《GAN实战生成对抗网络》笔记 第三章 图像风格跨域转换
目录:
第一章 深度学习概述
第二章 无监督学习GAN
第三章 图像风格跨域转换
第四章 从文本构建逼真的图像
第五章 利用多种生成模型生成图像
第六章 将机器学习带入生产环境
3.1 弥补监督学习和无监督学习之间的空隙
GAN采用监督学习的方法来做无监督学习任务,使用分类判别器监督学习,但最终使用生成器实现了解真实数据分布或密度的预估从而根据学到的知识生成新的数据;
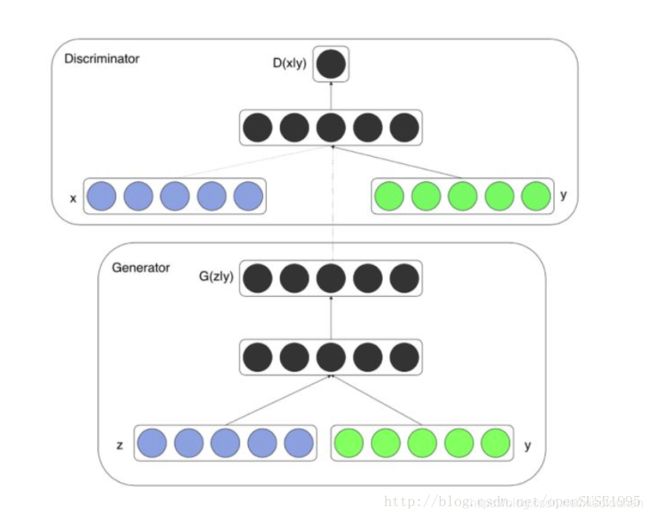
3.2 条件GAN
Conditional GAN, CGAN
3.2.1 利用CGAN生成时尚衣柜
Fashion-MNIST+CGAN
python download.py
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import subprocess
# Download Fashion MNIST
def download_mnist(dirpath):
if os.path.exists(dirpath):
print('Found MNIST - skip')
return
else:
os.makedirs(dirpath)
url_base = 'http://fashion-mnist.s3-website.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/'
file_names = ['train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz','train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz','t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz','t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz']
for file_name in file_names:
url = (url_base+file_name).format(**locals())
print(url)
out_path = os.path.join(dirpath,file_name)
cmd = ['curl', url, '-o', out_path]
print('Downloading ', file_name)
subprocess.call(cmd)
if __name__ == '__main__':
download_mnist('./data/fashion/')python simple-cgan.py
import numpy
import math
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import os
import numpy as np
# model parameter
noise_dim = 10 # input noise size of Generator
Dhidden = 256 # hidden units of Discriminator's network
Ghidden = 512 # hidden units of Generator's network
K = 8 # maxout units of Discriminator
mini_batch_size = 50
epoch = 50
nsamples = 12 # drawing samples
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./data/fashion", one_hot=True)
N, num_features = mnist.train.images.shape
num_labels = 10
period = N // mini_batch_size
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, num_features))
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, num_labels))
Z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, noise_dim))
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
GW1z = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([noise_dim, Ghidden], stddev=0.1), name="GW1z")
GW1y = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([num_labels, Ghidden], stddev=0.1), name="GW1y")
Gb1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(Ghidden), name="Gb1")
GW2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([Ghidden, num_features], stddev=0.1), name="GW2")
Gb2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(num_features), name="Gb2")
DW1x = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([num_features, K * Dhidden], stddev=0.01), name="DW1x")
DW1y = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([num_labels, K * Dhidden], stddev=0.01), name="DW1y")
Db1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(K * Dhidden), name="Db1")
DW2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([Dhidden, 1], stddev=0.01), name="DW2")
Db2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(1), name="Db2")
def discriminator(x, y):
u = tf.reshape(tf.matmul(x, DW1x) + tf.matmul(y, DW1y) + Db1, [-1, K, Dhidden])
Dh1 = tf.nn.dropout(tf.reduce_max(u, reduction_indices=[1]), keep_prob)
return tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(Dh1, DW2) + Db2)
def generator(z,y):
Gh1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(Z, GW1z) + tf.matmul(Y, GW1y) + Gb1)
G = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(Gh1, GW2) + Gb2)
return G
G_sample = generator(Z, Y)
DG = discriminator(G_sample, Y)
Dloss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(discriminator(X, Y)) + tf.log(1 - DG))
Gloss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(1 - DG) - tf.log(DG + 1e-9)) # the second term for stable learning
vars = tf.trainable_variables()
Dvars = [v for v in vars if v.name.startswith("D")]
Gvars = [v for v in vars if v.name.startswith("G")]
Doptimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(Dloss, var_list=Dvars)
Goptimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(Gloss, var_list=Gvars)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
def plot(samples):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(4, 4)
gs.update(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05)
for i, sample in enumerate(samples):
ax = plt.subplot(gs[i])
plt.axis('off')
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
ax.set_aspect('equal')
plt.imshow(sample.reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys_r')
return fig
def sample_Z(m, n):
return np.random.uniform(-1., 1., size=[m, n])
if not os.path.exists('out/'):
os.makedirs('out/')
i = 0
for it in range(1000000):
if it % 1000 == 0:
Z_sample = sample_Z(nsamples, noise_dim)
y_sample = np.zeros(shape=[nsamples, num_labels])
y_sample[:, 4] = 1 # generating image based on label
samples = sess.run(G_sample, feed_dict={Z: Z_sample, Y:y_sample})
fig = plot(samples)
plt.savefig('output/{}.png'.format(str(i).zfill(3)), bbox_inches='tight')
i += 1
plt.close(fig)
X_mb, y_mb = mnist.train.next_batch(mini_batch_size)
Z_sample = sample_Z(mini_batch_size, noise_dim)
_, D_loss_curr = sess.run([Doptimizer, Dloss], feed_dict={X: X_mb, Z: Z_sample, Y:y_mb, keep_prob:0.5})
_, G_loss_curr = sess.run([Goptimizer, Gloss], feed_dict={Z: Z_sample, Y:y_mb, keep_prob:1.0})
if it % 1000 == 0:
print('Iter: {}'.format(it))
print('D loss: {:.4}'. format(D_loss_curr))
print('G_loss: {:.4}'.format(G_loss_curr))
print()
3.2.2 利用边界均衡固化GAN训练
原始GAN问题:模型坍塌/评估收敛指标;
Wasserstein GAN:Earth-Mover距离(EM距离),推土机距离
BEGAN:允许每一步以对抗方式同时训练两个网络,最终M可以用来衡量大致收敛过程;
3.3 BEGAN的训练过程
# Clone Git repo
git clone https://github.com/carpedm20/BEGAN-tensorflow.git
cd BEGAN-tensorflow
# Download celebA dataset
python download.py
# Training
python main.py --dataset=CelebA --use_gpu=True3.4 利用CycleGAN实现图像风格的转换
循环一致生成网络(Cycle Consistent Generative Network, CycleGAN):
两个转换器F和G,其中F会将图像从域A转换到域B,而G会将图像从域B转换到域A
**** Apple to Orange *****
# Clone Git repo
git clone https://github.com/xhujoy/CycleGAN-tensorflow
cd CycleGAN-tensorflow
# Download celebA dataset
bash ./download_dataset.sh apple2orange
# Training
python main.py --dataset_dir=apple2orange
# Tensorboard Visualization
tensorboard --logdir=./logs
http://localhost:6006/
**** Horse to Zebra *****
# Clone Git repo
git clone https://github.com/xhujoy/CycleGAN-tensorflow
cd CycleGAN-tensorflow
# Download celebA dataset
bash ./download_dataset.sh horse2zebra
# Training
python main.py --dataset_dir=horse2zebra
# Tensorboard Visualization
tensorboard --logdir=./logs
http://localhost:6006/