(1)条件式if、unless、case
Ruby不需要分号结尾
代码块用end结尾
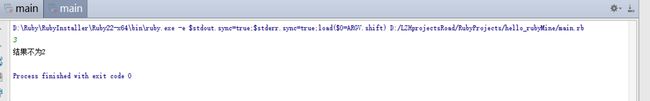
a=gets.to_i
if a==2
puts "这里判断等于"
end
if后面结果为false或者nil就不执行
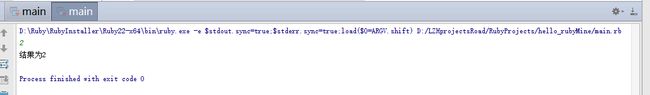
a=gets.chomp().to_i #ruby的方法后面要不要括号都可以,所以chomp后面的括号写不写都行,上一随笔就没写括号
if a==2
puts "结果为2"
else
puts "结果不为2"
end在ruby中注释使用#
Ctrl+/快速注释
if的另一种写法
a.gets.to_i
puts "结果为5"
if a==5a=gets.to_i
puts "结果为6" if a==6与if相反,unless是值为false或nil才执行
a=gets.to_i
unless a==10
puts "123"
else
puts "321"
endcase语句case object
when condition
when condition
end其他语言中switch case,case后面只能是具体的值不能是表达式,而且需要每个case加break。而ruby中case后面可以是判断表达式,而且不用break。
object=gets.to_i
case object
when 1..2
puts "two"
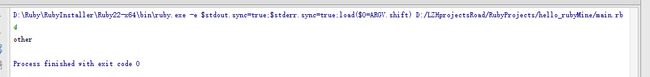
when 4...8 #[4,8),左闭右开
puts "other"
end(2)循环while、until,关键字break、next
object=gets.to_i
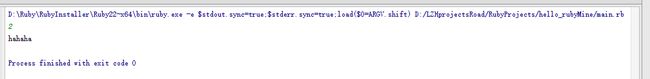
while object!=0
puts "hahaha"
end输入不为0那么就一直输出hahaha
until与while相反(输入为0才输出),就像if和unless相反一样
object=gets.to_i
until object!=0
puts "hahaha"
end
object=gets.to_i
while object!=0
puts "hahaha"
break if object==2
end
object=gets.to_i
while object!=0
puts "hahaha"
break if object==2
next if input==3 #next作用等价于java的continue
puts "hehehe"
end没有定义input变量,编译不报错,输入数字后再执行才会执行input的语句,这时才会报错。
object=gets.to_i
while object!=0
puts "hahaha"
break if object==2
next if object==3 #next作用等价于java的continue
puts "hehehe"
end输入不为3就循环输出"hahaha""hehehe",输入为3就循环输出"hahaha"
next作用就相当于continue碰到它直接回到循环开始继续执行,而不再向下执行puts "hehehe"
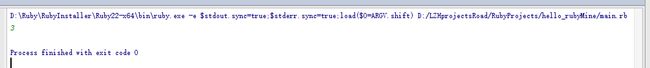
计算1到100和的两种方法:
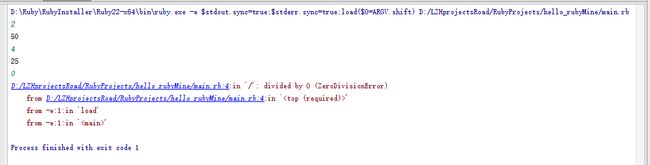
第七行错误但是后面很多空行错误行数就是最后一行
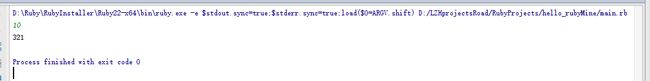
sum=0
i=1
while true
sum+=i
i+=1
break if i==101
end
puts sum 利用迭代器each的方法
sum=0
(1..100).each{|i|
sum+=i
}
puts sum 就是将1到100取出每一个赋值给i,然后sum加i
(3)异常
a=100
while true
b=gets.to_i
puts a/b
end
a=100
while true
b=gets.to_i
begin
puts a/b
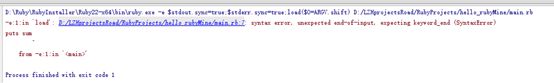
rescue Exception=>
puts "请不要输入零"
end
end
a=100
while true
b=gets.to_i
begin
puts a/b
rescue Exception=>e
puts "请不要输入零"
end
end异常处理有两种方案,一种就是用if给出提示并next跳回循环第一句,另外一种就是begin、rescue异常关键字
可以看到使用异常,程序还能继续输入和运行,这就是目的
a=100
while true
b=gets.to_i
begin
puts a/b
rescue Exception=>e
puts e #e就是异常的具体信息
end
end