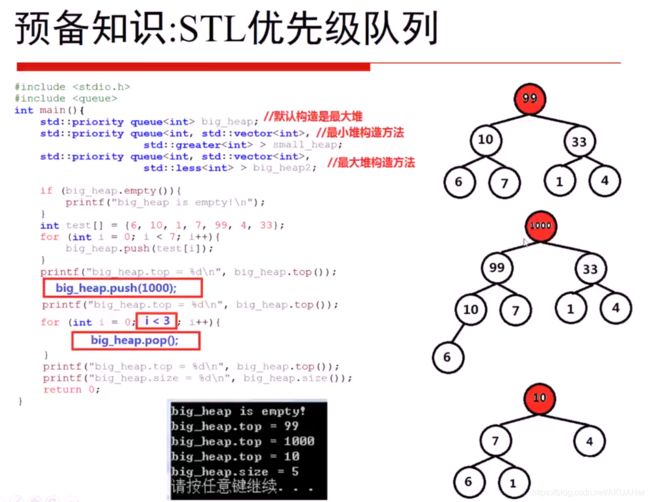
STL-优先级队列(priority queue) 实现 堆(heap)
最大堆最小堆
priority queue<int> bigheap; //默认是最大堆
priority queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > bigheap;
//大根堆
priority queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > smallheap;
//小根堆
练习题- 堆
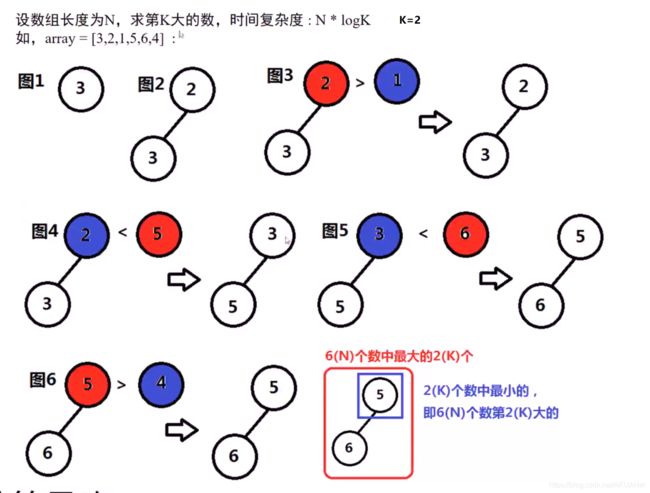
第k大的数字 -LC215
思路:
way: 数组排序,返回第k个位置 O(nlogn)
way2:维持堆的规模为K , O(nlogk)
小根堆
当规模
如果堆顶<新元素,则新元素加入堆,堆顶弹出
保证了入堆的都是大数, 余下了K个,小根堆 所以堆顶K个数据里最小的那个;
#include
greater
#include way2:
#include //算法
sort(myvec.begin(),myvec.end());
#include 获取中位数
way1:
未构造 - 每次添加元素的时候,对数组进行排序
插入O(n) , 查找中位数O(1)
已构造 - 每次查询中位数的时候进行排序
插入O(1),查询中位数O(nlogn)
若以上操作是随机操作,复杂度为O(n^2)
way2: 维护两个堆, 一个大根堆一个小根堆
大根堆的 堆顶 , 比 小根堆的堆顶 要 小
理解: 降序序列的最大值 , 比升序序列的最小值 要小,则 降序序列的所有值都比升序序列小
当数组为偶数 , 则 两堆堆顶 /2 = 中位数
当数组为奇数,则 谁堆的元素多, 谁的堆顶就是中位数

核心 : 维护两个状态
状态1 :大根堆和小根堆的元素数量差值<1
状态2: 大根堆的堆顶 比 小根堆的堆顶 小
过程
3种情况:
差值 = 0
大根堆>小根堆
小根堆>大根堆
每种情况又有2种可能:
新元素 < 大根堆
新元素 > 大根堆
组合起来就是6种可能