FAST算法学习
算法简介
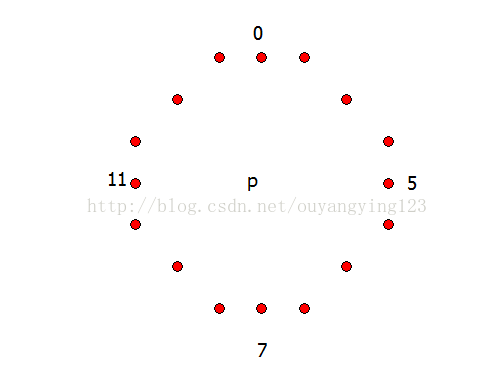
FAST 全称 Features from accelerated segment test,一种用于角点检测的算法,该算法的原理是取图像中检测点,以该点为圆心的周围的16个像素点判断检测点是否为角点。通俗的讲就是中心的的像素值比大部分周围的像素值要亮一个阈值 或者 暗一个阈值则为角点。
实现过程
1.角点检测
对于检测点p,若周围的16个像素点中有N个连续的点的像素值都比其小一个阈值 或 大 一个阈值,则该点可作为角点。即img[x] < img[p] - threshold 或 img[x] > img[p] + threshold,
threshold为阈值,img[x]为任意连续的10个像素点值,img[p]为中心像素点值。
2.非极大值抑制
该步骤用于筛选出合适的角点,比如在人脸检测的时候测出有三个窗口的人脸,但要确定一个最合适的窗口就需要进行非极大值抑制。
(1)根据得分函数求得每个角点得分
得分函数的规则为:周围16个点中最大的 连续10个点的绝对值差的最小值,且满足x>threshold的值即为得分。
(2)在3x3的区域中比较得分,选取分值最大的那个点。
代码实现
上opencv的fast实现(CV_SSE2已舍去)
void FAST_t(InputArray _img, std::vector& keypoints, int threshold, bool nonmax_suppression)
{
Mat img = _img.getMat();
const int K = patternSize / 2, N = patternSize + K + 1;
int i, j, k, pixel[25];
/*
计算周围16个像素点在实际图像中的相对位置
*/
makeOffsets(pixel, (int)img.step, patternSize);
keypoints.clear();
threshold = std::min(std::max(threshold, 0), 255);
/*
于筛选出角点,threshold_tab表中的值分为三个区域:
-255~-threshold为 1 :img[x] < img[p] - threshold
-threshold ~ threshold为 0
threshold ~ 255 为2 : img[x] > img[p] + threshold
通过周围点与像素值的差值确定像素点属于哪个区域
*/
uchar threshold_tab[512];
for (i = -255; i <= 255; i++)
threshold_tab[i + 255] = (uchar)(i < -threshold ? 1 : i > threshold ? 2 : 0);
AutoBuffer _buf((img.cols + 16) * 3 * (sizeof(int)+sizeof(uchar)) + 128);
uchar* buf[3];
buf[0] = _buf; buf[1] = buf[0] + img.cols; buf[2] = buf[1] + img.cols;
int* cpbuf[3];
cpbuf[0] = (int*)alignPtr(buf[2] + img.cols, sizeof(int)) + 1;
cpbuf[1] = cpbuf[0] + img.cols + 1;
cpbuf[2] = cpbuf[1] + img.cols + 1;
memset(buf[0], 0, img.cols * 3);
for (i = 3; i < img.rows - 2; i++)
{
const uchar* ptr = img.ptr(i) +3;
uchar* curr = buf[(i - 3) % 3];
int* cornerpos = cpbuf[(i - 3) % 3];
memset(curr, 0, img.cols);
int ncorners = 0;
if (i < img.rows - 3)
{
j = 3;
for (; j < img.cols - 3; j++, ptr++)
{
int v = ptr[0];
const uchar* tab = &threshold_tab[0] - v + 255;
/*
pixel[x] 为周围某个像素点在实际图像中的相对位置
ptr[pixel[0]]为该位置的像素值
tab[ptr[pixel[0]]]为该位置像素点相对于中心点所属的区域
*/
int d = tab[ptr[pixel[0]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[8]]];
if (d == 0)
continue;
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[2]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[10]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[4]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[12]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[6]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[14]]];
if (d == 0)
continue;
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[1]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[9]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[3]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[11]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[5]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[13]]];
d &= tab[ptr[pixel[7]]] | tab[ptr[pixel[15]]];
if (d & 1)
{
int vt = v - threshold, count = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
int x = ptr[pixel[k]];
if (x < vt)
{
if (++count > K)
{
/*
求得分,cornerpos记录具体位置,curr记录当前位置得分
*/
cornerpos[ncorners++] = j;
if (nonmax_suppression)
curr[j] = (uchar)cornerScore(ptr, pixel, threshold);
break;
}
}
else
count = 0;
}
}
if (d & 2)
{
int vt = v + threshold, count = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
int x = ptr[pixel[k]];
if (x > vt)
{
if (++count > K)
{
cornerpos[ncorners++] = j;
if (nonmax_suppression)
curr[j] = (uchar)cornerScore(ptr, pixel, threshold);
break;
}
}
else
count = 0;
}
}
}
}
cornerpos[-1] = ncorners;
/*这里重点说一下为什么是i==3的时候跳过,因为进行非极大值抑制的时候是对prev行进行操作的,这样操作可实现非极大值抑制也是从第三行开始*/
if (i == 3)
continue;
const uchar* prev = buf[(i - 4 + 3) % 3];
const uchar* pprev = buf[(i - 5 + 3) % 3];
cornerpos = cpbuf[(i - 4 + 3) % 3];
ncorners = cornerpos[-1];
/*
假设当前行为第 i 行 curr,
对应第i-1行prev,
第i-2行pprev
此时cornerpos记录的是第i-1行prev的角点位置信息,
最后求出的的非极大值抑制是相对于第i-1行prev的,
因为要3x3的区域中进行,只有下一行求出后才可进行当前行的计算。
*/
for (k = 0; k < ncorners; k++)
{
j = cornerpos[k];
int score = prev[j];
if (!nonmax_suppression ||
(score > prev[j + 1] && score > prev[j - 1] &&
score > pprev[j - 1] && score > pprev[j] && score > pprev[j + 1] &&
score > curr[j - 1] && score > curr[j] && score > curr[j + 1]))
{
keypoints.push_back(KeyPoint((float)j, (float)(i - 1), 7.f, -1, (float)score));
}
}
}
}
void makeOffsets(int pixel[25], int rowStride, int patternSize)
{
static const int offsets16[][2] =
{
{0, 3}, { 1, 3}, { 2, 2}, { 3, 1}, { 3, 0}, { 3, -1}, { 2, -2}, { 1, -3},
{0, -3}, {-1, -3}, {-2, -2}, {-3, -1}, {-3, 0}, {-3, 1}, {-2, 2}, {-1, 3}
};
static const int offsets12[][2] =
{
{0, 2}, { 1, 2}, { 2, 1}, { 2, 0}, { 2, -1}, { 1, -2},
{0, -2}, {-1, -2}, {-2, -1}, {-2, 0}, {-2, 1}, {-1, 2}
};
static const int offsets8[][2] =
{
{0, 1}, { 1, 1}, { 1, 0}, { 1, -1},
{0, -1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}
};
const int (*offsets)[2] = patternSize == 16 ? offsets16 :
patternSize == 12 ? offsets12 :
patternSize == 8 ? offsets8 : 0;
CV_Assert(pixel && offsets);
int k = 0;
for( ; k < patternSize; k++ )
pixel[k] = offsets[k][0] + offsets[k][1] * rowStride;
for( ; k < 25; k++ )
pixel[k] = pixel[k - patternSize];
}求得分函数:
template<>
int cornerScore<16>(const uchar* ptr, const int pixel[], int threshold)
{
const int K = 8, N = K * 3 + 1;
int k, v = ptr[0];
short d[N];
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
d[k] = (short)(v - ptr[pixel[k]]);
//对应img[x] > img[p] + threshold
int a0 = threshold;
for (k = 0; k < 16; k += 2)
{
int a = std::min((int)d[k + 1], (int)d[k + 2]);
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 3]);
if (a <= a0)
continue;
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 4]);
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 5]);
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 6]);
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 7]);
a = std::min(a, (int)d[k + 8]);
a0 = std::max(a0, std::min(a, (int)d[k]));
a0 = std::max(a0, std::min(a, (int)d[k + 9]));
}
//对应img[x] < img[p] - threshold
int b0 = -a0;
for (k = 0; k < 16; k += 2)
{
int b = std::max((int)d[k + 1], (int)d[k + 2]);
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 3]);
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 4]);
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 5]);
if (b >= b0)
continue;
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 6]);
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 7]);
b = std::max(b, (int)d[k + 8]);
b0 = std::min(b0, std::max(b, (int)d[k]));
b0 = std::min(b0, std::max(b, (int)d[k + 9]));
}
threshold = -b0 - 1;
return threshold;
}在代码实现中,对角点的检测 以及得分函数的实现写法值得一看。
如果不想用opencv原生库的话,可以自己实现cornerScore 以及 makeOffsets函数,
然后申请空间使用std::allocator
http://blog.csdn.net/zhaocj/article/details/40301561
http://blog.csdn.net/cxp2205455256/article/details/41312143#