BiLSTM+CRF基于pytorch实现命名实体识别,对pytorch官网给出的例子实现优化,附学习思路和源代码
学习思路
BiLSTM + CRF
本文建立在读者已有一定深度学习知识的基础上,可以看看pytorch实现验证码图片识别,基本的反向传播思想,以及机器学习的相关概念(损失函数、随机梯度下降、训练集测试集等等)。
LSTM看这一篇就够了。
接下来给出我学习CRF的思路
- 看这篇的Section1,2,3,了解基本的朴素贝叶斯和最大熵模型,我个人觉得这篇CRF的部分讲得不清楚
- 看这篇全部,了解CRF的特征向量、CRF建模的对象、对数极大似然函数以及CRF的损失函数、以及viterbi解码(decode)和迭代计算所有路径分数的思想
- 再对照这篇博客看pytorch官网BiLSTM+CRF教程中对CRF的路径分数等的定义,初步实现模型
- 最后,基于这篇博客实现简化版模型,但我觉得这篇博客没搞清楚特征向量和分数的关系,所以只要看迭代计算那里就行
Requirements
- python==3.7.6,
- torch==1.4.0+cu92
- 安装环境可以参考这篇博客
运行结果
随便编了3个句子,用前两句训练100轮后预测第三句,结果如下:
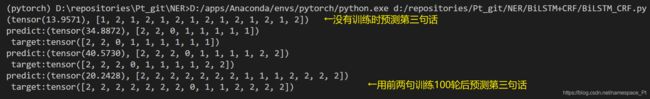
可以看到效果还是不错的。
源代码
import torch
import torch.autograd as autograd
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from utils import prepare_sequence
def prepare_sequence(seq, to_ix):
idxs = [to_ix[w] for w in seq]
return torch.tensor(idxs, dtype=torch.long)
class BiLSTM_CRF(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, tag_to_ix, embedding_dim, hidden_dim):
super().__init__()
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.tag_to_ix = tag_to_ix
self.tagset_size = len(tag_to_ix)
self.word_embeds = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim // 2,
num_layers=1, bidirectional=True)
self.hidden2tag = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, self.tagset_size)
self.transitions = nn.Parameter(
torch.randn(self.tagset_size, self.tagset_size))
# never transfer to the start tag and never transfer from stop tag
self.transitions.data[tag_to_ix[START_TAG], :] = -10000
self.transitions.data[:, tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]] = -10000
def _viterbi_decode(self, feats):
# backpointers:(n,m) where n is length of feats and m is tagset_size
# 存储feat中到当前所有tag最优的tag(相当于一步延迟)
# backpointers[i]意味着到feat_i的各个tags的最大可能的tag_pre
backpointers = []
# 初始化一个表示开始前的feat的向量,除了start_tag为0,其余都是-10000,这样由于argmax则feat_0的各个tags都以start_tag为前序
init_vvars = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000.)
init_vvars[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0.
# 将初始状态寄存在forward_var中,用作后续更新
pre_feat_var = init_vvars[0]
# 对于句子中每一个字的标签特征表示
for feat in feats:
pre_compute_var = torch.stack([pre_feat_var]*self.tagset_size)
crt_feat_var = pre_compute_var + self.transitions
pre_feat_var, best_pre = torch.max(crt_feat_var, dim=1)
backpointers.append(best_pre.tolist())
pre_feat_var += feat
terminal_var = pre_feat_var + \
self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
total_var, best_tag_id = torch.max(terminal_var, dim=0)
best_path = [best_tag_id.item()]
for backpointer in reversed(backpointers):
best_tag_id = backpointer[best_tag_id]
best_path.append(best_tag_id)
start = best_path.pop()
assert start == self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]
best_path.reverse()
return total_var, best_path
def _forward_alg(self, feats):
# 初始化,是否需要初始化为-10000还需研究
init_vars = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000)
init_vars[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0
#init_vars = torch.zeros((1,self.tagset_size))
# pre_feat:(1,tagset_size),用来保存到前序feat的各个tag的score
pre_feat = init_vars[0]
# 对于每一个feat
for feat in feats:
# 将pre_feat铺为tagset_size*tagset_size,方便计算
pre_compute_var = torch.stack([pre_feat]*self.tagset_size)
# 当前feat的Emission Vector即crt_emit_var[i]为当前feat被标为第i个tag的非归一化概率
crt_emit_var = torch.unsqueeze(feat, dim=0).view(-1, 1)
# 当前feat的总特征向亮=Emission + Transition,crt_feat_var[i][j]为当前feat的前序feat被标为第j个tag的情况下当前feat被标为第i个tag的特征值
crt_feat_var = crt_emit_var+self.transitions
# 迭代计算,因为log(exp(log(exp(\sum{x}))+y)) = log(exp(\sum{x})+exp(y)),得到当前feat的总score
feat_var = pre_compute_var + crt_feat_var
# 更新pre_feat,计算logsumexp即到当前feat的各个tag的各种情况的score
pre_feat = feat_var.logsumexp(dim=1)
# 同理,计算到终点的总score,即所有情况(len(feats)^{tagset_size}种)的总score
terminal_var = pre_feat + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
total_score = terminal_var.unsqueeze(dim=0).logsumexp(dim=1)[0]
return total_score
def _get_lstm_features(self, sentence):
embeds = self.word_embeds(sentence).view(len(sentence), 1, -1)
lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(embeds)
lstm_out = lstm_out.view(len(sentence), self.hidden_dim)
lstm_feats = self.hidden2tag(lstm_out)
return lstm_feats
def _score_sentence(self, feats, tags):
# Gives the score of a provided tag sequence
score = torch.zeros(1)
tags = torch.cat(
[torch.tensor([self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]], dtype=torch.long), tags])
for i, feat in enumerate(feats):
score = score + \
self.transitions[tags[i + 1], tags[i]] + feat[tags[i + 1]]
score = score + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG], tags[-1]]
return score
# 损失函数,来源于log的最大似然函数
def neg_log_likelihood(self, sentence, tags):
feats = self._get_lstm_features(sentence)
total_score = self._forward_alg(feats)
tagged_score = self._score_sentence(feats, tags)
return total_score - tagged_score
def forward(self, sentence): # dont confuse this with _forward_alg above.
# Get the emission scores from the BiLSTM
lstm_feats = self._get_lstm_features(sentence)
# Find the best path, given the features.
score, tag_seq = self._viterbi_decode(lstm_feats)
return score, tag_seq
if __name__ == "__main__":
START_TAG = ""
STOP_TAG = ""
EMBEDDING_DIM = 300
HIDDEN_DIM = 256
training_data = [(
"参 加 北 京 智 源 大 会".split(),
"O O B I I I I I I ".split()
), (
"他 出 席 计 算 机 协 会 会 长".split(),
"O O O B I I I I O O".split()
),
(
"作 为 主 讲 人 参 加 教 研 会 应 对 疫 情".split(),
"O O O O O O O B I I O O O O".split()
)]
word_to_ix = {}
for sentence, tags in training_data:
for word in sentence:
if word not in word_to_ix:
word_to_ix[word] = len(word_to_ix)
tag_to_ix = {"B": 0, "I": 1, "O": 2, START_TAG: 3, STOP_TAG: 4}
model = BiLSTM_CRF(len(word_to_ix), tag_to_ix, EMBEDDING_DIM, HIDDEN_DIM)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=1e-4)
# 测试为训练模型
with torch.no_grad():
precheck_sent = prepare_sequence(training_data[-1][0], word_to_ix)
precheck_tags = torch.tensor(
[tag_to_ix[t] for t in training_data[0][1]], dtype=torch.long)
print(model(precheck_sent))
for epoch in range(100):
for sentence, tags in training_data[0:-1]:
model.zero_grad()
sentence_in = prepare_sequence(sentence, word_to_ix)
targets = torch.tensor([tag_to_ix[t]
for t in tags], dtype=torch.long)
loss = model.neg_log_likelihood(sentence_in, targets)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
for i in range(len(training_data)):
precheck_sent = prepare_sequence(training_data[i][0], word_to_ix)
print("predict:{}\n target:{}".format(model(precheck_sent),
prepare_sequence(training_data[i][1], tag_to_ix)))