java网络编程基础小结
部分来源于蓝桥杯学习
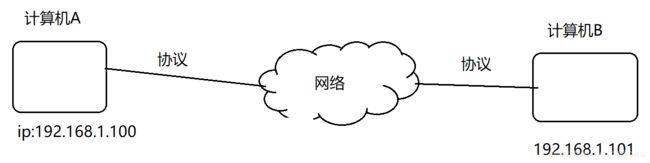
ip地址:网络上的 唯一标识
ip的组成:32位,由4个8位二进制组成 (每一位最大值是255,每一位十进制标识 0-255)
11000000.10101000.00000001.01100100 二进制不容易被记忆,改成十进制:192.168.1.100
192.168.300.101 错 (每一位最大值是255,每一位十进制标识 0-255)
协议
协议: 为了让网络中不同计算机之间能够相互通信而建立的规则、标准、约定。本课程使用的TCP、UDP
- TCP协议:面向连接的、可靠的(不丢失、不重复、有序)、基于字节流的传输通信协议。传输速度相对慢。
- UDP协议:无连接的协议。在传输数据之前,客户端和服务端之间不建立和维护连接。提供不可靠的数据传输。传输速度相对快。
socket(套接字):基于TCP协议的网络通信,可以提供双向安全连接的网络通信。socket需要借助于数据流(字节流)来完成数据的传递工作
服务端
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class MyServer {
//
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.准备服务.ip:默认本机127.0.0.1,端口8888
ServerSocket serverSocket = null ;
Socket socket = null ;
InputStream in = null ;
BufferedReader reader = null ;
OutputStream out = null ;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888) ;
System.out.println("服务器启动");
//准备完毕,可以监听客户端请求
socket = serverSocket.accept();//一直阻塞,直到有客户端连接
System.out.println("服务端检测到客户端连接成功!");
//
//
// 2.通过socket生成inputstream/outputstream(准备发送数据)
//3.使用inputstream/outputstream进行发送、接受数据
in = socket.getInputStream();
//带缓冲区的字符流(字节流-转换流-字符流)
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String info = null ;
while( (info=reader.readLine()) != null ){
System.out.println("I am server,接受到客户端信息是:" + info);
}
//
socket.shutdownInput();
//
//
//
//服务端做出反馈
out = socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("welcome client....".getBytes());
//
socket.shutdownOutput();
//
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
// 4.关闭inputstream/outputstream、socket
if(reader !=null) reader.close();
if(out !=null) out.close();
if(in !=null) in.close();
if(socket !=null) socket.close();
if(serverSocket !=null) serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
//
public class MyClient {
//
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null ;
OutputStream out = null ;
InputStream in = null ;
BufferedReader reader = null ;
try {
socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
System.out.println("客户端链接成功!");
out = socket.getOutputStream();
out.write( "hello server".getBytes() );
socket.shutdownOutput();
//
//接收服务端的反馈
in = socket.getInputStream();
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String info = null;
while( (info=reader.readLine()) != null ){
System.out.println("I am client,接收到的服务端消息:"+info);
}
//
socket.shutdownInput();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(out!=null) out.close();
if(in!=null) in.close();
if(socket!=null) socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
另一个案例
服务端
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class DailyAdviceSever {
String[] adviceList= {"A day an apple,doctor keep me away",
"Take smaller bites","You might want to rethink that haircut"};
public void go() {
try {
//准备服务
//监听客户端在机器4242端口上的要求
ServerSocket serversocket=new ServerSocket(5000);
while(true) {
//这个方法会停下来等待要求到达才会继续
Socket sock=serversocket.accept();
System.out.println("客户端链接成功");
//PrintWriter将字符写入
PrintWriter writer=new PrintWriter(sock.getOutputStream());
String advice=getAdvice();
writer.println(advice);
writer.close();
System.out.println(advice);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String getAdvice() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int random=(int)(Math.random()*adviceList.length);
return adviceList[random];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DailyAdviceSever server=new DailyAdviceSever();
server.go();
}
}
客户端
package socketTest;
//客户端程序
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;//网络功能包
public class DailyAdviceCilent {
private Socket s;
public void go() {
try {
//链接服务端
s = new Socket("127.0.0.1",5000);
//建立连接到Socket上底层输入串流
InputStreamReader streamReader=new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream());
//用BufferedReader来读取
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(streamReader);
String advice=reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Today you should:"+advice);
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DailyAdviceCilent Cilent=new DailyAdviceCilent();
Cilent.go();
}
}
发送数据用输出流,接收数据用输入流
线程
客户端代码不变;服务端:每当有一个客户端,就开启一个新线程去处理(每个线程专门处理一个客户端对象)。
//建立新的线程
Thread t=new Thread();
t.start();
线程是独立的线程,他代表独立的执行空间,每个Java会启动一个主线程-main()。
如何启动新的线程
- 建立Runnable对象(线程的任务)
//Runnable是个接口
Runnable threadJob=new MyRunnable();
- 建立Tread对象(执行工人)并赋值任务Runnable(任务)
Thread myThread=new Thread(threadJob)
- 启动Thread
mythread.start();
Runnable接口
只有一个方法需要实现
public void run(){
//要执行的任务
}
线程调度器
决定哪个线程从等待状态被挑出来运行
package socketTest;
//建立与启动两个线程
public class RunThreads implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
RunThreads runner=new RunThreads();
Thread alpha=new Thread(runner);
Thread beta=new Thread(runner);
beta.setName("beta");
alpha.setName("alpha");
alpha.start();
beta.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
String threadName=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName);
}
}
}
也可以用Thread的子类来覆盖掉run方法
package socketTest;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyServer1 {
//服务端
//使用多线程处理
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7777) ;
System.out.println("服务器启动");
while(true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//阻塞,接受客户端请求
ServerThread serverThread = new ServerThread(socket) ;
serverThread.start();
}
//
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package socketTest;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyCilent1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null ;
OutputStream out = null ;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null ;
try {
socket = new Socket("localhost",7777) ;
//
Student student = new Student(1001,"zs",23);
//
out = socket.getOutputStream();
//将OutputStream转为对象流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out) ;
oos.writeObject( student );//发送对象
socket.shutdownOutput();
//
//接受服务端的反馈
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[100] ;
in.read(buf) ;
System.out.println("接收到的服务端反馈:" + new String(buf) );
//
//
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
if(oos!=null) oos.close();
if(out!=null) out.close();
if(socket!=null) socket.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//
}
}
}
package socketTest;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyCilent2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null ;
OutputStream out = null ;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null ;
try {
socket = new Socket("localhost",7777) ;
//
Student student = new Student(1002,"ls",24);
//
out = socket.getOutputStream();
//将OutputStream转为对象流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out) ;
oos.writeObject( student );//发送对象
socket.shutdownOutput();
//
//接受服务端的反馈
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[100] ;
in.read(buf) ;
System.out.println("接收到的服务端反馈:" + new String(buf) );
//
//
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
if(oos!=null) oos.close();
if(out!=null) out.close();
if(socket!=null) socket.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//
}
}
}
package socketTest;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyCilent3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null ;
OutputStream out = null ;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null ;
try {
socket = new Socket("localhost",7777) ;
//
Student student = new Student(1003,"wu",25);
//
out = socket.getOutputStream();
//将OutputStream转为对象流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out) ;
oos.writeObject( student );//发送对象
socket.shutdownOutput();
//
//接受服务端的反馈
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[100] ;
in.read(buf) ;
System.out.println("接收到的服务端反馈:" + new String(buf) );
//
//
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
if(oos!=null) oos.close();
if(out!=null) out.close();
if(socket!=null) socket.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//
}
}
}
package socketTest;
//
import java.io.Serializable;
//
public class Student implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(int id,String name,int age) {
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
//
}
线程补充
线程可以驱动任务,因此我们需要一种描述任务的方式,由Runnable接口提供
public class LiftOff implements Runnable {
protected int countDown = 10; // Default
private static int taskCount = 0;
private final int id = taskCount++;
public LiftOff() {
}
//
public LiftOff(int countDown) {
this.countDown = countDown;
}
//
public String status() {
return "#" + id + "(" + (countDown > 0 ? countDown : "Liftoff!") + "), ";
}
//
public void run() {
while (countDown-- > 0) {
System.out.print(status());
Thread.yield();// 对线程调度器的一种建议
}
}
} /// :~
public class MainThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LiftOff lunch=new LiftOff();
lunch.run();
}
}
/*
* #0(9), #0(8), #0(7),
* #0(6), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!), */
Thread类
public class BasicThreads {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t=new Thread(new LiftOff());//将Runnable对象提交给Thread构造器
t.start();//执行了必须的初始化操作
System.out.println("Waiting for LiftOff");//先执行
}
}
/* Waiting for LiftOff
#0(9), #0(8), #0(7), #0(6), #0(5),
#0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!), */
输出不同
//线程调度器
public class MoreBasicThreads {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
new Thread(new LiftOff()).start();
System.out.println("Waiting for LiftOff");
}
}
/*#0(9), #4(9), #3(9), #1(9), Waiting for LiftOff
#2(9), #1(8), #1(7), #3(8), #3(7), #3(6), #4(8),
#0(8), #0(7), #4(7), #4(6), #4(5), #3(5), #3(4),
#3(3), #3(2), #3(1), #1(6), #1(5), #1(4), #1(3),
#1(2), #1(1), #2(8), #2(7), #2(6), #2(5), #2(4),
#2(3), #2(2), #1(Liftoff!), #3(Liftoff!), #4(4),
#0(6), #4(3), #2(1), #4(2), #0(5), #0(4), #4(1),
#4(Liftoff!), #2(Liftoff!), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
*/
Executor
Executor在客户端和任务之间提供了一个间接层
CachedThreadPool将为每个任务创建一个新的线程
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//Exexcutor执行器将会管理Thread对象
public class CachedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {//线程池
ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//使用静态方法创建
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
exec.execute(new LiftOff());
exec.shutdown();
}
}
/*#0(9), #0(8), #0(7), #2(9), #2(8), #2(7), #2(6), #3(9), #3(8),
* #3(7), #3(6), #3(5), #3(4), #3(3), #3(2), #3(1), #4(9), #4(8),
* #4(7), #4(6), #4(5), #4(4), #1(9), #1(8), #1(7), #1(6), #4(3),
* #4(2), #4(1), #4(Liftoff!), #3(Liftoff!), #2(5), #2(4), #2(3),
* #2(2), #0(6), #2(1), #2(Liftoff!), #1(5), #1(4), #1(3), #1(2),
* #1(1), #1(Liftoff!), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
* */
有限线程集
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class FixedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//预设线程数量
ExecutorService exec=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
exec.execute(new LiftOff());
exec.shutdown();
}
}
/*#0(9), #1(9), #4(9), #4(8), #4(7), #4(6), #4(5), #4(4), #4(3),
* #4(2), #4(1), #3(9), #2(9), #2(8), #2(7), #2(6), #3(8), #3(7),
* #3(6), #3(5), #3(4), #4(Liftoff!), #1(8), #0(8), #1(7), #3(3),
* #2(5), #2(4), #2(3), #2(2), #2(1), #2(Liftoff!), #3(2), #1(6),
* #0(7), #0(6), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
* #1(5), #3(1), #1(4), #1(3), #1(2), #1(1), #1(Liftoff!), #3(Liftoff!),
* */
单个线程
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//一次处理单个线程
public class SignleThreadExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
exec.execute(new LiftOff());
exec.shutdown();
}
}
/* #0(9), #0(8), #0(7), #0(6), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
* #1(9), #1(8), #1(7), #1(6), #1(5), #1(4), #1(3), #1(2), #1(1), #1(Liftoff!),
* #2(9), #2(8), #2(7), #2(6), #2(5), #2(4), #2(3), #2(2), #2(1), #2(Liftoff!),
* #3(9), #3(8), #3(7), #3(6), #3(5), #3(4), #3(3), #3(2), #3(1), #3(Liftoff!),
* #4(9), #4(8), #4(7), #4(6), #4(5), #4(4), #4(3), #4(2), #4(1), #4(Liftoff!),
*/
从任务中返回值
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
//从任务中产生返回值 实现Callable接口
class TaskWithResult implements Callable<String> {
private int id;
public TaskWithResult(int id) {
this.id = id;
}//返回值
public String call() {
return "result of TaskWithResult " + id;
}
}
//
public class CallableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ArrayList<Future<String>> results =
new ArrayList<Future<String>>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)//submit方法调用 产生future对象
results.add(exec.submit(new TaskWithResult(i)));
for(Future<String> fs : results)
try {
// get() blocks until completion:
System.out.println(fs.get());
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
return;
} catch(ExecutionException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} finally {
exec.shutdown();
}
}
} /* Output:
result of TaskWithResult 0
result of TaskWithResult 1
result of TaskWithResult 2
result of TaskWithResult 3
result of TaskWithResult 4
result of TaskWithResult 5
result of TaskWithResult 6
result of TaskWithResult 7
result of TaskWithResult 8
result of TaskWithResult 9
*///:~
休眠
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class SleepingTask extends LiftOff {
public void run() {
try {//异常要在本地处理
while(countDown-- > 0) {
System.out.print(status());
// Old-style:
// Thread.sleep(100);
// Java SE5/6-style:
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("Interrupted");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
exec.execute(new SleepingTask());
exec.shutdown();
}
} /* Output:
#0(9), #1(9), #2(9), #3(9), #4(9), #0(8), #1(8), #2(8), #3(8), #4(8), #0(7), #1(7), #2(7), #3(7), #4(7), #0(6), #1(6), #2(6), #3(6), #4(6), #0(5), #1(5), #2(5), #3(5), #4(5), #0(4), #1(4), #2(4), #3(4), #4(4), #0(3), #1(3), #2(3), #3(3), #4(3), #0(2), #1(2), #2(2), #3(2), #4(2), #0(1), #1(1), #2(1), #3(1), #4(1), #0(Liftoff!), #1(Liftoff!), #2(Liftoff!), #3(Liftoff!), #4(Liftoff!),
*///:~
优先级
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class SimplePriorities implements Runnable {
private int countDown = 5;
private volatile double d; // No optimization
private int priority;
public SimplePriorities(int priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
public String toString() {//获得对驱动该任务的Thread对象
return Thread.currentThread() + ": " + countDown;
}
public void run() {
//在开头部分设置优先级
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(priority);
while(true) {
// An expensive, interruptable operation:
for(int i = 1; i < 100000; i++) {
d += (Math.PI + Math.E) / (double)i;
if(i % 1000 == 0)
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(this);
if(--countDown == 0) return;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
exec.execute(
new SimplePriorities(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY));
exec.execute(
new SimplePriorities(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY));
exec.shutdown();
}
} /* Output: (70% match)
Thread[pool-1-thread-6,10,main]: 5
Thread[pool-1-thread-6,10,main]: 4
Thread[pool-1-thread-6,10,main]: 3
Thread[pool-1-thread-6,10,main]: 2
Thread[pool-1-thread-6,10,main]: 1
Thread[pool-1-thread-3,1,main]: 5
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,1,main]: 5
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,1,main]: 5
Thread[pool-1-thread-5,1,main]: 5
Thread[pool-1-thread-4,1,main]: 5
...
*///:~
后台线程
后台线程,是指程序在运行时后在后台提供的一种通用服务线程
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class SimpleDaemons implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " " + this);
}
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("sleep() interrupted");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread daemon = new Thread(new SimpleDaemons());
//设置为后台线程
daemon.setDaemon(true); // Must call before start()
daemon.start();
}
// 设置短暂休眠,观察后台执行结果
System.out.println("All daemons started");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
}
} /* Output: (Sample)
All daemons started
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] SimpleDaemons@530daa
Thread[Thread-1,5,main] SimpleDaemons@a62fc3
Thread[Thread-2,5,main] SimpleDaemons@89ae9e
Thread[Thread-3,5,main] SimpleDaemons@1270b73
Thread[Thread-4,5,main] SimpleDaemons@60aeb0
Thread[Thread-5,5,main] SimpleDaemons@16caf43
Thread[Thread-6,5,main] SimpleDaemons@66848c
Thread[Thread-7,5,main] SimpleDaemons@8813f2
Thread[Thread-8,5,main] SimpleDaemons@1d58aae
Thread[Thread-9,5,main] SimpleDaemons@83cc67
...
*///:~
编写定制ThreadFactory可以定制由Executor创建线程的属性(后台,优先级,名称)
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class DaemonThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setDaemon(true);//全部设置为后台线程
return t;
}
} ///:~
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class DaemonFromFactory implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " " + this);
}
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
//
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
new DaemonThreadFactory());//作为参数
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
exec.execute(new DaemonFromFactory());//执行任务
System.out.println("All daemons started");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); // Run for a while
}
}
/* (Execute to see output) *///:~
/*
* All daemons started
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@530f8d1b
Thread[Thread-2,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@8dd480f
Thread[Thread-3,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@2082e058
Thread[Thread-5,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@509afc84
Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3a313c09
Thread[Thread-4,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@466d0fc5
Thread[Thread-6,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3165be7c
Thread[Thread-7,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@46158e71
Thread[Thread-8,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@472210cb
Thread[Thread-9,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@708ac03e
Thread[Thread-2,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@8dd480f
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@530f8d1b
Thread[Thread-5,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@509afc84
Thread[Thread-4,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@466d0fc5
Thread[Thread-9,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@708ac03e
Thread[Thread-6,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3165be7c
Thread[Thread-7,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@46158e71
Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3a313c09
Thread[Thread-3,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@2082e058
Thread[Thread-8,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@472210cb
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@530f8d1b
Thread[Thread-2,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@8dd480f
Thread[Thread-5,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@509afc84
Thread[Thread-6,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3165be7c
Thread[Thread-4,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@466d0fc5
Thread[Thread-9,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@708ac03e
Thread[Thread-7,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@46158e71
Thread[Thread-3,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@2082e058
Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3a313c09
Thread[Thread-8,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@472210cb
Thread[Thread-5,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@509afc84
Thread[Thread-2,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@8dd480f
Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@530f8d1b
Thread[Thread-4,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@466d0fc5
Thread[Thread-9,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@708ac03e
Thread[Thread-6,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3165be7c
Thread[Thread-3,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@2082e058
Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@3a313c09
Thread[Thread-7,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@46158e71
Thread[Thread-8,5,main] 线程.DaemonFromFactory@472210cb*/
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
class ADaemon implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("Starting ADaemon");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Exiting via InterruptedException");
} finally {
System.out.println("This should always run?");
}
}
}
//当最后一个非后台线程终止,后台线程会“突然终止”,一旦main()退出,jvm会关闭所有后台进程
//所以finall不会执行
public class DaemonsDontRunFinally {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread t = new Thread(new ADaemon());
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
}
} /* Output:
Starting ADaemon
*///:~
编码的变体
在非常简单的情况下,可以直接从Thread继承 ,重写run方法
加入一个线程
//一个线程可以在其他线程之上调用join()方法
class Sleeper extends Thread {
private int duration;//持续时间
public Sleeper(String name, int sleepTime) {
super(name);
duration = sleepTime;
start();
}//直接继承
public void run() {
try {
sleep(duration);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(getName() + " was interrupted. " +
"isInterrupted(): " + isInterrupted());
return;
}
System.out.println(getName() + " has awakened");
}
}
//
class Joiner extends Thread {
private Sleeper sleeper;
public Joiner(String name, Sleeper sleeper) {
super(name);
this.sleeper = sleeper;
start();
}
public void run() {
try {//调用另一个线程 Joiner线程将会挂起
sleeper.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
System.out.println(getName() + " join completed");
}
}
//
public class Joining {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sleeper
sleepy = new Sleeper("Sleepy", 1500),
grumpy = new Sleeper("Grumpy", 1500);
Joiner
dopey = new Joiner("Dopey", sleepy),
doc = new Joiner("Doc", grumpy);
// grumpy.interrupt();//这个线程中止
}
} /* Output:
Grumpy was interrupted. isInterrupted(): false
Doc join completed
Sleepy has awakened
Dopey join completed
*///:~
捕获异常
线程里的异常不能捕获
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//
public class ExceptionThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
exec.execute(new ExceptionThread());
}
} ///:~
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//异常线程类
class ExceptionThread2 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("run() by " + t);
System.out.println(
"eh = " + t.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());//获得
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
//
//Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler接口
class MyUncaughtExceptionHandler implements
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
//uncaughtException方法会在线程临近死亡时调用
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("caught " + e);
}
}
//
class HandlerThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
System.out.println(this + " creating new Thread");
Thread t = new Thread(r);
System.out.println("created " + t);
t.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(
new MyUncaughtExceptionHandler());
System.out.println(
"eh = " + t.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
return t;
}
}
//
public class CaptureUncaughtException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
new HandlerThreadFactory());
exec.execute(new ExceptionThread2());
}
} /* Output: (90% match)
HandlerThreadFactory@de6ced creating new Thread
created Thread[Thread-0,5,main]
eh = MyUncaughtExceptionHandler@1fb8ee3
run() by Thread[Thread-0,5,main]
eh = MyUncaughtExceptionHandler@1fb8ee3
caught java.lang.RuntimeException
*///:~