java8,Stream的理解和使用
1、Stream 在java8中是对集合Collection对象功能的增强
2、专注于对集合对象进行便利,高效聚合,大批量数据操作
3、常用方法:filter,map,limit等等…
实例代码:
.....
List listStr= listObj.stream()
//筛选出卡路里大于400的
.filter(d -> d.getCalories() < 400)
//抽取名字属性创建一个新的流
.map(Dish::getName)
//这个流按List类型返回
.collect(toList());
4、这段代码 filter 和 map 是中间操作,中间操作会返回一个新流。
collect称终端操作,终端操作会让整个流执行并关闭(也就是说每个流只能遍历一次,因为在collect后这个流就已经关闭了)。
5.并行和串行
Stream分为 串行 和 并行 两种,就是单线程和多线程的执行:
default Stream stream() : 返回串行流
default Stream parallelStream() : 返回并行流
6.使用
Stream.of(T… t):
要使用Stream,那就必须得先创建一个String类型的Stream
Stream StrStream = Stream.of("a", "b");
Stream.collect(Collector collector)的使用:所谓map,从字面理解就是映射。这里指的是对象关系的映射,比如从对象集合映射到属性结合:
List names = Stream.of(new Student("zhangSan"), new Student("liSi"))
.map(student -> student.getName())
.collect(toList());
从小写字母映射到大写字母:
List collected = Stream.of("a", "b", "hello")
.map(string -> string.toUpperCase())
.collect(toList());
Stream.filter(Predicate predicate)
// 筛选年龄大于19的学生
List stu = Stream.of(new Student("zhangSan", 19), new Student("liSi"), 20)
.filter(student -> student.getAge() > 19)
.collect(toList());
Stream.flatMap(Function> mapper)
flatMap扁平化映射,即将数据元素为数组的Stream转化为单个元素
Stream stringStream = Stream.of("Hello Aron.");
// 返回值为数组
Stream stringArrayStream = stringStream.map(word -> word.split(" "));
// flatMap扁平化映射后,元素都合并了
Stream flatResult = stringArrayStream.flatMap(arr -> Arrays.stream(arr))
Stream.max(Comparator comparator)
max即最大,类似SQL中的函数max(),从数据中根据一定的条件筛选出最值
// 筛选年龄最大/小的学生
Stream studentStream = Stream.of(new Student("zhangSam", 19), new Student("liSi", 20));
Optional max = studentStream.max(Comparator.comparing(student -> student.getAge()));
// Optional max = studentStream.min(Comparator.comparing(student -> student.getAge()));
// 年龄最大/小的学生
Student student = max.get();
Sream.reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator binaryOperator)
reduce操作实现从一组值中生成一个值,上面的max、min实际上都是reduce操作。
参数Identity 表示初始值,
参数binaryOperator是一个函数接口,表示二元操作,可用于数学运算
// 使用reduce() 求和 (不推荐生产环境使用)
int count = Stream.of(1, 2, 3).reduce(0, (acc, element) -> acc + element);
上面代码,展开reduce() 操作
BinaryOperator accumulator = (acc, element) -> acc + element;
int count = accumulator.apply( accumulator.apply(accumulator.apply(0, 1),2), 3);
综合操作
// 查找所有姓张的同学并按字典顺序排序,存储到list
List newList = studentList.Stream()
.filter(student -> student.getName().startsWith("张"))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(student -> student.getName())
.collect(toList());
第二:lambda表达式
比较最重要的函数接口
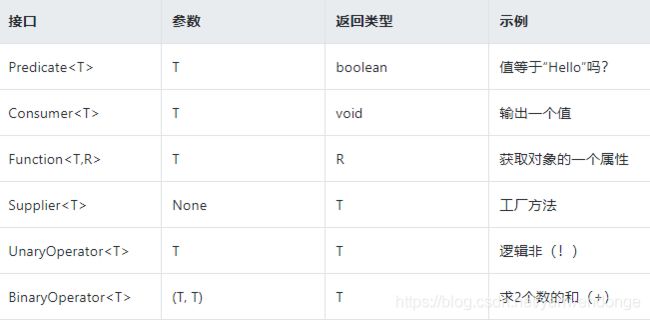
示例:
BinaryOperator addLongs = (x, y) -> x + y;
(x, y)没有申明方法的参数类型的,却能执行数学运算 +。
这里根据函数接口指定的泛型类为Long,即可推断方法的参数为Long,然后执行x + y。
Lambda小结:
Lambda表达式是一个匿名方法,简化了匿名内部类的写法,把模板语法屏蔽,突出业务语句,传达的更像一种行为。
Lambda表达式是有类型的,JDK内置了众多函数接口
Lambda的3段式结构:(…)-> { …}