基于矩阵实现的最短路径算法
1.最短路径
图中最短路径是指:寻找图(由结点和路径组成的)中两结点之间的权重最小的路径。Wikipedia上最短路径(Shortest Path)的定义如下:In graph theory, the shortest path problem is the problem of finding a path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph such that the sum of the weights of its constituent edges is minimized.
2.传统算法
2.1Dijkstra算法
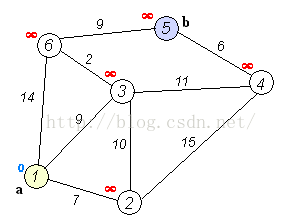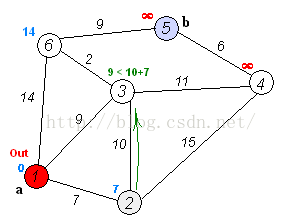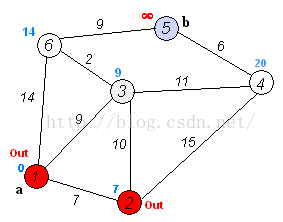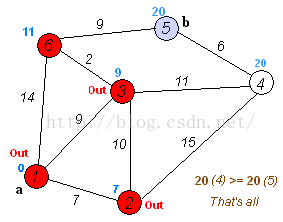
Dijkstra算法是目前公认的求解最短路径的算法。其算法思想是:用指定的起点作为根,生成最短路径树(Shortest Path Tree)。然后利用两个集合,一个是包含最短路径树顶点的集合sptSet,一个是不包含最短路径树的顶点集合U。算法的每一步都将从不包含最短路径树的顶点集合U中找到一个点,使得从起点到它有最短路径。参考网址: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-6-dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm/Dijkstra算法的步骤是:
- 创建一个集合sptSet(Shortest Path Tree Set),用来记录最短路径树中的点,并且初始化为空。如,起点到哪些点的最短路径计算完成了。
- 计算图中所有点的距离值,并用无穷大初始化所有距离值。但是,起点的距离值设为0.
- 当sptSet没有包含图中所有点时,1.从U中选取一个距离起点最小的顶点k,并加入到sptSet中(选定的距离就是v到k的最短路径长度),2.以k为中间点,若从起点到顶点u的距离(经过顶点k)比起点到顶点u的距离(不经过顶点k)短,则修改到顶点u的距离。
2.2算法实现
用Python实现的代码:import numpy as np
from numpy.random import rand
def init(dimension):
mat = (rand(dimension, dimension) * dimension ** 2)
mat[(rand(dimension) * dimension).astype(int), (rand(dimension) * dimension).astype(int)] = np.inf
for i in range(dimension):
mat[i, i] = 0
return mat
#A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value, from
#the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree
def minDistance(distances, sptSet, dimension):
min = np.inf
min_index = 0
for i in range(dimension):
if((sptSet[i] == False) and (distances[i] < min)):
min = distances[i]
min_index = i
return min_index
def dijkstra(graph, dimension, source = 0):
sptSet = []
distances = []
#Initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for i in range(dimension):
distances.append(np.inf)
sptSet.append(False)
#Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0
distances[source] = 0
#Find shortest path for all vertices
for i in range(dimension - 1):
#Pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices not
#yet processed. u is always equal to src in first iteration.
u = minDistance(distances, sptSet, dimension)
#Mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = True
for j in range(dimension):
if((not sptSet[j]) and (distances[u] + graph[u][j] < distances[j])):
distances[j] = distances[u] + graph[u][j]
return distances
if __name__ == "__main__":
dimension = 6
data = init(dimension)
data1 = [[0, 7, 9, np.inf, np.inf, 14],
[7, 0, 10, 15, np.inf, np.inf],
[9, 10, 0, 11, np.inf, 2],
[np.inf, 15, 11, 0, 6, 0],
[np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 6, 0, 9],
[14, np.inf, 2, np.inf, 9, 0]]
data3 = [[0, 4, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 8, np.inf],
[4, 0, 8, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 11, np.inf],
[np.inf, 8, 0, 7, np.inf, 4, np.inf, np.inf, 2],
[np.inf, np.inf, 7, 0, 9, 14, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf],
[np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 9, 0, 10, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf],
[np.inf, np.inf, 4, np.inf, 10, 0, 2, np.inf, np.inf],
[np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 14, np.inf, 2, 0, 1, 6],
[8, 11, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 1, 0, 7],
[np.inf, np.inf, 2, np.inf, np.inf, np.inf, 6, 7, 0]]
print(dijkstra(data1, dimension, 0))
3.基于矩阵的实现算法
3.1算法推导
邻接矩阵的定义形式:对角线元素值为0,即结点i到结点i的最短路径长度为0;非邻结点权值为无穷大,即结点i和结点j非邻结,则邻接矩阵的(i,j)值为无穷大;邻结点权值是权重,即结点i和结点j邻结,则邻接矩阵的(i,j)值为权重,表示如下:而起点向量定义如下:
列向量![]() 与邻接矩阵A(N*N)的第j列相加,然后取最小值,表示经过k条路径到达第j个结点的最短路径,公式表示如下:
与邻接矩阵A(N*N)的第j列相加,然后取最小值,表示经过k条路径到达第j个结点的最短路径,公式表示如下:
也可以写成:
![]()
由此,可以得到通式:
![]()
3.2算法实现
用Python实现的算法代码:import numpy as np
from numpy.random import rand
def shortestPath(adjacencyMat, distances, dimension):
for it in range(dimension):
# for i in range(n):
# distances[i] = np.min(distances + adjacencyMat[:, i])
distances = (distances + adjacencyMat).min(axis = 0).reshape(dimension, 1)
# print(distances)
return distances
#######################################################################################################
# distances[v] = |0 if v = startVertex
# |np.inf otherwise
#
# adjacencyMat[u, v] = |k if u -> v, and weight = k
# |0 if i == j
# |np.inf if u -/> v
#######################################################################################################
def init(dimension, startVertex):
distances = np.zeros((dimension, 1))
mat = (rand(dimension, dimension) * dimension)
mat[(rand(dimension) * dimension).astype(int), (rand(dimension) * dimension).astype(int)] = np.inf
for i in range(dimension):
distances[i] = np.inf
mat[i, i] = 0
distances[startVertex] = 0
return mat, distances
if __name__ == "__main__":
startVertex = 0
dimension = 4
adjacencyMat, distances = init(dimension, startVertex)
adjacencyMat2 = np.array([[0,2,4,2],[np.inf,0,1,0],[3,np.inf,0,np.inf],[1,np.inf,2,0]])
adjacencyMat3 = np.array([[ 0 , 3.08968315, np.inf , np.inf ],
[ 0.21511113 , 0 , 1.52008847 , 3.66431105],
[ 2.50440191 , np.inf , 0 , 3.35943021],
[ 3.84022903 , np.inf , 0.5134998 , 0 ]])
adjacencyMat4 = np.array([[0,1,2,np.inf],[1,0,2,4],[2,2,0,3],[np.inf,4,3,0]])
result = shortestPath(adjacencyMat3, distances, dimension)
print(result.T)4.评价
基于矩阵运算实现的图算法,有以下几点优势:
- 易于实现。利用矩阵可以仅仅通过矩阵与矩阵或矩阵与向量的运算就可以实现一些图算法。
- 易于并行。在超大矩阵运算中,可以采用分块的方式平行处理矩阵运算。同理,也可以很容易的移植分布式上(可以参考我的博文基于Spark实现的超大矩阵运算)。
- 效率更高。基于矩阵的图形算法更清晰突出的数据访问模式,可以很容易地优化(实验测试工作已完成)。
- 易于理解。这个需要对离散数学或者图论有一定基础,知道每一步矩阵运算所对应的物理意义或数学意义。