Android资源管理框架-------之资源的筛选(八)
我们知道Android资源管理框架的一个重要作用就是为Android应用兼容不同的软硬环境。具体到实现上,就是每一个Android应用要想兼容某种场景,就要为这种场景提供特定的资源。比如,我们在App中想要兼容中文、德文、韩文,那么我们就可以在app中分别提供这三种语言的资源,也就是在values-zh-rCN、values-de-rDE、values-ko-rKR这三个目录下分别提供中文、德文、韩文的资源。在APK运行的时候,系统就会根据设备当前的设置来决定使用哪个目录下的资源,也就是哪种语言了。这里面有两个问题:当我们的APK中有多种配置的资源时,Android到底是如何来选择哪种最适合当前配置的;还有就是设备当前的配置信息是如何生成、更新的。比如当我们的手机旋转了一下屏幕,由竖屏变成了横屏,系统是如何通知我们的APK中的AssetManager设备的屏幕方向变成横屏了;我们的APK收到这个通知后,又是如何去判断出横屏的资源更适合当前设备的配置信息的。我们先来看Android是如何判定哪种配置的资源更适合当前设备的,也就是资源的筛选过程。
在说这个问题之前,我们还是得先回顾一下Android资源信息在resources.arsc以及ResTable中的组织形式,因为这个非常重要,看下图:
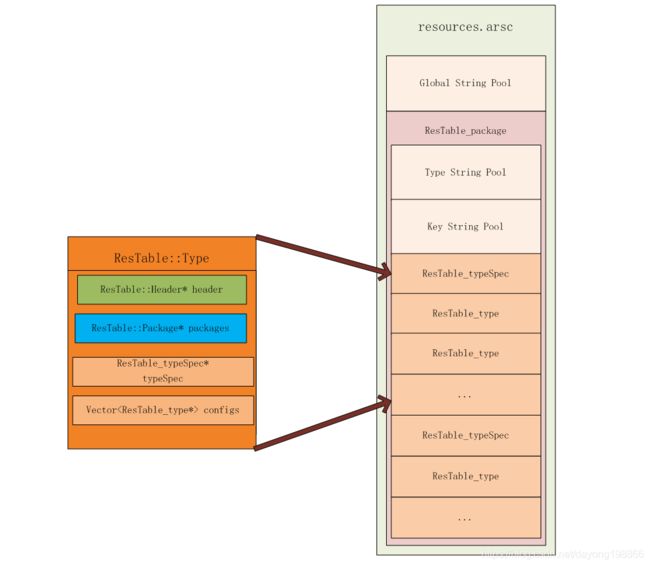
我们先稍作解释,图中右侧是resources.arsc中的数据结构,一个resources.arsc中包含一个Global String Pool(也叫Value String Pool)和一个ResTable_package结构;一个ResTable_package中包含多个ResTable_typeSpec;每个ResTable_typeSpec表示对某种类型(比如drawable或者layout)的所有资源(包含drawable、drawable-ldpi、drawable-mdpi、drawable-hdpi等等所有配置)的描述信息,它后面会跟多个ResTable_type结构;每个ResTable_type结构表示一种配置(比如mdpi)下某种资源,比如drawable-mdpi下的所有资源,其实每个ResTable_type结构体内部会有一个ResTable_config结构体来表示这个ResTable_type所对应的配置信息。而ResTable::Type结构体在这里则可以看作是对ResTable_typeSpec和ResTable_package的封装。总结起来就是,不论在resources.arsc中还是在ResTable中,每种类型的资源都是按照不同的配置来分开存储的,如果您觉得还是没太看懂,请点击这里Android资源管理框架-------之resources.arsc(三)和Android资源管理框架-------之资源管理的基本数据结构和Bag资源(四)。
说了这么多资源配置信息,到底什么是资源配置信息呢?在Android资源管理框架中有没有与之对应的数据结构,如果有,是什么呢?
图中是一个APP中的res目录,大家都比较熟悉,所谓的配置信息就是指图中各个文件夹的名字中"-"后面的信息,比如hdpi、ldrtl、land、sw600dp等等。老罗大神在Android资源管理框架(Asset Manager)简要介绍和学习计划一文中将Android资源的配置信息分成了18个维度。我们这里参照aapt的源代码,也做了梳理:
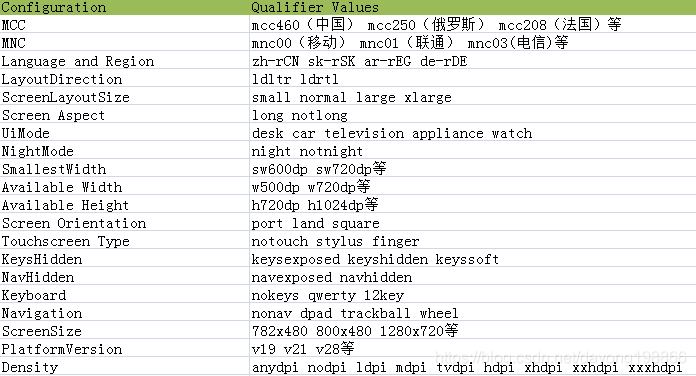
大家可能发现和老罗的不太一样:mcc和mnc分开了,增加了ScreenSize(800x480 1280x720)这一项(这个可能是老罗基于的版本比较老,毕竟那么久了)。另外,老罗说Android在比较某种配置的资源的时候,是按照这个表中的顺序去比较的,这种说法不太确切,我们看到我们表中的顺序和老罗表中的也不太一致。因为android在选取最适合设备当前配置的资源的过程大概分三个步骤:
- 淘汰掉不符合设备当前配置的资源,确切地说是
ResTable_type,经过这一步后剩下的都是符合当前配置的 - 选取最符合当前设备的
ResTable_type - 如果无法比较哪个匹配得更好,那么选择更详细的那个。
老罗表中的那个顺序是指第二个步骤中的比较顺序,其实在第一个和第三个步骤中,Android根本就不会去比较Density(ldpi xxhdpi这些)这一项的。另外,资源配置信息在java层与之对应的数据结构是Configuration.java,在native层或者resources.arsc中与之对应的数据结构是ResTable_config。这两个数据结构记录的也都是表中列出的那些信息,我们就不再贴代码了,直接介绍android选取最适合设备当前配置资源的过程,让我们先回到ResTable::getEntry()方法(建议大家再看一遍Android资源管理框架-------之最简单的资源信息的获取(六)里对这个方法的分析):
//frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ResourceTypes.cpp
status_t ResTable::getEntry(
const PackageGroup* packageGroup, int typeIndex, int entryIndex,
const ResTable_config* config,
Entry* outEntry) const
{
//记录最符合设备当前配置的ResTable_type
const ResTable_type* bestType = NULL;
//记录最符合设备当前配置的ResTable_type的配置信息
ResTable_config bestConfig;
//......
//省略次要代码,主要是去拿到对应的ResTable::Type对象
/**
* 该种类型的资源总共有多少种配置
* 比如我们的drawable类型的资源有drawable、drawable-hdpi、drawable-xxhdpi
* 那么numConfigs == 3,其实就是res目录下同种资源
* 的不同目录的个数
* typeSpec 为我们获取到的ResTable::Type对象,别被名字蒙蔽啦
*/
const size_t numConfigs = typeSpec->configs.size();
for (size_t c = 0; c < numConfigs; c++) {
//遍历每个ResTable_type
const ResTable_type* const thisType = typeSpec->configs[c];
//当前ResTable_type的config
ResTable_config thisConfig;
thisConfig.copyFromDtoH(thisType->config);
/**
* config 为getEntry方法的参数,表示设备当前的config
* 也就是说,如果当前的ResTable_type的配置如果不符合
* 设备当前的配置,那么就直接跳过这个ResTable_type
* 看下一个了,也就是我所说的第一步,淘汰不符合设备当前配置的资源
*/
if (config != NULL && !thisConfig.match(*config)) {
continue;
}
/**
* 如果侥幸符合当前设备的配置,并且之前我们也已经找到了最符合当前设备的
* ResTable_type了,那就要比一比当前这个和我们之前找到的最好的哪个更好
*/
if (bestType != NULL) {
// Check if this one is less specific than the last found. If so,
// we will skip it. We check starting with things we most care
// about to those we least care about.
//如果当前这个没有之前我们已经找到的好,那么当前这个也就可以被淘汰了
//所以 continue
if (!thisConfig.isBetterThan(bestConfig, config)) {
if (!currentTypeIsOverlay || thisConfig.compare(bestConfig) != 0) {
continue;
}
}
/**
* 如果当前这个ResTable_type对应的config比我们之前找到的最好的还好
* 那最好的当然就应该是当前的这个啦,故更新bestType和bestConfig
*/
bestType = thisType;
bestConfig = thisConfig;
//....
}
}
//根据entryIndex从bestType中获取对应的资源,非本文重点,略
}
这个方法总结起来就是:先去掉不合适的,再从剩下的之中挑选最好的。这里就涉及到了本文的重点ResTable_config::match和ResTable_config::isBetterThan两个方法,我们先看前者,它负责先淘汰掉不符合设备当前配置的ResTable_type:
//frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ResourceTypes.cpp
/**
* 判断该ResTable_config是否符合设备的配置
* settings 设备的配置
*/
bool ResTable_config::match(const ResTable_config& settings) const {
//mcc和mnc是imsi的高低位 union关系
//mcc和mnc如果当前config中有指定,且和设备的不等,则不符合
if (imsi != 0) {
if (mcc != 0 && mcc != settings.mcc) {
return false;
}
if (mnc != 0 && mnc != settings.mnc) {
return false;
}
}
//同样language和country也是locale的高低位 union关系
//language和country如果当前config中有指定,必须和设备的配置一样,否则返回false,表示不符合
if (locale != 0) {
// Don't consider the script & variants when deciding matches.
//
// If we two configs differ only in their script or language, they
// can be weeded out in the isMoreSpecificThan test.
if (language[0] != 0
&& (language[0] != settings.language[0]
|| language[1] != settings.language[1])) {
return false;
}
if (country[0] != 0
&& (country[0] != settings.country[0]
|| country[1] != settings.country[1])) {
return false;
}
}
//screenConfig和这个if里的子项也是高地位union关系
if (screenConfig != 0) {
const int layoutDir = screenLayout&MASK_LAYOUTDIR;
const int setLayoutDir = settings.screenLayout&MASK_LAYOUTDIR;
//布局方向如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//ldltr ldrtl
if (layoutDir != 0 && layoutDir != setLayoutDir) {
return false;
}
const int screenSize = screenLayout&MASK_SCREENSIZE;
const int setScreenSize = settings.screenLayout&MASK_SCREENSIZE;
// Any screen sizes for larger screens than the setting do not
// match.
//screenSize如果有指定,且比设备的size"大",则返回false
//注意这里的大不是具体的数值,而是比如xlarge的config的资源
//放在small的设备上,肯定不行,显示不全,设备太“小”
//small normal large xlarge
if (screenSize != 0 && screenSize > setScreenSize) {
return false;
}
const int screenLong = screenLayout&MASK_SCREENLONG;
const int setScreenLong = settings.screenLayout&MASK_SCREENLONG;
//screenLong如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//long notlong
if (screenLong != 0 && screenLong != setScreenLong) {
return false;
}
const int uiModeType = uiMode&MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE;
const int setUiModeType = settings.uiMode&MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE;
//uiModeType如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//desk car television appliance watch
if (uiModeType != 0 && uiModeType != setUiModeType) {
return false;
}
const int uiModeNight = uiMode&MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT;
const int setUiModeNight = settings.uiMode&MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT;
//uiModeNight如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//night notnight
if (uiModeNight != 0 && uiModeNight != setUiModeNight) {
return false;
}
//和前面的screenSize一样的道理
//sw600dp sw720dp等
if (smallestScreenWidthDp != 0
&& smallestScreenWidthDp > settings.smallestScreenWidthDp) {
return false;
}
}
//和前面的screenSize一样的道理
//w500dp w720dp h720dp h1024dp等
if (screenSizeDp != 0) {
if (screenWidthDp != 0 && screenWidthDp > settings.screenWidthDp) {
//ALOGI("Filtering out width %d in requested %d", screenWidthDp, settings.screenWidthDp);
return false;
}
if (screenHeightDp != 0 && screenHeightDp > settings.screenHeightDp) {
//ALOGI("Filtering out height %d in requested %d", screenHeightDp, settings.screenHeightDp);
return false;
}
}
if (screenType != 0) {
//orientation如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//port land square
if (orientation != 0 && orientation != settings.orientation) {
return false;
}
// density always matches - we can scale it. See isBetterThan
//touchscreen如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
//notouch stylus finger
if (touchscreen != 0 && touchscreen != settings.touchscreen) {
return false;
}
}
//input如果有指定,且和设备不符,则返回false
if (input != 0) {
const int keysHidden = inputFlags&MASK_KEYSHIDDEN;
const int setKeysHidden = settings.inputFlags&MASK_KEYSHIDDEN;
//keysHidden:keysexposed keyshidden keyssoft
if (keysHidden != 0 && keysHidden != setKeysHidden) {
// For compatibility, we count a request for KEYSHIDDEN_NO as also
// matching the more recent KEYSHIDDEN_SOFT. Basically
// KEYSHIDDEN_NO means there is some kind of keyboard available.
//ALOGI("Matching keysHidden: have=%d, config=%d\n", keysHidden, setKeysHidden);
if (keysHidden != KEYSHIDDEN_NO || setKeysHidden != KEYSHIDDEN_SOFT) {
//ALOGI("No match!");
return false;
}
}
const int navHidden = inputFlags&MASK_NAVHIDDEN;
const int setNavHidden = settings.inputFlags&MASK_NAVHIDDEN;
//navHidden:navexposed navhidden
if (navHidden != 0 && navHidden != setNavHidden) {
return false;
}
//keyboard:nokeys qwerty 12key
if (keyboard != 0 && keyboard != settings.keyboard) {
return false;
}
//navigation: nonav dpad trackball wheel
if (navigation != 0 && navigation != settings.navigation) {
return false;
}
}
//和前面的screenSize一样的道理
//782x480 800x480 1280x720等
if (screenSize != 0) {
if (screenWidth != 0 && screenWidth > settings.screenWidth) {
return false;
}
if (screenHeight != 0 && screenHeight > settings.screenHeight) {
return false;
}
}
//v19 v21 v28等
//给高版本准备的资源,在低版本的设备上肯定会被无视
if (version != 0) {
if (sdkVersion != 0 && sdkVersion > settings.sdkVersion) {
return false;
}
//所有都是0,这一样相当于不比较
if (minorVersion != 0 && minorVersion != settings.minorVersion) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
ResTable_config::match方法虽然比较常,但逻辑相当明显,不过我们要注意以下几点:
- 我们看到这个方法默认是返回true的,只有在比较的时候才有可能返回false,这就是说,这个方法其实是比较宽容的,只有该config明确和设备的config不符时才会返回false。
- 我们看到在比较每个配置项之前,都会判断这个配置项是否为空(也就是是否设置了),只有在不为空的时候才会去比较。当我们
ResTable_type的config所有字段都是0(也就是不设置值)的时候,不论设备的config是什么都会返回true,即不设置就不会和设备的冲突。比如我们values目录下面的资源,不论设备当前是何种语言,values都是匹配的;但values-de下的资源,只有当设备切换成德语的时候才能匹配,切换成其它语言都会返回false。 - 在比较这些配置项的时候,是有顺序也就是优先级的。如果mcc都不匹配,那就直接返回false了,也就不会看后面的screenSize、sdkVersion了。我们表中的顺序就是match方法的比较顺序。
- Density也就是屏幕密度(hdpi、xxhdpi等这些)是没有参与比较的,也就是说,不论density的值是什么都不会被match方法淘汰。
经过ResTable_config::match方法的筛选后,还要和之前的匹配的最好的进行比较,这就要看ResTable_config::isBetterThan方法了:
//frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ResourceTypes.cpp
/**
* 和另外一个 ResTable_config 比较谁更符合设备当前配置
* o 和谁比较
* requested 比较的标准,也就是设备当前的配置
*/
bool ResTable_config::isBetterThan(const ResTable_config& o,
const ResTable_config* requested) const {
//requested不为空表示有标准可依,那么可以比较了
if (requested) {
/**
* 请注意这里this.mcc和o.mcc都是match requested的
* 不然就会在match方法中被淘汰,走不到这里
* 换句话说,this.mcc和o.mcc要么是0,要么等于requested.mcc
*/
if (imsi || o.imsi) {
//只比较两者mcc不等,并且设备配置的mcc不空的情况
//如果两者相等,或者配置信息没有指定(那就没必要比较了)
if ((mcc != o.mcc) && requested->mcc) {
return (mcc);
}
//mnc的情况和mcc一样
if ((mnc != o.mnc) && requested->mnc) {
return (mnc);
}
}
//道理和前面的imsi一模一样,不再详述
if (locale || o.locale) {
if ((language[0] != o.language[0]) && requested->language[0]) {
return (language[0]);
}
if ((country[0] != o.country[0]) && requested->country[0]) {
return (country[0]);
}
}
/**
* localeScript和localeVariant在match方法中也没有参与比较
* 这里的比较比较宽容,只要requested和this的不为空,就返回true
*/
if (localeScript[0] || o.localeScript[0]) {
if (localeScript[0] != o.localeScript[0] && requested->localeScript[0]) {
return localeScript[0];
}
}
if (localeVariant[0] || o.localeVariant[0]) {
if (localeVariant[0] != o.localeVariant[0] && requested->localeVariant[0]) {
return localeVariant[0];
}
}
道理和前面的imsi一模一样,不再详述
if (screenLayout || o.screenLayout) {
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_LAYOUTDIR) != 0
&& (requested->screenLayout & MASK_LAYOUTDIR)) {
int myLayoutDir = screenLayout & MASK_LAYOUTDIR;
int oLayoutDir = o.screenLayout & MASK_LAYOUTDIR;
//因为myLayoutDir只可能是ldltr或者ldrtl,所以这里虽然是大于号
//但实际比较的是仍然是myLayoutDir和oLayoutDir中是否有空的
return (myLayoutDir > oLayoutDir);
}
}
/**
* 注意隐含条件,smallestScreenWidthDp, o.smallestScreenWidthDp
* 都是小于或者等于requested.smallestScreenWidthDp的,否则过不了match那一关
* 既然大家要求的最小宽度都比设备的宽度小,那就选大一些的吧,因为它比较接近设备的宽度
*/
if (smallestScreenWidthDp || o.smallestScreenWidthDp) {
// The configuration closest to the actual size is best.
// We assume that larger configs have already been filtered
// out at this point. That means we just want the largest one.
if (smallestScreenWidthDp != o.smallestScreenWidthDp) {
return smallestScreenWidthDp > o.smallestScreenWidthDp;
}
}
//和前面的smallestScreenWidthDp的比较类似,选择和设备差距小的
//不过这里综合了宽度和高度
if (screenSizeDp || o.screenSizeDp) {
// "Better" is based on the sum of the difference between both
// width and height from the requested dimensions. We are
// assuming the invalid configs (with smaller dimens) have
// already been filtered. Note that if a particular dimension
// is unspecified, we will end up with a large value (the
// difference between 0 and the requested dimension), which is
// good since we will prefer a config that has specified a
// dimension value.
int myDelta = 0, otherDelta = 0;
if (requested->screenWidthDp) {
myDelta += requested->screenWidthDp - screenWidthDp;
otherDelta += requested->screenWidthDp - o.screenWidthDp;
}
if (requested->screenHeightDp) {
myDelta += requested->screenHeightDp - screenHeightDp;
otherDelta += requested->screenHeightDp - o.screenHeightDp;
}
//ALOGI("Comparing this %dx%d to other %dx%d in %dx%d: myDelta=%d otherDelta=%d",
// screenWidthDp, screenHeightDp, o.screenWidthDp, o.screenHeightDp,
// requested->screenWidthDp, requested->screenHeightDp, myDelta, otherDelta);
if (myDelta != otherDelta) {
return myDelta < otherDelta;
}
}
if (screenLayout || o.screenLayout) {
/**
* screenLayout和o.screenLayout不等,它们都小于或者等于requested->screenLayout
* 这里的大于或者小于也不是指具体的数值而是
* small < normal < large < xlarge
* 或者说SCREENSIZE_SMALL < SCREENSIZE_NORMAL < SCREENSIZE_LARGE
* < SCREENSIZE_XLARGE
*/
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_SCREENSIZE) != 0
&& (requested->screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE)) {
// A little backwards compatibility here: undefined is
// considered equivalent to normal. But only if the
// requested size is at least normal; otherwise, small
// is better than the default.
int mySL = (screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE);
int oSL = (o.screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE);
int fixedMySL = mySL;
int fixedOSL = oSL;
//设备的屏幕大小大于SCREENSIZE_NORMAL的时候,如果没有指定,则默认为SCREENSIZE_NORMAL
//否则默认为SCREENSIZE_SMALL
if ((requested->screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE) >= SCREENSIZE_NORMAL) {
if (fixedMySL == 0) fixedMySL = SCREENSIZE_NORMAL;
if (fixedOSL == 0) fixedOSL = SCREENSIZE_NORMAL;
}
// For screen size, the best match is the one that is
// closest to the requested screen size, but not over
// (the not over part is dealt with in match() below).
//经过修正后有可能相等了,如果相等,肯定有一个被修正了,因为原本它们不等的
if (fixedMySL == fixedOSL) {
// If the two are the same, but 'this' is actually
// undefined, then the other is really a better match.
//被修正的是this,那么this肯定不如o的好啦
if (mySL == 0) return false;
//否则this好
return true;
}
//不等的话,选择大的那个,因为大家都比requested的小
//那就选大的,因为它比较接近requested
if (fixedMySL != fixedOSL) {
return fixedMySL > fixedOSL;
}
}
//和前面的imsi的比较类似,不赘述
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_SCREENLONG) != 0
&& (requested->screenLayout & MASK_SCREENLONG)) {
return (screenLayout & MASK_SCREENLONG);
}
}
//和前面的imsi的比较类似,不赘述
if ((orientation != o.orientation) && requested->orientation) {
return (orientation);
}
//直接用异或了,很好理解
if (uiMode || o.uiMode) {
if (((uiMode^o.uiMode) & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE) != 0
&& (requested->uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE)) {
return (uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE);
}
if (((uiMode^o.uiMode) & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT) != 0
&& (requested->uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT)) {
return (uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT);
}
}
if (screenType || o.screenType) {
if (density != o.density) {
// Use the system default density (DENSITY_MEDIUM, 160dpi) if none specified.
//修正,默认值mdpi
const int thisDensity = density ? density : int(ResTable_config::DENSITY_MEDIUM);
const int otherDensity = o.density ? o.density : int(ResTable_config::DENSITY_MEDIUM);
// We always prefer DENSITY_ANY over scaling a density bucket.
//DENSITY_ANY的优先级最高
if (thisDensity == ResTable_config::DENSITY_ANY) {
return true;
} else if (otherDensity == ResTable_config::DENSITY_ANY) {
return false;
}
//修正,默认值mdpi
int requestedDensity = requested->density;
if (requested->density == 0 ||
requested->density == ResTable_config::DENSITY_ANY) {
requestedDensity = ResTable_config::DENSITY_MEDIUM;
}
// DENSITY_ANY is now dealt with. We should look to
// pick a density bucket and potentially scale it.
// Any density is potentially useful
// because the system will scale it. Scaling down
// is generally better than scaling up.
int h = thisDensity;
int l = otherDensity;
bool bImBigger = true;
if (l > h) {
int t = h;
h = l;
l = t;
bImBigger = false;
}
/**
* 这段代码的意思是,如果requestedDensity比this的和other的都高
* 那就在this和othre中选择dpi比较高的那个,其实还是比较接近的那个
* 这样显示效果会好些,图像不会显得特别小
*/
if (requestedDensity >= h) {
// requested value higher than both l and h, give h
return bImBigger;
}
/**
* 这段代码的意思是,如果requestedDensity比this的和other的都低
* 那就在this和othre中选择dpi比较低的那个,其实还是比较接近的那个
* 这样显示效果会好些,图像不会显得特别大
*/
if (l >= requestedDensity) {
// requested value lower than both l and h, give l
return !bImBigger;
}
//剩下的情况就是requested介于l和h之间了
// saying that scaling down is 2x better than up
if (((2 * l) - requestedDensity) * h > requestedDensity * requestedDensity) {
//选择dpi低的那个,至于为什么是上面的那个不等式,可能跟图形学有关吧,
//这种情况下缩小比放大好2倍
return !bImBigger;
} else {
return bImBigger;
}
}
if ((touchscreen != o.touchscreen) && requested->touchscreen) {
return (touchscreen);
}
}
if (input || o.input) {
const int keysHidden = inputFlags & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN;
const int oKeysHidden = o.inputFlags & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN;
if (keysHidden != oKeysHidden) {
const int reqKeysHidden =
requested->inputFlags & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN;
if (reqKeysHidden) {
if (!keysHidden) return false;
if (!oKeysHidden) return true;
// For compatibility, we count KEYSHIDDEN_NO as being
// the same as KEYSHIDDEN_SOFT. Here we disambiguate
// these by making an exact match more specific.
if (reqKeysHidden == keysHidden) return true;
if (reqKeysHidden == oKeysHidden) return false;
}
}
const int navHidden = inputFlags & MASK_NAVHIDDEN;
const int oNavHidden = o.inputFlags & MASK_NAVHIDDEN;
if (navHidden != oNavHidden) {
const int reqNavHidden =
requested->inputFlags & MASK_NAVHIDDEN;
if (reqNavHidden) {
if (!navHidden) return false;
if (!oNavHidden) return true;
}
}
if ((keyboard != o.keyboard) && requested->keyboard) {
return (keyboard);
}
if ((navigation != o.navigation) && requested->navigation) {
return (navigation);
}
}
//和前面的screenSizeDp的处理类似,不再赘述
if (screenSize || o.screenSize) {
// "Better" is based on the sum of the difference between both
// width and height from the requested dimensions. We are
// assuming the invalid configs (with smaller sizes) have
// already been filtered. Note that if a particular dimension
// is unspecified, we will end up with a large value (the
// difference between 0 and the requested dimension), which is
// good since we will prefer a config that has specified a
// size value.
int myDelta = 0, otherDelta = 0;
if (requested->screenWidth) {
myDelta += requested->screenWidth - screenWidth;
otherDelta += requested->screenWidth - o.screenWidth;
}
if (requested->screenHeight) {
myDelta += requested->screenHeight - screenHeight;
otherDelta += requested->screenHeight - o.screenHeight;
}
if (myDelta != otherDelta) {
return myDelta < otherDelta;
}
}
//sdkVersion和o.sdkVersion都会比requested->sdkVersion小
//否则match不上,选高的
//这个也好理解,设备是v28,v19和v22的资源肯定选v22的
if (version || o.version) {
if ((sdkVersion != o.sdkVersion) && requested->sdkVersion) {
return (sdkVersion > o.sdkVersion);
}
//都是0,等于没比较
if ((minorVersion != o.minorVersion) &&
requested->minorVersion) {
return (minorVersion);
}
}
//如果前面的比较项一个都没比,那直接忽略当前的这个
//这说明这个isBetterThan是比较严苛的,除非是真的好,不然就返回false
return false;
}//if(requested)
/**
* 如果标准都没有指定,那还怎么比较呢?
* 只能比比谁更详细了,选择更详细的那个
*/
return isMoreSpecificThan(o);
}
在ResTable_config::isBetterThan方法中,会先看传过来的设备配置信息(requested指针)是否为空,如果为空,那么我们就失去了比较的标准,也就没法比较this和o哪个更好了,只能比较一下那个更详细,然后选择更详细的那个。如果传过来的设备配置信息不为空,才会进行比较:
- 和
match方法不同,isBetterThan默认返回false,因此它是比较严苛的,只有在真的好的时候才返回true - 比较项同样是有顺序的,并且和
match的顺序还有不同 - Density在这里参与了比较,比较的原则可以概括为,选择和设备最接近的或者显示效果最好的(感觉有些废话,还是看代码说事儿吧,哈哈)
- 这个方法在执行的时候有个隐含条件,那就是this和o都是经过了
match方法筛选的,否则直接在match的时候就pass了
下面一起瞅瞅ResTable_config::isMoreSpecificThan方法吧:
//frameworks/base/libs/androidfw/ResourceTypes.cpp
/**
* 这个方法只需详细看一两个比较项就可以了,模式都是一模一样的
* 后面的比较项大概瞅一眼就行,这里贴出代码只是为了让大家注意比较的
* 优先级和顺序
*/
bool ResTable_config::isMoreSpecificThan(const ResTable_config& o) const {
// The order of the following tests defines the importance of one
// configuration parameter over another. Those tests first are more
// important, trumping any values in those following them.
if (imsi || o.imsi) {
if (mcc != o.mcc) {
if (!mcc) return false;
if (!o.mcc) return true;
}
if (mnc != o.mnc) {
if (!mnc) return false;
if (!o.mnc) return true;
}
}
if (locale || o.locale) {
const int diff = isLocaleMoreSpecificThan(o);
if (diff < 0) {
return false;
}
if (diff > 0) {
return true;
}
}
if (screenLayout || o.screenLayout) {
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_LAYOUTDIR) != 0) {
if (!(screenLayout & MASK_LAYOUTDIR)) return false;
if (!(o.screenLayout & MASK_LAYOUTDIR)) return true;
}
}
if (smallestScreenWidthDp || o.smallestScreenWidthDp) {
if (smallestScreenWidthDp != o.smallestScreenWidthDp) {
if (!smallestScreenWidthDp) return false;
if (!o.smallestScreenWidthDp) return true;
}
}
if (screenSizeDp || o.screenSizeDp) {
if (screenWidthDp != o.screenWidthDp) {
if (!screenWidthDp) return false;
if (!o.screenWidthDp) return true;
}
if (screenHeightDp != o.screenHeightDp) {
if (!screenHeightDp) return false;
if (!o.screenHeightDp) return true;
}
}
if (screenLayout || o.screenLayout) {
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_SCREENSIZE) != 0) {
if (!(screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE)) return false;
if (!(o.screenLayout & MASK_SCREENSIZE)) return true;
}
if (((screenLayout^o.screenLayout) & MASK_SCREENLONG) != 0) {
if (!(screenLayout & MASK_SCREENLONG)) return false;
if (!(o.screenLayout & MASK_SCREENLONG)) return true;
}
}
if (orientation != o.orientation) {
if (!orientation) return false;
if (!o.orientation) return true;
}
if (uiMode || o.uiMode) {
if (((uiMode^o.uiMode) & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE) != 0) {
if (!(uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE)) return false;
if (!(o.uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_TYPE)) return true;
}
if (((uiMode^o.uiMode) & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT) != 0) {
if (!(uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT)) return false;
if (!(o.uiMode & MASK_UI_MODE_NIGHT)) return true;
}
}
// density is never 'more specific'
// as the default just equals 160
if (touchscreen != o.touchscreen) {
if (!touchscreen) return false;
if (!o.touchscreen) return true;
}
if (input || o.input) {
if (((inputFlags^o.inputFlags) & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN) != 0) {
if (!(inputFlags & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN)) return false;
if (!(o.inputFlags & MASK_KEYSHIDDEN)) return true;
}
if (((inputFlags^o.inputFlags) & MASK_NAVHIDDEN) != 0) {
if (!(inputFlags & MASK_NAVHIDDEN)) return false;
if (!(o.inputFlags & MASK_NAVHIDDEN)) return true;
}
if (keyboard != o.keyboard) {
if (!keyboard) return false;
if (!o.keyboard) return true;
}
if (navigation != o.navigation) {
if (!navigation) return false;
if (!o.navigation) return true;
}
}
if (screenSize || o.screenSize) {
if (screenWidth != o.screenWidth) {
if (!screenWidth) return false;
if (!o.screenWidth) return true;
}
if (screenHeight != o.screenHeight) {
if (!screenHeight) return false;
if (!o.screenHeight) return true;
}
}
if (version || o.version) {
if (sdkVersion != o.sdkVersion) {
if (!sdkVersion) return false;
if (!o.sdkVersion) return true;
}
if (minorVersion != o.minorVersion) {
if (!minorVersion) return false;
if (!o.minorVersion) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
ResTable_config::isMoreSpecificThan的比较模式非常简单,不用多说,大家要注意的有:
- 比较的每一项的优先级也就是顺序
- Density不参与这个比较
下一篇介绍资源配置的更新,设备的配置信息变动后,这个改变是如何一步一步通知到资源管理框架的。