Android OpenGL ES 简明开发教程_材质渲染
该系列文章均转载自
http://blog.csdn.net/mapdigit/article/details/7526556
由于原文好像无法打开,正好自己有记录,所以正好分享出来,其中也对一些API作了解释。
前面讨论了如何给 3D 图形染色,更一般的情況是使用点阵图來给 Mesh 上色(渲染材质)。主要步骤如下:
创建 Bitmap 对象
使用材质渲染,首先需要构建用来渲染的Bitmap对象,Bitmap对象可以从资源文件中读取或者是从网络加载,或者是用代码构造,为简单起见,本例从资源中获取:
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.mipmap.jay);
要注意的是,有些设备对使用的 Bitmap 的大小有要求,要求 Bitmap 的宽度和长度为 2 的几次幂(1,2,4,8,16,32,64.。。。),如果使用不合要求的 Bitmap 来渲染,可能只会显示白色。
创建材质(Generating a texture)
下一步使用 OpenGL 库创建一个材质(Texture),首先是获取一個 Texture Id。
// 创建一个int类型的数组,长度表示需要几个Texture
int[] textures = new int[1];
// 使用OpenGL库创建材质
gl.glGenTextures(1,textures,0);textures 中存放了创建的 Texture ID,使用同样的 Texture Id ,也可以来刪除一个 Texture:
// 删除材质
gl.glDeleteTextures(1,textures,0);有了 Texture Id 之后,就可以通知 OpenGL 库使用这个 Texture:
/**
* 通知OpenGL库使用这个Texture
* 参数:
* target——指明纹理要绑定的目标,必须是GL_TEXTURE_2D。
texture——指明纹理的名称。
*/
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D,textures[0]);设置 Texture 参数 glTexParameter
下一步需要給 Texture 填充设置参数,用来渲染的 Texture 可能比要渲染的区域大或者小,这是需要设置 Texture 需要放大或是缩小时 OpenGL 的模式:
// Scale up if the texture if smaller.放大
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,GL10.GL_LINEAR);
// scale linearly when image smalled than texture 缩小
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,GL10.GL_LINEAR);常用的两种模式为 GL10.GL_LINEAR 和 GL10.GL_NEAREST。
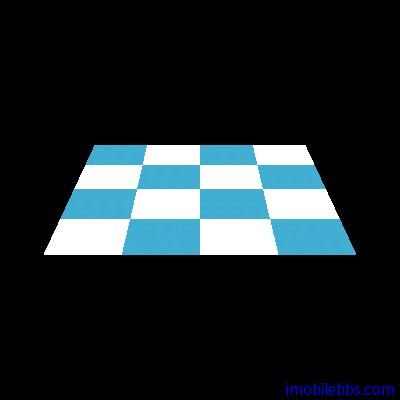
而使用 GL10.GL_LINEAR 则会得到一个较模糊的图像:
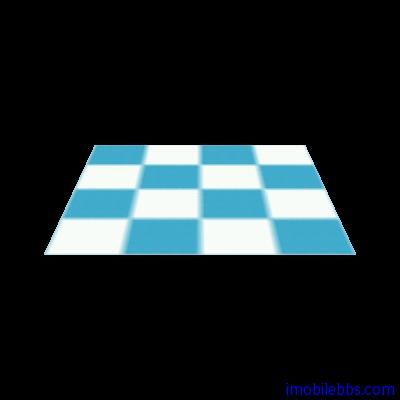
UV Mapping
下一步要告知 OpenGL 库如何将 Bitmap 的像素映射到 Mesh 上。这可以分为两步来完成:
1.定义 UV 坐标
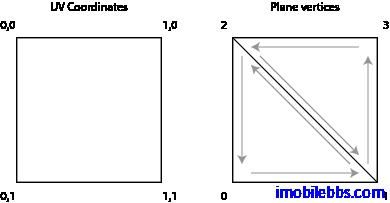
UV Mapping 指将 Bitmap 的像素映射到 Mesh 上的顶点。UV 坐标定义为左上角(0,0),右下角(1,1)(因为使用的 2D Texture),下图坐标显示了 UV 坐标,右边為我们需要染色的平面的顶点順序:
为了能正确的匹配,需要把 UV 坐标中的(0,1)映射到顶点 0,(1,1)映射到顶点 2 等等。
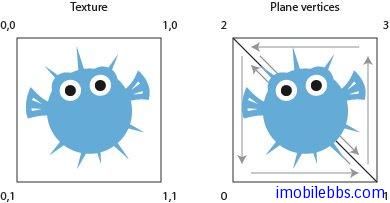
float textureCoordinates[] = {0.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f, 0.0f };如果使用如下坐标定义:
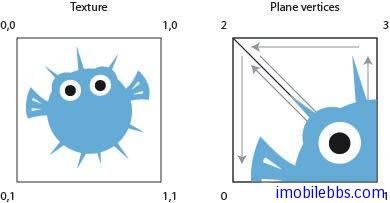
float textureCoordinates[] = {0.0f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f,
0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.0f };而
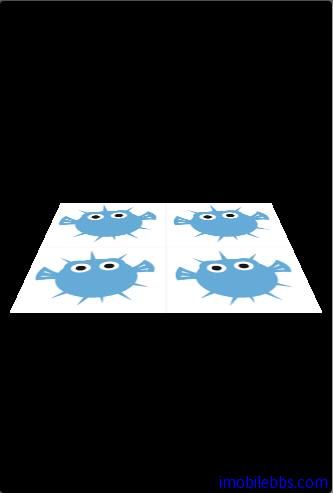
float textureCoordinates[] = {0.0f, 2.0f,
2.0f, 2.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f,
2.0f, 0.0f };將使用一些不存在的 Texture 去渲染平面(UV 坐标为 0,0-1,1 而 (0,0)-(2,2)定义超过 UV 定义的大小),这时需要告诉 OpenGL 库如何去渲染这些不存在的 Texture 部分。
有两种设置
- GL_REPEAT 重复 Texture。
- GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE 只靠边线复制一次。
- 下面有四种不同組合:
本例使用如下配置:
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S,
GL10.GL_REPEAT);
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T,
GL10.GL_REPEAT);
然后是将 Bitmap 资源和 Texture 绑定起來:
GLUtils.texImage2D(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, bitmap, 0);2.使用 Texture
为了能够使用上面定义的 Texture,需要创建一 Buffer 來存储 UV 坐标:
FloatBuffer byteBuf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(texture.length * 4);
byteBuf.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
textureBuffer = byteBuf.asFloatBuffer();
textureBuffer.put(textureCoordinates);
textureBuffer.position(0); 渲染
// Telling OpenGL to enable textures.
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Tell OpenGL where our texture is located.
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textures[0]);
// Tell OpenGL to enable the use of UV coordinates.
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
// Telling OpenGL where our UV coordinates are.
gl.glTexCoordPointer(2, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, textureBuffer);
// ... here goes the rendering of the mesh ...
// Disable the use of UV coordinates.
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
// Disable the use of textures.
gl.glDisable(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D); 本例代码是在一个平面上(SimplePlane)下使用 Texture 来渲染,首先是修改 Mesh 基类,使它能够支持定义 UV 坐标:
// Our UV texture buffer.
private FloatBuffer mTextureBuffer;
/**
* Set the texture coordinates.
*
* @param textureCoords
*/
protected void setTextureCoordinates(float[] textureCoords) {
// float is 4 bytes, therefore we multiply the number if
// vertices with 4.
ByteBuffer byteBuf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(
textureCoords.length * 4);
byteBuf.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
mTextureBuffer = byteBuf.asFloatBuffer();
mTextureBuffer.put(textureCoords);
mTextureBuffer.position(0);
} 并添加设置 Bitmap 和创建 Texture 的方法:
// Our texture id.
private int mTextureId = -1;
// The bitmap we want to load as a texture.
private Bitmap mBitmap;
/**
* Set the bitmap to load into a texture.
*
* @param bitmap
*/
public void loadBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) {
this.mBitmap = bitmap;
mShouldLoadTexture = true;
}
/**
* Loads the texture.
*
* @param gl
*/
private void loadGLTexture(GL10 gl) {
// Generate one texture pointer...
int[] textures = new int[1];
gl.glGenTextures(1, textures, 0);
mTextureId = textures[0];
// ...and bind it to our array
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, mTextureId);
// Create Nearest Filtered Texture
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,
GL10.GL_LINEAR);
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,
GL10.GL_LINEAR);
// Different possible texture parameters, e.g. GL10.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S,
GL10.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T,
GL10.GL_REPEAT);
// Use the Android GLUtils to specify a two-dimensional texture image
// from our bitmap
GLUtils.texImage2D(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, mBitmap, 0);
} 最后修改 draw 方法來渲染材质:
// Indicates if we need to load the texture.
private boolean mShouldLoadTexture = false;
/**
* Render the mesh.
*
* @param gl
* the OpenGL context to render to.
*/
public void draw(GL10 gl) {
...
// Smooth color
if (mColorBuffer != null) {
// Enable the color array buffer to be used during rendering.
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_COLOR_ARRAY);
gl.glColorPointer(4, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, mColorBuffer);
}
if (mShouldLoadTexture) {
loadGLTexture(gl);
mShouldLoadTexture = false;
}
if (mTextureId != -1 && mTextureBuffer != null) {
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Enable the texture state
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
// Point to our buffers
gl.glTexCoordPointer(2, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, mTextureBuffer);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, mTextureId);
}
gl.glTranslatef(x, y, z);
...
// Point out the where the color buffer is.
gl.glDrawElements(GL10.GL_TRIANGLES, mNumOfIndices,
GL10.GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, mIndicesBuffer);
...
if (mTextureId != -1 && mTextureBuffer != null) {
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
}
...
} 本例使用的 SimplePlane 定义如下:
/**
* SimplePlane is a setup class for Mesh that creates a plane mesh.
*
* @author Per-Erik Bergman ([email protected])
*
*/
public class SimplePlane extends Mesh {
/**
* Create a plane with a default with and height of 1 unit.
*/
public SimplePlane() {
this(1, 1);
}
/**
* Create a plane.
*
* @param width
* the width of the plane.
* @param height
* the height of the plane.
*/
public SimplePlane(float width, float height) {
// Mapping coordinates for the vertices
float textureCoordinates[] = { 0.0f, 2.0f, //
2.0f, 2.0f, //
0.0f, 0.0f, //
2.0f, 0.0f, //
};
short[] indices = new short[] { 0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2 };
float[] vertices = new float[] { -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f };
setIndices(indices);
setVertices(vertices);
setTextureCoordinates(textureCoordinates);
}
}