3.1paddlepaddle数字识别,多层感知机(MLP)、卷积神经网络(CNN)
识别黑白图片中的数字
-
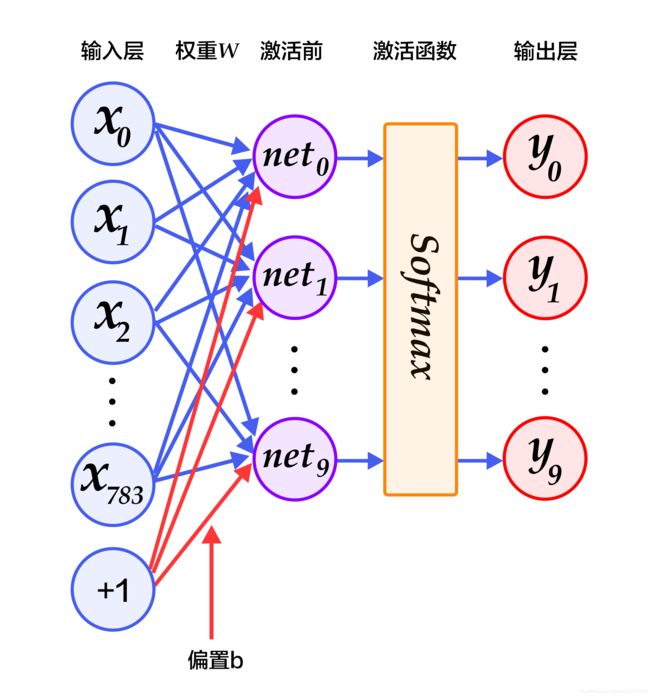
X是输入:MNIST图片是28×28 的二维图像,为了进行计算,我们将其转化为784维向量,即 X = ( x 0 , x 1 , … , x 783 ) X=\left ( x_0, x_1, \dots, x_{783} \right ) X=(x0,x1,…,x783)
-
Y是输出:分类器的输出是10类数字(0-9),即 Y = ( y 0 , y 1 , … , y 9 ) Y=(y_0,y_1,…,y_9) Y=(y0,y1,…,y9),每一维 y i y_i yi代表图片分类为第i类数字的概率
-
如某张图片上的数字为2,则它的标签为(0,0,1,0,…,0)
多层感知机(MLP)
交叉熵代价损失函数(cross entropy loss),公式如下:
L c r o s s − e n t r o p y ( l a b e l , y ) = − ∑ i l a b e l i l o g ( y i ) L_{cross-entropy}(label,y)=-\sum_ilabel_i log(y_i) Lcross−entropy(label,y)=−∑ilabelilog(yi)
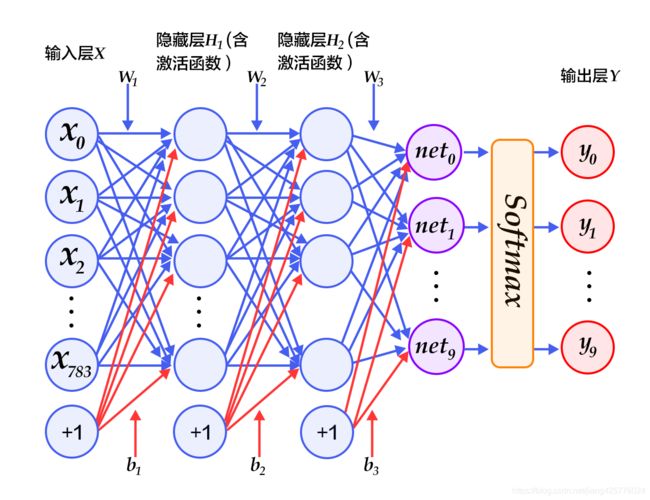
- 经过第一个隐藏层,可以得到 H1=ϕ(W1X+b1),其中ϕ代表激活函数,常见的有sigmoid、tanh或ReLU等函数。
- 经过第二个隐藏层,可以得到 H2=ϕ(W2H1+b2)
- 最后,再经过输出层,得到的Y=softmax(W3H2+b3),即为最后的分类结果向量。
paddle官方介绍:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/beginners_guide/basics/recognize_digits/README.cn.html
paddle.fluid.DataFeeder:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/fluid_cn/DataFeeder_cn.html#datafeeder
import numpy as np
import paddle as paddle
import paddle.dataset.mnist as mnist
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def multilayer_perceptron(ipt):
hidden1 = paddle.fluid.layers.fc(input=ipt, size=100, act='relu')
hidden2 = paddle.fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden1, size=100, act='relu')
# 输出10个类别的概率
out = paddle.fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden2, size=10, act='softmax')
return out
def define_data():
# 输入单张数据的大小,也可以把1变成-1,意味着任意大小,通常框架中第一个维度是批量数据batch size的大小
image = fluid.layers.data(name='image', shape=[1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
label = fluid.layers.data(name='label', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
return image, label
def cost(outy, label):
cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=outy, label=label)
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
acc = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=outy, label=label)
return avg_cost, acc
def optimizer(cost):
# 定义优化方法
fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(cost)
def execut():
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
return place, exe
def train(test_program,feeder, train_reader, test_reader, avg_cost, acc, exe):
# 开始训练和测试
for pass_id in range(10):
# 进行训练
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
train_cost, train_acc = exe.run(program=fluid.default_main_program(),
feed=feeder.feed(data),
fetch_list=[avg_cost, acc])
# 每100个batch打印一次信息
if batch_id % 1000 == 0:
print('Pass:%d, Batch:%d, Cost:%0.5f, Accuracy:%0.5f' %
(pass_id, batch_id, train_cost[0], train_acc[0]))
# 进行测试
test_accs = []
test_costs = []
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_reader()):
test_cost, test_acc = exe.run(program=test_program,
feed=feeder.feed(data),
fetch_list=[avg_cost, acc])
test_accs.append(test_acc[0])
test_costs.append(test_cost[0])
# 求测试结果的平均值
test_cost = (sum(test_costs) / len(test_costs))
test_acc = (sum(test_accs) / len(test_accs))
# print('Test:%d, Cost:%0.5f, Accuracy:%0.5f' % (pass_id, test_cost, test_acc))
def load_image(file):
im = Image.open(file).convert('L')
im = im.resize((28, 28), Image.ANTIALIAS)
im = np.array(im).reshape(1, 1, 28, 28).astype(np.float32)
im = im / 255.0 * 2.0 - 1.0
return im
def test(test_program, model, exe):
img = Image.open('9.png')
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
img = load_image('9.png')
# 设置一个假的label值传进去
results = exe.run(program=test_program,
feed={'image': img, "label": np.array([[0]]).astype("int64")},
fetch_list=[model])
print(results)
lab = np.argsort(results)
print("该图片的预测结果的label为: %d" % lab[0][0][-1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
image, label = define_data()
model = multilayer_perceptron(image)
avg_cost, acc = cost(model, label)
# 在模型定义输出后,优化之前,拷贝好测试程序
test_program = fluid.default_main_program().clone(for_test=True)
optimizer(avg_cost)
place, exe = execut()
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
# 训练数据
train_reader = paddle.batch(mnist.train(), batch_size=128)
test_reader = paddle.batch(mnist.test(), batch_size=128)
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(place=place, feed_list=[image, label])
train(test_program,feeder, train_reader, test_reader, avg_cost, acc, exe)
test(test_program, model, exe)
# 效果一般,图像还是用卷积的好
卷积神经网络(CNN)
import numpy as np
import paddle as paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from PIL import Image
def convolutional_neural_network(img):
# 使用20个5*5的滤波器,池化大小为2,池化步长为2,激活函数为Relu
conv_pool_1 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
input=img,
filter_size=5,
num_filters=20,
pool_size=2,
pool_stride=2,
act="relu")
conv_pool_1 = fluid.layers.batch_norm(conv_pool_1)
# 第二个卷积-池化层
# 使用50个5*5的滤波器,池化大小为2,池化步长为2,激活函数为Relu
conv_pool_2 = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(
input=conv_pool_1,
filter_size=5,
num_filters=50,
pool_size=2,
pool_stride=2,
act="relu")
# 以softmax为激活函数的全连接输出层,输出层的大小必须为数字的个数10
prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=conv_pool_2, size=10, act='softmax')
return prediction
def train(feeder, train_reader, test_reader, avg_cost, acc, test_prog=None, train_prog=None, exe=None):
# 开始训练和测试
for pass_id in range(2):
total_loss = 0.00
total_acc = 0.00
# 进行训练
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
train_cost, train_acc = exe.run(program=train_prog,
feed=feeder.feed(data),
fetch_list=[avg_cost, acc])
total_loss += np.mean(train_cost)
total_acc += np.mean(train_acc)
# 每100个batch打印一次信息
if batch_id % 100 == 0:
print('Pass:%d, Batch:%d,Loss:%.3f, acc :%.3f' %
(pass_id, batch_id, total_loss / 100.00, total_acc / 100.00))
total_loss = 0.00
total_acc = 0.00
# save model
if pass_id % 100 == 0:
save(params_dirname='卷积', feeded_var_names=['image'], target_vars=[predict], executor=exe)
# 进行测试
test_accs = 0.0
test_costs = 0.0
test_num = 0
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_reader()):
test_cost, test_acc = exe.run(program=test_prog,
feed=feeder.feed(data),
fetch_list=[avg_cost, acc])
test_accs += np.mean(test_acc)
test_costs += np.mean(test_cost)
test_num += 1
# 求测试结果的平均值
test_cost = test_costs / test_num
test_acc = test_accs / test_num
print('Test:%d, Cost:%0.5f, Accuracy:%0.5f' % (pass_id, test_cost, test_acc))
def load_image(file):
im = Image.open(file).convert('L')
im = im.resize((28, 28), Image.ANTIALIAS)
im = np.array(im).reshape(1, 1, 28, 28).astype(np.float32)
im = im / 255.0 * 2.0 - 1.0
return im
def save(params_dirname, feeded_var_names, target_vars, executor):
fluid.io.save_inference_model(dirname=params_dirname, feeded_var_names=feeded_var_names,
target_vars=target_vars, executor=executor)
print("Saved checkpoint: %s" % (params_dirname))
def test(model, compiled_test_prog, exe):
img = Image.open('image/9.png')
# plt.imshow(img)
# plt.show()
# 设置一个假的label值传进去
results = exe.run(program=compiled_test_prog,
feed={'image': img},
fetch_list=[model])
lab = np.argsort(results)
print("该图片的预测结果的label为: %d" % lab[0][0][-1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = fluid.data(name='image', shape=[None, 1, 28, 28], dtype='float32')
label = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[None, 1], dtype='int64')
if_cuda = True
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if if_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
# model
predict = convolutional_neural_network(image)
acc = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=predict, label=label)
# cost
cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
# 测试程序,在优化器还没搭上之前,但是模型已经有输出之后,创建
test_program = fluid.default_main_program().clone(for_test=True)
# optimizer
fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(avg_cost)
# init args
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
# strategy
exec_strategy = fluid.ExecutionStrategy()
# # 线程数等于设备数
exec_strategy.num_threads = fluid.core.get_cuda_device_count()
print('----exec_strategy.num_threads :%d-----' % (exec_strategy.num_threads))
exec_strategy.num_iteration_per_drop_scope = 10
build_strategy = fluid.BuildStrategy()
compiled_train_prog = fluid.compiler.CompiledProgram(fluid.default_main_program()).with_data_parallel(loss_name=avg_cost.name, build_strategy=build_strategy, exec_strategy=exec_strategy)
compiled_test_prog = fluid.compiler.CompiledProgram(test_program).with_data_parallel(share_vars_from=compiled_train_prog)
BATCH_SIZE = 64
train_reader = paddle.batch(paddle.reader.shuffle(paddle.dataset.mnist.train(), buf_size=500),batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
test_reader = paddle.batch(paddle.dataset.mnist.test(), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(place=place, feed_list=[image, label])
train(feeder, train_reader, test_reader, avg_cost, acc, test_prog=compiled_test_prog,train_prog=compiled_train_prog, exe=exe)