Android Low on memory问题
话不多说,先贴上测试提出来的bug
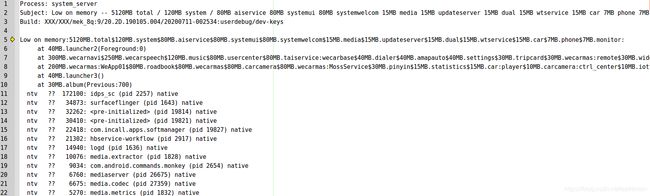
尽管我极力说,这个不算bug,但是人家就是不相信,只好给测试萌妹写一个分析过程了。
这句log在logcat 中的输出如下:
26780 19882 I ActivityManager: Low on memory:
26780 19882 I ActivityManager: ntv ?? 172100: idps_sc (pid 2257) native
26780 19882 I ActivityManager: ntv ?? 34873: surfaceflinger (pid 1643) nativ
...
说明是 ActivityManagerService打印出来的,那么我们看一下代码打印的地方
void reportMemUsage(ArrayList memInfos) {
...省略
tag.append("Low on memory -- ");
appendMemBucket(tag, totalPss, "total", false);
appendMemBucket(stack, totalPss, "total", true);
...省略
}
调用这个方法地方在
case REPORT_MEM_USAGE_MSG: {
final ArrayList memInfos = (ArrayList)msg.obj;
Thread thread = new Thread() {
@Override public void run() {
reportMemUsage(memInfos);
}
};
thread.start();
break;
}
REPORT_MEM_USAGE_MSG这个这个消息是在
final void doLowMemReportIfNeededLocked(ProcessRecord dyingProc) {
...省略
if (!haveBg) {
// 1.只有当ro.debuggable 为1的时候 doReport才为true ,大概率是在userdebug版本
boolean doReport = "1".equals(SystemProperties.get(SYSTEM_DEBUGGABLE, "0"));
...省略
}
if (doReport) {
// 2. 当doReport为true的时候才会发出REPORT_MEM_USAGE_MSG 这条消息
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(REPORT_MEM_USAGE_MSG, memInfos);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
scheduleAppGcsLocked();
}
}
而doLowMemReportIfNeededLocked这个方法的调用:
1、在killAllBackgroundProcesses里面
2、在appDiedLocked里面,在appDiedLocked中会先判断app.killedByAm,如果是am kill的,则不会report信息,但是日志中的是lmk杀死的,则会report这条信息
如果要看appDiedLocked这个方法,首先要知道在ActivityThread.main()中,从这里开始进程创建之后会从这个方法开始绑定AMS,在AMS中通过调用AMS.attachApplicationLocked()这个方法开始绑定,在这个方法中会有对ApplicationThreadProxy绑定通知,见代码:
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
//绑定死亡通知,此处thread真实数据类型为ApplicationThreadProxy
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(app, pid, thread);
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0);
app.deathRecipient = adr;
}
在这个过程中,当我们binder server挂掉后,会回调AppDeathRecipient.binderDied()方法通知client端。
那到这里我们的server端是指应用进程的ApplicationThread,其中ApplicationThread是在ActivityThread中创建的此时属于新建的进程(比如新建app的进程)。client就是ApplicationThreadProxy对象,这个对象是在AMS中,AMS是在system_server中。所以当我们binder server端死亡的时候(app进程死亡)我们system_server进程就会收到通知,然后做一些处理。在这盗用一波别人花的流程图:
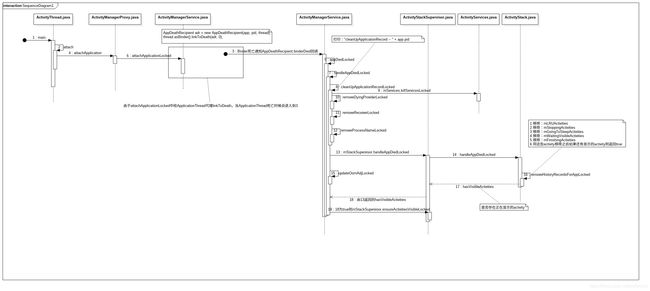
然后我们看一下appDiedLocked这个方法
@GuardedBy("this")
final void appDiedLocked(ProcessRecord app) {
appDiedLocked(app, app.pid, app.thread, false);
}
@GuardedBy("this")
final void appDiedLocked(ProcessRecord app, int pid, IApplicationThread thread,
boolean fromBinderDied) {
// First check if this ProcessRecord is actually active for the pid.
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
ProcessRecord curProc = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
if (curProc != app) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Spurious death for " + app + ", curProc for " + pid + ": " + curProc);
return;
}
}
BatteryStatsImpl stats = mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics();
synchronized (stats) {
stats.noteProcessDiedLocked(app.info.uid, pid);
}
//当进程还没有设置已被杀的标记,则进入该分支杀掉相应进程
if (!app.killed) {
//非binder死亡回调,而是上层直接调用该方法,则进入该分支
if (!fromBinderDied) {
killProcessQuiet(pid);
}
killProcessGroup(app.uid, pid);
app.killed = true;
}
// Clean up already done if the process has been re-started.
if (app.pid == pid && app.thread != null &&
app.thread.asBinder() == thread.asBinder()) {
//这个地方一般为true
boolean doLowMem = app.instr == null;
boolean doOomAdj = doLowMem;
//当app不是由am所杀,通常情况下都是lmk所杀
if (!app.killedByAm) {
reportUidInfoMessageLocked(TAG,
"Process " + app.processName + " (pid " + pid + ") has died: "
+ ProcessList.makeOomAdjString(app.setAdj)
+ ProcessList.makeProcStateString(app.setProcState), app.info.uid);
//既然是由lmk所杀,说明当时内存比较紧张,这时希望能被杀
mAllowLowerMemLevel = true;
} else {
// Note that we always want to do oom adj to update our state with the
// new number of procs.
mAllowLowerMemLevel = false;
doLowMem = false;
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_DIED, app.userId, app.pid, app.processName,
app.setAdj, app.setProcState);
if (DEBUG_CLEANUP) Slog.v(TAG_CLEANUP,
"Dying app: " + app + ", pid: " + pid + ", thread: " + thread.asBinder());
/从ams移除该进程以及connections
handleAppDiedLocked(app, false, true);
//一般为true,则需要更新各个进程的adj
if (doOomAdj) {
updateOomAdjLocked();
}
//当进程是由lmkd所杀,则进入该分支
if (doLowMem) {
//只有当mLruProcesses中所有进程都运行在前台,才报告内存信息
//mLruProcesses以LRU顺序存储了当前运行的应用程序进程信息,mLruProcesses中的第一个元素就是最近最少使用的进程对应的ProcessRecord,用于管理应用程序进程
//3种情况可以更新mLruProcesses:
//1.应用程序异常退出:调用handleAppDiedLocked更新mLruProcesses
//2.显式“杀死”指定进程:调用AMS显式“杀死”进程时需要更新mLruProcesses
//3.启动和调度应用程序4大组件:调用updateLruProcessLocked更新mLruProcesses
// 应用程序异常退出后,其进程也会被“杀死”。因此1、2情况都是从mLruProcesses列表中删除该进程信息。
doLowMemReportIfNeededLocked(app);
}
} else if (app.pid != pid) {
// A new process has already been started.
reportUidInfoMessageLocked(TAG,
"Process " + app.processName + " (pid " + pid
+ ") has died and restarted (pid " + app.pid + ").", app.info.uid);
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_DIED, app.userId, app.pid, app.processName);
} else if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) {
Slog.d(TAG_PROCESSES, "Received spurious death notification for thread "
+ thread.asBinder());
}
// On the device which doesn't have Cgroup, log LmkStateChanged which is used as a signal
// for pulling memory stats of other running processes when this process died.
if (!hasMemcg()) {
StatsLog.write(StatsLog.APP_DIED, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
}
我们再看上述方法中handleAppDiedLocked()这个方法,这个方法就是要从AMS中移除这个进程的信息以及一些组件信息
/**
* Main function for removing an existing process from the activity manager
* as a result of that process going away. Clears out all connections
* to the process.
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
private final void handleAppDiedLocked(ProcessRecord app,
boolean restarting, boolean allowRestart) {
int pid = app.pid;
final boolean clearLaunchStartTime = !restarting && app.removed && app.foregroundActivities;
//清理应用程序servcie,content providers,BroadcastReceiver
boolean kept = cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked(app, restarting, allowRestart, -1,
false /*replacingPid*/);
//这里主要看这个进程信息是不是还需要保存,如果不需要保存,并且不需要重启
//则会在lruProcess中去除这个进程信息,并且在ProcessList中移除掉
if (!kept && !restarting) {
removeLruProcessLocked(app);
if (pid > 0) {
ProcessList.remove(pid);
}
}
if (mProfileProc == app) {
clearProfilerLocked();
}
// Remove this application's activities from active lists.
//清理activity相关信息, 当应用存在可见的activity则返回true
boolean hasVisibleActivities = mStackSupervisor.handleAppDiedLocked(app);
app.clearRecentTasks();
app.activities.clear();
if (app.instr != null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Crash of app " + app.processName
+ " running instrumentation " + app.instr.mClass);
Bundle info = new Bundle();
info.putString("shortMsg", "Process crashed.");
finishInstrumentationLocked(app, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, info);
}
mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
try {
//当死亡的app存在可见的Activity, 则恢复栈顶第一个非finish的activity
if (!restarting && hasVisibleActivities
&& !mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked()) {
//恢复top activity失败,则再次确保有可见的activity
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
} finally {
mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
//......
}
先通过cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked()清除应用里面有关service, BroadcastReceiver, ContentProvider的记录相关,然后清理activity相关信息,当应用存在可见的activity则返回true尝试进行恢复,注意有个参数allowRestart
接下来我们看在appDiedLocked中调用的的cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked方法,这个方法有点长
private final boolean cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked(ProcessRecord app,
boolean restarting, boolean allowRestart, int index, boolean replacingPid) {
if (index >= 0) {
removeLruProcessLocked(app);
ProcessList.remove(app.pid);
}
mProcessesToGc.remove(app);
mPendingPssProcesses.remove(app);
ProcessList.abortNextPssTime(app.procStateMemTracker);
// ------------------------清除crashing的弹框------------------------------
//如果存在,则清除crash/anr/wait对话框
// Dismiss any open dialogs.
if (app.crashDialog != null && !app.forceCrashReport) {
app.crashDialog.dismiss();
app.crashDialog = null;
}
if (app.anrDialog != null) {
app.anrDialog.dismiss();
app.anrDialog = null;
}
if (app.waitDialog != null) {
app.waitDialog.dismiss();
app.waitDialog = null;
}
app.crashing = false;
app.notResponding = false;
------------------------做一些基本的清理工作------------------------------
app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats); //重置包列表
app.unlinkDeathRecipient(); //接触死亡回调
app.makeInactive(mProcessStats);
app.waitingToKill = null;
app.forcingToImportant = null;
updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false); //将app从前台进程移除
app.foregroundActivities = false;
app.hasShownUi = false;
app.treatLikeActivity = false;
app.hasAboveClient = false;
app.hasClientActivities = false;
------------------------清理service------------------------------
mServices.killServicesLocked(app, allowRestart);
boolean restart = false;
------------------------清理ContentProvider------------------------------
// Remove published content providers.
for (int i = app.pubProviders.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//获取该进程已发表的ContentProvider
ContentProviderRecord cpr = app.pubProviders.valueAt(i);
final boolean always = app.bad || !allowRestart;
//ContentProvider服务端被杀,则client端进程也会被杀
boolean inLaunching = removeDyingProviderLocked(app, cpr, always);
if ((inLaunching || always) && cpr.hasConnectionOrHandle()) {
// We left the provider in the launching list, need to
// restart it.
restart = true;
}
cpr.provider = null;
cpr.proc = null;
}
app.pubProviders.clear();
// Take care of any launching providers waiting for this process.
//处理正在启动并且是有client端正在等待的ContentProvider
if (cleanupAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(app, false)) {
restart = true;
}
// Unregister from connected content providers.
//取消已连接的ContentProvider的注册
if (!app.conProviders.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = app.conProviders.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ContentProviderConnection conn = app.conProviders.get(i);
conn.provider.connections.remove(conn);
stopAssociationLocked(app.uid, app.processName, conn.provider.uid,
conn.provider.name);
}
app.conProviders.clear();
}
// At this point there may be remaining entries in mLaunchingProviders
// where we were the only one waiting, so they are no longer of use.
// Look for these and clean up if found.
// XXX Commented out for now. Trying to figure out a way to reproduce
// the actual situation to identify what is actually going on.
if (false) {
for (int i = mLaunchingProviders.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ContentProviderRecord cpr = mLaunchingProviders.get(i);
if (cpr.connections.size() <= 0 && !cpr.hasExternalProcessHandles()) {
synchronized (cpr) {
cpr.launchingApp = null;
cpr.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
------------------------清理BroadcastReceiver------------------------------
skipCurrentReceiverLocked(app);
// Unregister any receivers.
// 取消注册的广播接收者
for (int i = app.receivers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
removeReceiverLocked(app.receivers.valueAt(i));
}
---------------------------清理process------------------------------
app.receivers.clear();
// If the app is undergoing backup, tell the backup manager about it
if (mBackupTarget != null && app.pid == mBackupTarget.app.pid) {
if (DEBUG_BACKUP || DEBUG_CLEANUP) Slog.d(TAG_CLEANUP, "App "
+ mBackupTarget.appInfo + " died during backup");
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run(){
try {
IBackupManager bm = IBackupManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE));
bm.agentDisconnected(app.info.packageName);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// can't happen; backup manager is local
}
}
});
}
for (int i = mPendingProcessChanges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ProcessChangeItem item = mPendingProcessChanges.get(i);
if (app.pid > 0 && item.pid == app.pid) {
mPendingProcessChanges.remove(i);
mAvailProcessChanges.add(item);
}
}
mUiHandler.obtainMessage(DISPATCH_PROCESS_DIED_UI_MSG, app.pid, app.info.uid,
null).sendToTarget();
// If the caller is restarting this app, then leave it in its
// current lists and let the caller take care of it.
if (restarting) {
return false;
}
if (!app.persistent || app.isolated) {
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES || DEBUG_CLEANUP) Slog.v(TAG_CLEANUP,
"Removing non-persistent process during cleanup: " + app);
if (!replacingPid) {
removeProcessNameLocked(app.processName, app.uid, app);
}
if (mHeavyWeightProcess == app) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(CANCEL_HEAVY_NOTIFICATION_MSG,
mHeavyWeightProcess.userId, 0));
mHeavyWeightProcess = null;
}
} else if (!app.removed) {
// This app is persistent, so we need to keep its record around.
// If it is not already on the pending app list, add it there
// and start a new process for it.
//对于persist的应用就重启一下
if (mPersistentStartingProcesses.indexOf(app) < 0) {
mPersistentStartingProcesses.add(app);
restart = true;
}
}
if ((DEBUG_PROCESSES || DEBUG_CLEANUP) && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(
TAG_CLEANUP, "Clean-up removing on hold: " + app);
//mProcessesOnHold:记录着试图在系统ready之前就启动的进程。
//在那时并不启动这些进程,先记录下来,等系统启动完成则启动这些进程。
mProcessesOnHold.remove(app);
if (app == mHomeProcess) {
mHomeProcess = null;
}
if (app == mPreviousProcess) {
mPreviousProcess = null;
}
if (restart && !app.isolated) {
// We have components that still need to be running in the
// process, so re-launch it.
/仍有组件需要运行在该进程中,因此重启该进程
if (index < 0) {
ProcessList.remove(app.pid);
}
addProcessNameLocked(app);
app.pendingStart = false;
startProcessLocked(app, "restart", app.processName);
return true;
} else if (app.pid > 0 && app.pid != MY_PID) {
// Goodbye!
//移除该进程相关信息
boolean removed;
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
mPidsSelfLocked.remove(app.pid);
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
}
mBatteryStatsService.noteProcessFinish(app.processName, app.info.uid);
if (app.isolated) {
mBatteryStatsService.removeIsolatedUid(app.uid, app.info.uid);
}
app.setPid(0);
}
return false;
}
然后吧,我就感觉扯远了。。。