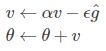Keras 自定义优化器,实现小内存大Batch更新梯度
1、“软batch”、梯度累计
我是用mask rcnn做分割,模型比较庞大,1080显卡最多也就能跑batch size=2,但又想起到batch size=64的效果,那可以怎么办呢?一种可以考虑的方案是,每次算batch size=2,然后把梯度缓存起来,32个batch后才更新参数。也就是说,每个小batch都算梯度,但每32个batch才更新一次参数。
我的需求是,SGD+Momentum实现梯度累加功能,借鉴了keras的optimizier的定义,可以看出每个优化器SGD、Adam等都是重载了Optimizer类,主要是需要重写get_updates方法。
2、思路:
学习速率 ϵ, 初始参数 θ, 初始速率v, 动量衰减参数α,每次迭代得到的梯度是g
计算梯度和误差,并更新速度v和参数θ:
使用SGD+momentum进行梯度下降,计算参数v和θ(new_p)的值:
v = self.momentum * sg / float(self.steps_per_update) - lr * g # velocity
new_p = p + v
假设每steps_per_update批次更新一次梯度,先判断当前迭代是否足够steps_per_update次,也就是条件:
cond = K.equal(self.iterations % self.steps_per_update, 0)
如果满足条件,更新参数v和θ,如下:
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(sg, v), p))
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(p, new_p), p))
并且重新累计梯度,若不满足条件,则直接累计梯度:
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(sg, g), K.update(sg, sg + g)))
3、我的完整实现如下:
class MySGD(Optimizer):
"""
Keras中简单自定义SGD优化器每隔一定的batch才更新一次参数
Includes support for momentum,
learning rate decay, and Nesterov momentum.
# Arguments
lr: float >= 0. Learning rate.
momentum: float >= 0. Parameter that accelerates SGD in the relevant direction and dampens oscillations.
decay: float >= 0. Learning rate decay over each update.
nesterov: boolean. Whether to apply Nesterov momentum.
steps_per_update: how many batch to update gradient
"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, momentum=0., decay=0.,
nesterov=False, steps_per_update=2, **kwargs):
super(MySGD, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with K.name_scope(self.__class__.__name__):
self.iterations = K.variable(0, dtype='int64', name='iterations')
self.lr = K.variable(lr, name='lr')
self.steps_per_update = steps_per_update # 多少batch才更新一次
self.momentum = K.variable(momentum, name='momentum')
self.decay = K.variable(decay, name='decay')
self.initial_decay = decay
self.nesterov = nesterov
print("每%dbatch更新一次梯度" % self.steps_per_update)
@interfaces.legacy_get_updates_support
def get_updates(self, loss, params):
"""主要的参数更新算法"""
# learning rate decay
lr = self.lr
if self.initial_decay > 0:
lr = lr * (1. / (1. + self.decay * K.cast(self.iterations,
K.dtype(self.decay))))
shapes = [K.int_shape(p) for p in params]
sum_grads = [K.zeros(shape) for shape in shapes] # 平均梯度,用来梯度下降
grads = self.get_gradients(loss, params) # 当前batch梯度
self.updates = [K.update_add(self.iterations, 1)] # 定义赋值算子集合
self.weights = [self.iterations] + sum_grads # 优化器带来的权重,在保存模型时会被保存
for p, g, sg in zip(params, grads, sum_grads):
# momentum 梯度下降
v = self.momentum * sg / float(self.steps_per_update) - lr * g # velocity
if self.nesterov:
new_p = p + self.momentum * v - lr * g
else:
new_p = p + v
# 如果有约束,对参数加上约束
if getattr(p, 'constraint', None) is not None:
new_p = p.constraint(new_p)
cond = K.equal(self.iterations % self.steps_per_update, 0)
# 满足条件才更新参数
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(sg, v), p))
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(p, new_p), p))
# 满足条件就要重新累积,不满足条件直接累积
self.updates.append(K.switch(cond, K.update(sg, g), K.update(sg, sg + g)))
return self.updates
def get_config(self):
config = {'lr': float(K.get_value(self.lr)),
'steps_per_update': self.steps_per_update,
'momentum': float(K.get_value(self.momentum)),
'decay': float(K.get_value(self.decay)),
'nesterov': self.nesterov
}
base_config = super(MySGD, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
4、keras的optimizier代码如下:
class Optimizer(object):
"""Abstract optimizer base class.
Note: this is the parent class of all optimizers, not an actual optimizer
that can be used for training models.
All Keras optimizers support the following keyword arguments:
clipnorm: float >= 0. Gradients will be clipped
when their L2 norm exceeds this value.
clipvalue: float >= 0. Gradients will be clipped
when their absolute value exceeds this value.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
allowed_kwargs = {'clipnorm', 'clipvalue'}
for k in kwargs:
if k not in allowed_kwargs:
raise TypeError('Unexpected keyword argument '
'passed to optimizer: ' + str(k))
self.__dict__.update(kwargs)
self.updates = []
self.weights = []
@interfaces.legacy_get_updates_support
def get_updates(self, loss, params):
raise NotImplementedError
def get_gradients(self, loss, params):
grads = K.gradients(loss, params)
if None in grads:
raise ValueError('An operation has `None` for gradient. '
'Please make sure that all of your ops have a '
'gradient defined (i.e. are differentiable). '
'Common ops without gradient: '
'K.argmax, K.round, K.eval.')
if hasattr(self, 'clipnorm') and self.clipnorm > 0:
norm = K.sqrt(sum([K.sum(K.square(g)) for g in grads]))
grads = [clip_norm(g, self.clipnorm, norm) for g in grads]
if hasattr(self, 'clipvalue') and self.clipvalue > 0:
grads = [K.clip(g, -self.clipvalue, self.clipvalue) for g in grads]
return grads
def set_weights(self, weights):
"""Sets the weights of the optimizer, from Numpy arrays.
Should only be called after computing the gradients
(otherwise the optimizer has no weights).
# Arguments
weights: a list of Numpy arrays. The number
of arrays and their shape must match
number of the dimensions of the weights
of the optimizer (i.e. it should match the
output of `get_weights`).
# Raises
ValueError: in case of incompatible weight shapes.
"""
params = self.weights
if len(params) != len(weights):
raise ValueError('Length of the specified weight list (' +
str(len(weights)) +
') does not match the number of weights ' +
'of the optimizer (' + str(len(params)) + ')')
weight_value_tuples = []
param_values = K.batch_get_value(params)
for pv, p, w in zip(param_values, params, weights):
if pv.shape != w.shape:
raise ValueError('Optimizer weight shape ' +
str(pv.shape) +
' not compatible with '
'provided weight shape ' + str(w.shape))
weight_value_tuples.append((p, w))
K.batch_set_value(weight_value_tuples)
def get_weights(self):
"""Returns the current value of the weights of the optimizer.
# Returns
A list of numpy arrays.
"""
return K.batch_get_value(self.weights)
def get_config(self):
config = {}
if hasattr(self, 'clipnorm'):
config['clipnorm'] = self.clipnorm
if hasattr(self, 'clipvalue'):
config['clipvalue'] = self.clipvalue
return config
@classmethod
def from_config(cls, config):
return cls(**config)
class SGD(Optimizer):
"""Stochastic gradient descent optimizer.
Includes support for momentum,
learning rate decay, and Nesterov momentum.
# Arguments
lr: float >= 0. Learning rate.
momentum: float >= 0. Parameter that accelerates SGD
in the relevant direction and dampens oscillations.
decay: float >= 0. Learning rate decay over each update.
nesterov: boolean. Whether to apply Nesterov momentum.
"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, momentum=0., decay=0.,
nesterov=False, **kwargs):
super(SGD, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with K.name_scope(self.__class__.__name__):
self.iterations = K.variable(0, dtype='int64', name='iterations')
self.lr = K.variable(lr, name='lr')
self.momentum = K.variable(momentum, name='momentum')
self.decay = K.variable(decay, name='decay')
self.initial_decay = decay
self.nesterov = nesterov
@interfaces.legacy_get_updates_support
def get_updates(self, loss, params):
grads = self.get_gradients(loss, params)
self.updates = [K.update_add(self.iterations, 1)]
lr = self.lr
if self.initial_decay > 0:
lr = lr * (1. / (1. + self.decay * K.cast(self.iterations,
K.dtype(self.decay))))
# momentum
shapes = [K.int_shape(p) for p in params]
moments = [K.zeros(shape) for shape in shapes]
self.weights = [self.iterations] + moments
for p, g, m in zip(params, grads, moments):
v = self.momentum * m - lr * g # velocity
self.updates.append(K.update(m, v))
if self.nesterov:
new_p = p + self.momentum * v - lr * g
else:
new_p = p + v
# Apply constraints.
if getattr(p, 'constraint', None) is not None:
new_p = p.constraint(new_p)
self.updates.append(K.update(p, new_p))
return self.updates
def get_config(self):
config = {'lr': float(K.get_value(self.lr)),
'momentum': float(K.get_value(self.momentum)),
'decay': float(K.get_value(self.decay)),
'nesterov': self.nesterov}
base_config = super(SGD, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
5、总结
梯度累加就是,每次获取1个batch的数据,计算1次梯度,梯度不清空,不断累加,累加一定次数后,根据累加的梯度更新网络参数,然后清空梯度,进行下一次循环。
一定条件下,batchsize越大训练效果越好,梯度累加则实现了batchsize的变相扩大,如果accumulation_steps为8,则batchsize '变相' 扩大了8倍,是解决显存受限的一个不错的trick,使用时需要注意,学习率也要适当放大。
不过accumulation_steps=8和真实的batchsize放大八倍相比,效果自然是差一些,毕竟八倍Batchsize的BN估算出来的均值和方差肯定更精准一些。
https://blog.csdn.net/zywvvd/article/details/90731631