二维前缀和
Monitor
Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 163840/163840 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 514 Accepted Submission(s): 160
Problem Description
Xiaoteng has a large area of land for growing crops, and the land can be seen as a rectangle of n×m .
But recently Xiaoteng found that his crops were often stolen by a group of people, so he decided to install some monitors to find all the people and then negotiate with them.
However, Xiao Teng bought bad monitors, each monitor can only monitor the crops inside a rectangle. There are p monitors installed by Xiaoteng, and the rectangle monitored by each monitor is known.
Xiao Teng guess that the thieves would also steal q times of crops. he also guessed the range they were going to steal, which was also a rectangle. Xiao Teng wants to know if his monitors can see all the thieves at a time.
Input
There are mutiple test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing two integers n,m(1≤n,1≤m,n×m≤107) which represent the area of the land.
And the secend line contain a integer p(1≤p≤106) which represent the number of the monitor Xiaoteng has installed. This is followed by p lines each describing a rectangle. Each of these lines contains four intergers x1,y1,x2 and y2(1≤x1≤x2≤n,1≤y1≤y2≤m) ,meaning the lower left corner and upper right corner of the rectangle.
Next line contain a integer q(1≤q≤106) which represent the number of times that thieves will steal the crops.This is followed by q lines each describing a rectangle. Each of these lines contains four intergers x1,y1,x2 and y2(1≤x1≤x2≤n,1≤y1≤y2≤m) ,meaning the lower left corner and upper right corner of the rectangle.
Output
For each case you should print q lines.
Each line containing YES or NO mean the all thieves whether can be seen.
Sample Input
6 6
3
2 2 4 4
3 3 5 6
5 1 6 2
2
3 2 5 4
1 5 6 5
Sample Output
YES
NO
Hint
In the picture,the red solid rectangles mean the monitor Xiaoteng installed, and the blue dotted rectangles mean the area will be stolen.
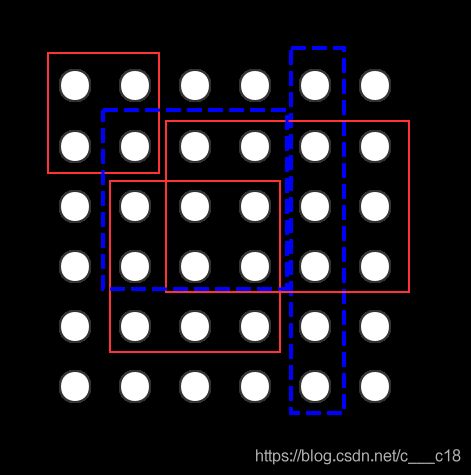
题目大意:
给你n和m,表示有一个nm的矩阵(nm<=1e7),初始全0,接下来一个数p(p<=1e6),接下来p个矩阵的左下角和右上角的坐标。
把这位于这些矩阵内的格子置为1,再接下来一个数q(1<=1e6),接下来q个矩阵的左下角和右上角的坐标,对于每个矩阵,如果它包含的每个格子都是1,则输出YES,否则输出NO。
理论基础:
https://blog.csdn.net/k_r_forever/article/details/81775899
分析:
用前缀和的方法计算出每个格子是否被覆盖(p个矩阵都进行二维前缀和的加1更新操作,然后统计一遍前缀和即可得出每个格子是否被覆盖,大于等于1即为被覆盖)
然后把被覆盖的格子都置为1,重新统计一遍前缀和(这时候前缀和就表示矩形(1,1,x,y)包含的被覆盖的格子数了)。方便我们接下来的判断。
还有一点需要注意的就是要动态开辟空间。
#include