Android app换肤原理及其简单实现
Android一键式换肤原理
一.换肤原理
- 下载皮肤资源包 (Apk,lib)到本地目录中
- 主APP中使用动态加载技术动态加载皮肤资源包的资源对象(真正的资源管理者AssetManager)
- 获取所有需要换肤的控件以及控件的textColor,background,src属性 (xml加载监听)
- 根据需要换肤控件的资源ID去资源包中匹配对应的资源ID,然后进行替换
二.加载皮肤资源包
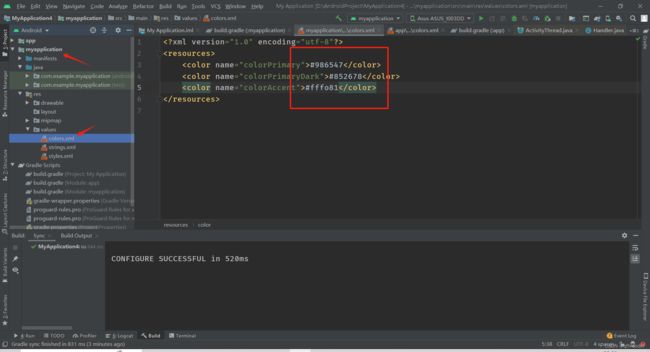
新建资源包
一般没有activity
修改皮肤包下面的颜色,方便演示,名字要一样,
主模块是这三种颜色
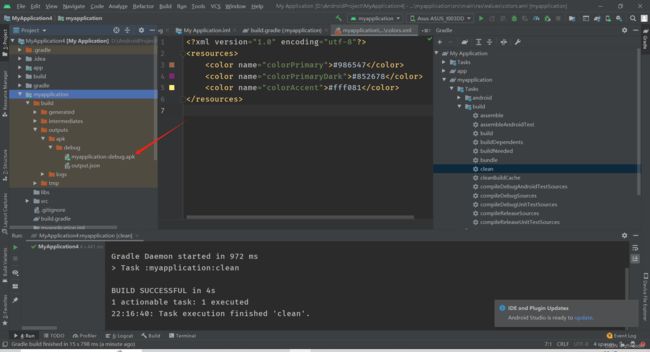
生成apk资源包,build一下
放到本地设备sd卡根目录上
写一个资源包管理类
代码
@file:Suppress("JAVA_CLASS_ON_COMPANION", "RECEIVER_NULLABILITY_MISMATCH_BASED_ON_JAVA_ANNOTATIONS")
package com.example.myapplication
import android.content.Context
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import android.content.res.AssetManager
import android.content.res.Resources
import java.lang.Exception
//单例模式
object SkinManager {
private var context: Context? = null
private var skinPackageName: String? = null
fun loadSkinApk(context: Context, path: String) {
this.context = context
val packageManager = context.packageManager
val packageArchiveInfo =
packageManager.getPackageArchiveInfo(path, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES)
skinPackageName = packageArchiveInfo.packageName
val assetManager = AssetManager::class.java.newInstance()
try {
val method =
assetManager.javaClass.getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath", String.javaClass)
method.invoke(assetManager, path)
val resources = Resources(
assetManager,
context.resources.displayMetrics,
context.resources.configuration
)
} catch (e: Exception) {
}
}
}
三.解析皮肤包资源
@file:Suppress("JAVA_CLASS_ON_COMPANION", "RECEIVER_NULLABILITY_MISMATCH_BASED_ON_JAVA_ANNOTATIONS")
package com.example.myapplication
import android.content.Context
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import android.content.res.AssetManager
import android.content.res.Resources
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat
import java.lang.Exception
//单例模式
object SkinManager {
private lateinit var context: Context
private var skinPackageName: String? = null
private var resources: Resources? = null
fun loadSkinApk(context: Context, path: String) {
this.context = context
val packageManager = context.packageManager
val packageArchiveInfo =
packageManager.getPackageArchiveInfo(path, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES)
skinPackageName = packageArchiveInfo.packageName
val assetManager = AssetManager::class.java.newInstance()
try {
val method =
assetManager.javaClass.getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath", String.javaClass)
method.invoke(assetManager, path)
resources = Resources(
assetManager,
context.resources.displayMetrics,
context.resources.configuration
)
} catch (e: Exception) {
}
}
/**去资源包的资源对象中欢取颜色资源
* @param id 当前应用中的资源ID
* @return 当前应用中的资源id所匹配的在皮肤资源中的ID
*/
fun getColor(id: Int): Int? {
if (resources == null) {
return id
}
//获取到传进来的id在资源中的类型,color,drawable,mipmap
val resourceTypeName = context.resources?.getResourceTypeName(id)
//获取到传进来id在资源中的名字,colorPrimary
val resourceEntryName = context.resources?.getResourceEntryName(id)
val identifier =
resources?.getIdentifier(resourceEntryName, resourceTypeName, skinPackageName)
if (identifier == 0) {
return id
}
return identifier?.let { resources?.getColor(it) }
}
fun getDrawable(id: Int): Drawable? {
if (resources == null) {
return ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, id)
}
//获取到传进来的id在资源中的类型,color,drawable,mipmap
val resourceTypeName = context?.resources?.getResourceTypeName(id)
//获取到传进来id在资源中的名字,colorPrimary
val resourceEntryName = context?.resources?.getResourceEntryName(id)
val identifier =
resources?.getIdentifier(resourceEntryName, resourceTypeName, skinPackageName)
if (identifier == 0) {
return ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, id)
}
return identifier?.let { resources?.getDrawable(it) }
}
}
四.xml布局加载监听
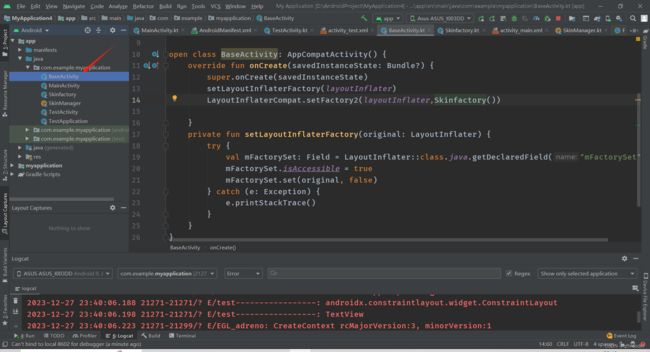
新建基类
BaseActivity
package com.example.myapplication
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.LayoutInflaterCompat
import java.lang.reflect.Field
open class BaseActivity: AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setLayoutInflaterFactory(layoutInflater)
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(layoutInflater,Skinfactory())
}
private fun setLayoutInflaterFactory(original: LayoutInflater) {
try {
val mFactorySet: Field = LayoutInflater::class.java.getDeclaredField("mFactorySet")
mFactorySet.isAccessible = true
mFactorySet.set(original, false)
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
}
新建工厂类
Skinfactory
package com.example.myapplication
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.Context
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.util.Log
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import kotlin.math.log
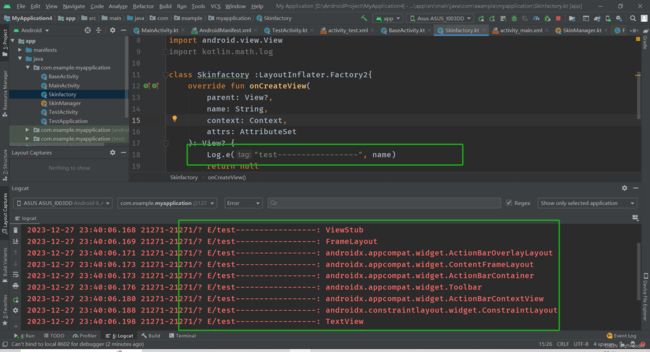
class Skinfactory :LayoutInflater.Factory2{
override fun onCreateView(
parent: View?,
name: String,
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet
): View? {
Log.e("test-----------------", name)
return null
}
@SuppressLint("LongLogTag")
override fun onCreateView(name: String, context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet): View? {
Log.e("test=====================", name)
return null
}
}
运行发现onCreateView中的name打印的都是我们布局中的view的名字
五.换肤属性封装
创建view
封装两个类,一个是view,一个是属性
package com.example.myapplication
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.Context
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.util.Log
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import kotlin.math.log
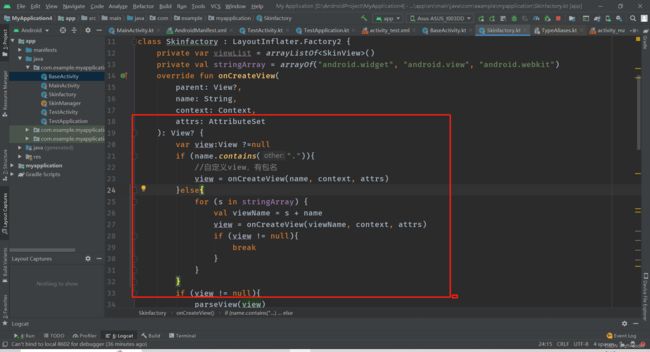
class Skinfactory : LayoutInflater.Factory2 {
private var viewList = arrayListOf<SkinView>()
private val stringArray = arrayOf("android.widget", "android.view", "android.webkit")
override fun onCreateView(
parent: View?,
name: String,
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet
): View? {
var view:View ?=null
if (name.contains(".")){
//自定义view,有包名
view = onCreateView(name, context, attrs)
}else{
for (s in stringArray) {
val viewName = s + name
view = onCreateView(viewName, context, attrs)
if (view != null){
break
}
}
}
if (view != null){
parseView(view)
}
return view
}
/**判断这个控件是不是符合我们的换肤的标准,如果符合就收集
* @param view
*/
private fun parseView(view: View) {
}
@SuppressLint("LongLogTag")
override fun onCreateView(name: String, context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet): View? {
Log.e("test=====================", name)
return null
}
class SkinView {
var skinItems: List<SkinItem>? = null
var view: View? = null
}
//每条属性的封装对象
class SkinItem {
//属性的名字,textColor,background
var name: String? = null
//属性的值的类型,color,drawable,mipmap
var typeName: String? = null
//属性的值的名字,colorPrimary
var entryName: String? = null
//属性值在R文件中的资源ID
var resId = 0
constructor(name: String?, typeName: String?, entryName: String?, resId: Int) {
this.name = name
this.typeName = typeName
this.entryName = entryName
this.resId = resId
}
}
}
六.皮肤资源匹配实现资源替换
package com.example.myapplication
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.Context
import android.os.Build
import android.text.TextUtils
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.util.Log
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.annotation.IntegerRes
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor
import kotlin.math.log
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
class Skinfactory : LayoutInflater.Factory2 {
private var viewList = arrayListOf<SkinView>()
private val stringArray = arrayOf("android.widget", "android.view", "android.webkit")
override fun onCreateView(
parent: View?,
name: String,
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet
): View? {
var view: View? = null
if (name.contains(".")) {
//自定义view,有包名
view = onCreateView(name, context, attrs)
} else {
for (s in stringArray) {
val viewName = s + name
view = onCreateView(viewName, context, attrs)
if (view != null) {
break
}
}
}
if (view != null) {
parseView(view, attrs)
}
return view
}
/**判断这个控件是不是符合我们的换肤的标准,如果符合就收集
* @param view
*/
private fun parseView(view: View, attrs: AttributeSet) {
var skinItems = arrayListOf<SkinItem>()
for (i in 0 until attrs.attributeCount) {
//获取到这条属性的名字
val attributeName = attrs.getAttributeName(i)
if (attributeName.contains("background") || attributeName.contains("textColor")) {
//获取到资源的ID @8917317
val attributeValue = attrs.getAttributeValue(i)
val resId: Int = attributeValue.substring(1).toInt()
//获取属性的名字,以及属性值的类型
val resourceEntryName = view.resources.getResourceEntryName(resId)
val resourceTypeName = view.resources.getResourceTypeName(resId)
val skinItem = SkinItem(attributeName, resourceTypeName, resourceEntryName, resId)
skinItems.add(skinItem)
}
}
if (skinItems.size > 0) {
val skinView = SkinView(skinItems, view)
viewList.add(skinView)
}
}
@SuppressLint("LongLogTag")
override fun onCreateView(name: String, context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet): View? {
var view: View?=null
val aClass: Class<*> = context.classLoader.loadClass(name)
val constructor: Constructor<out View> =
aClass.getConstructor(Context::class.java, AttributeSet::class.java) as Constructor<out View>
constructor.newInstance(context, attrs)
return view
}
class SkinView {
var skinItems: List<SkinItem>? = null
var view: View? = null
constructor(skinItems: List<SkinItem>?, view: View?) {
this.skinItems = skinItems
this.view = view
}
fun apply() {
skinItems?.forEach { skinItem ->
if (TextUtils.equals(skinItem.name, "background")) {
if (TextUtils.equals(skinItem.typeName, "color")) {
SkinManager.getColor(skinItem.resId)?.let { view?.setBackgroundColor(it) }
} else if (TextUtils.equals(skinItem.typeName, "drawable")) {
// if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN){
view?.background = SkinManager.getDrawable(skinItem.resId)
// }
}
} else if (TextUtils.equals(skinItem.name, "textColor")) {
if (view is TextView) {
SkinManager.getColor(skinItem.resId)?.let {
(view as TextView).setTextColor(
it
)
}
} else if (view is Button) {
SkinManager.getColor(skinItem.resId)?.let {
(view as Button).setTextColor(
it
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
//每条属性的封装对象
class SkinItem {
//属性的名字,textColor,background
var name: String? = null
//属性的值的类型,color,drawable,mipmap
var typeName: String? = null
//属性的值的名字,colorPrimary
var entryName: String? = null
//属性值在R文件中的资源ID
var resId = 0
constructor(name: String?, typeName: String?, entryName: String?, resId: Int) {
this.name = name
this.typeName = typeName
this.entryName = entryName
this.resId = resId
}
}
}