HDU3694 四边形的费马点
Fermat Point in Quadrangle
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1871 Accepted Submission(s): 325
Problem Description
In geometry the Fermat point of a triangle, also called Torricelli point, is a point such that the total distance from the three vertices of the triangle to the point is the minimum. It is so named because this problem is first raised by Fermat in a private letter. In the following picture, P
0 is the Fermat point. You may have already known the property that:
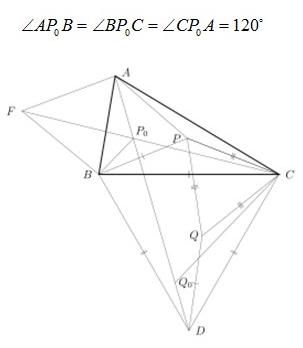
Alice and Bob are learning geometry. Recently they are studying about the Fermat Point.
Alice: I wonder whether there is a similar point for quadrangle.
Bob: I think there must exist one.
Alice: Then how to know where it is? How to prove?
Bob: I don’t know. Wait… the point may hold the similar property as the case in triangle.
Alice: It sounds reasonable. Why not use our computer to solve the problem? Find the Fermat point, and then verify your assumption.
Bob: A good idea.
So they ask you, the best programmer, to solve it. Find the Fermat point for a quadrangle, i.e. find a point such that the total distance from the four vertices of the quadrangle to that point is the minimum.

Alice and Bob are learning geometry. Recently they are studying about the Fermat Point.
Alice: I wonder whether there is a similar point for quadrangle.
Bob: I think there must exist one.
Alice: Then how to know where it is? How to prove?
Bob: I don’t know. Wait… the point may hold the similar property as the case in triangle.
Alice: It sounds reasonable. Why not use our computer to solve the problem? Find the Fermat point, and then verify your assumption.
Bob: A good idea.
So they ask you, the best programmer, to solve it. Find the Fermat point for a quadrangle, i.e. find a point such that the total distance from the four vertices of the quadrangle to that point is the minimum.
Input
The input contains no more than 1000 test cases.
Each test case is a single line which contains eight float numbers, and it is formatted as below:
x 1 y 1 x 2 y 2 x 3 y 3 x 4 y 4
x i, y i are the x- and y-coordinates of the ith vertices of a quadrangle. They are float numbers and satisfy 0 ≤ x i ≤ 1000 and 0 ≤ y i ≤ 1000 (i = 1, …, 4).
The input is ended by eight -1.
Each test case is a single line which contains eight float numbers, and it is formatted as below:
x 1 y 1 x 2 y 2 x 3 y 3 x 4 y 4
x i, y i are the x- and y-coordinates of the ith vertices of a quadrangle. They are float numbers and satisfy 0 ≤ x i ≤ 1000 and 0 ≤ y i ≤ 1000 (i = 1, …, 4).
The input is ended by eight -1.
Output
For each test case, find the Fermat point, and output the total distance from the four vertices to that point. The result should be rounded to four digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output
2.8284 0.0000
Source
2010 Asia Fuzhou Regional Contest
题意:给出四个点构成四边形(不按顺序给),求费马距离。
1.因为只有四个点,当这四个点可以构成凸四边形时(如图):对角线形成的交点是费马点。就是点1,根据三角形的两边大于第三边可证明。
2.当不能构成凸多边形时,就是那个凹点是费马点(如图):同理可证。
#define DeBUG
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include