【基础算法】(09)五大常用算法之五:分支限界法
【基础算法】(09)五大常用算法之五:分支限界法
Auther: Thomas Shen
E-mail: [email protected]
Date: 2017/10/27
All Copyrights reserved !
-
-
- 基础算法09五大常用算法之五分支限界法
- 简述
- 算法原理
- 1 分支限界法与回溯法
- 2 分支限界法思想
- 3 常见的两种分支限界法
- 案例一单源最短路径问题
- 案例二TSP问题中使用分支限界法
- References
- 基础算法09五大常用算法之五分支限界法
-
1. 简述:
本系列介绍了五大常用算法,其中本文是第五篇,介绍了 ‘分支限界法’ 的细节内容。
2. 算法原理:
分支限界法(branch and bound method)按广度优先策略搜索问题的解空间树,在搜索过程中,对待处理的节点根据限界函数估算目标函数的可能取值,从中选取使目标函数取得极值(极大或极小)的结点优先进行广度优先搜索,从而不断调整搜索方向,尽快找到问题的解。分支限界法适合求解最优化问题。
2.1 分支限界法与回溯法:
求解目标:回溯法的求解目标是找出解空间树中满足约束条件的所有解,而分支限界法的求解目标则是找出满足约束条件的一个解,或是在满足约束条件的解中找出在某种意义下的最优解。
搜索方式的不同:回溯法以深度优先的方式搜索解空间树,而分支限界法则以广度优先或以最小耗费优先的方式搜索解空间树。
2.2 分支限界法思想:
分支限界法首先要确定一个合理的限界函数(bound funciton),并根据限界函数确定目标函数的界[down ,up],按照广度优先策略搜索问题的解空间树,在分直结点上依次扩展该结点的孩子结点,分别估算孩子结点的目标函数可能值,如果某孩子结点的目标函数可能超出目标函数的界,则将其丢弃;否则将其加入待处理结点表(简称PT表),依次从表PT中选取使目标函数取得极值的结点成为当前扩展结点,重复上述过程,直到得到最优解。
2.3 常见的两种分支限界法:
- 队列式(FIFO)分支限界法
按照队列先进先出(FIFO)原则选取下一个结点为扩展结点。 - 优先队列式分支限界法
按照优先队列中规定的优先级选取优先级最高的结点成为当前扩展结点。
3. 案例一:单源最短路径问题
http://www.cnblogs.com/chinazhangjie/archive/2010/11/01/1866136.html
1. 问题描述:
在下图所给的有向图G中,每一边都有一个非负边权。要求图G的从源顶点s到目标顶点t之间的最短路径。
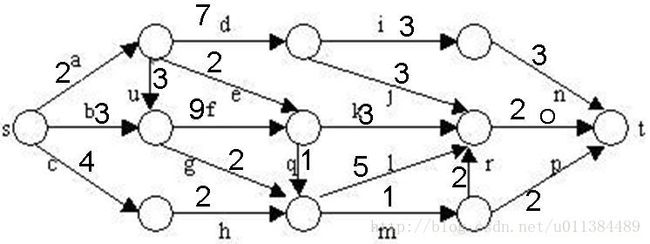
下图是用优先队列式分支限界法解有向图G的单源最短路径问题产生的解空间树。其中,每一个结点旁边的数字表示该结点所对应的当前路长。
![]()
找到一条路径:
![]()
目前的最短路径是8,一旦发现某个结点的下界不小于这个最短路进,则剪枝:
![]()
同一个结点选择最短的到达路径:
![]()
![]()
2. 剪枝策略:
在算法扩展结点的过程中,一旦发现一个结点的下界不小于当前找到的最短路长,则算法剪去以该结点为根的子树。
在算法中,利用结点间的控制关系进行剪枝。从源顶点s出发,2条不同路径到达图G的同一顶点。由于两条路径的路长不同,因此可以将路长长的路径所对应的树中的结点为根的子树剪去。
3. 算法思想:
解单源最短路径问题的优先队列式分支限界法用一极小堆来存储活结点表。其优先级是结点所对应的当前路长。
算法从图G的源顶点s和空优先队列开始。结点s被扩展后,它的儿子结点被依次插入堆中。此后,算法从堆中取出具有最小当前路长的结点作为当前扩展结点,并依次检查与当前扩展结点相邻的所有顶点。如果从当前扩展结点i到顶点j有边可达,且从源出发,途经顶点i再到顶点j的所相应的路径的长度小于当前最优路径长度,则将该顶点作为活结点插入到活结点优先队列中。这个结点的扩展过程一直继续到活结点优先队列为空时为止。
4. 实现:
/* 主题:单源最短路径问题
* 作者:chinazhangjie
* 邮箱:[email protected]
* 开发语言:C++
* 开发环境:Mircosoft Virsual Studio 2008
* 时间: 2010.11.01
*/
#include vector > min_heap;
min_heap.push (node_info(0,0)); // 将起始结点入队
while (true) {
node_info top = min_heap.top (); // 取出最大值
min_heap.pop ();
// 已到达目的结点
if (top.index == end_node) {
break ;
}
// 未到达则遍历
for (int i = 0; i < node_count; ++ i) {
// 顶点top.index和i间有边,且此路径长小于原先从原点到i的路径长
if (graph[top.index][i] != no_edge &&
(top.weight + graph[top.index][i]) < path[i].weight) {
min_heap.push (node_info (i,top.weight + graph[top.index][i]));
path[i].front_index = top.index;
path[i].weight = top.weight + graph[top.index][i];
}
}
if (min_heap.empty()) {
break ;
}
}
shortest_path = path[end_node].weight;
int index = end_node;
s_path_index.push_back(index) ;
while (true) {
index = path[index].front_index ;
s_path_index.push_back(index);
if (index == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int> > graph ; // 图的数组表示
int node_count; // 结点个数
const int no_edge; // 无通路
const int end_node; // 目的结点
vector<int> s_path_index; // 最短路径
int shortest_path; // 最短路径
};
int main()
{
const int size = 11;
vector<vector<int> > graph (size);
for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) {
graph[i].resize (size);
}
for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0;j < size; ++ j) {
graph[i][j] = -1;
}
}
graph[0][1] = 2;
graph[0][2] = 3;
graph[0][3] = 4;
graph[1][2] = 3;
graph[1][5] = 2;
graph[1][4] = 7;
graph[2][5] = 9;
graph[2][6] = 2;
graph[3][6] = 2;
graph[4][7] = 3;
graph[4][8] = 3;
graph[5][6] = 1;
graph[5][8] = 3;
graph[6][9] = 1;
graph[6][8] = 5;
graph[7][10] = 3;
graph[8][10] = 2;
graph[9][8] = 2;
graph[9][10] = 2;
ss_shortest_paths ssp (graph, 10);
ssp.shortest_paths ();
ssp.print_spaths ();
return 0;
} 测试数据(图):
![]()
测试结果
min weight : 8
path: 0 2 6 9 10
4. 案例二:TSP问题中使用分支限界法
http://blog.csdn.net/lovesummerforever/article/details/18622127
TSP问题是指旅行家要旅行n个城市,要求各个城市经理且仅经理依次然后回到出发城市,并要求所走的路程最短。我们以下图的无限图为例,采用分支限界法解决这个问题。
![]()
该无向图对应的代价矩阵如下所示:
![]()
代价矩阵是1到1,1到2,1到3,1到4,1到5距离写在第一行,第二行为2到1,2到2,2到3,2到4,、、、依次
找到目标函数的界。上界为,采用贪心算法求得上界,从节点1开始到节点3—>5—>4—>2—>1,路径,即为图中红色圈的路径,其路径长度为C=1+2+3+7+3=16。
下界为矩阵中每行中两个最小的相加,所有的行加起来的和的一半。( (3+1)+(3+6)+(1+2)+(3+4)+(2 +3) )/2=14
所以求得界为[14,16]。计算每个节点的限界值。
计算目标函数(限界函数),lb分为三部分,第一部分是经过路径的长度相加的2倍,加上第二部分离着路径首尾节点最近的距离相加(不在已知路径上的),加上第三部分除了路径上节点,矩阵中两个最短的距离相加,最后这三部分和相加,得到的结果除以2便是每个节点的限界值。画出PT图。如下所示。
![]()
根据上述所述得到最优解1–>3–>5–>4–>2–>1
//分支限界法
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define INF 100000
using namespace std;
/* n*n的一个矩阵 */
int n;
int mp[22][22];//最少3个点,最多15个点
/*输入距离矩阵*/
void in()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(i==j)
{
mp[i][j]=INF;
continue;
}
scanf("%d",&mp[i][j]);
}
}
}
struct node
{
int visp[22];//标记哪些点走了
int st;//起点
int st_p;//起点的邻接点
int ed;//终点
int ed_p;//终点的邻接点
int k;//走过的点数
int sumv;//经过路径的距离
int lb;//目标函数的值
bool operator <(const node &p )const
{
return lb>p.lb;
}
};
priority_queue q;
int low,up;
int inq[22];
//确定上界
int dfs(int u,int k,int l)
{
if(k==n) return l+mp[u][1];
int minlen=INF , p;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(inq[i]==0&&minlen>mp[u][i])/*取与所有点的连边中最小的边*/
{
minlen=mp[u][i];
p=i;
}
}
inq[p]=1;
return dfs(p,k+1,l+minlen);
}
int get_lb(node p)
{
int ret=p.sumv*2;//路径上的点的距离
int min1=INF,min2=INF;//起点和终点连出来的边
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(p.visp[i]==0&&min1>mp[i][p.st])
{
min1=mp[i][p.st];
}
}
ret+=min1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(p.visp[i]==0&&min2>mp[p.ed][i])
{
min2=mp[p.ed][i];
}
}
ret+=min2;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(p.visp[i]==0)
{
min1=min2=INF;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(min1>mp[i][j])
min1=mp[i][j];
}
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(min2>mp[j][i])
min2=mp[j][i];
}
ret+=min1+min2;
}
}
return ret%2==0?(ret/2):(ret/2+1);
}
void get_up()
{
inq[1]=1;
up=dfs(1,1,0);
}
void get_low()
{
low=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
/*通过排序求两个最小值*/
int min1=INF,min2=INF;
int tmpA[22];
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
tmpA[j]=mp[i][j];
}
sort(tmpA+1,tmpA+1+n);//对临时的数组进行排序
low+=tmpA[1];
}
}
int solve()
{
/*贪心法确定上界*/
get_up();
/*取每行最小的边之和作为下界*/
get_low();
/*设置初始点,默认从1开始 */
node star;
star.st=1;
star.ed=1;
star.k=1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) star.visp[i]=0;
star.visp[1]=1;
star.sumv=0;
star.lb=low;
/*ret为问题的解*/
int ret=INF;
q.push(star);
while(!q.empty())
{
node tmp=q.top();
q.pop();
if(tmp.k==n-1)
{
/*找最后一个没有走的点*/
int p;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(tmp.visp[i]==0)
{
p=i;
break;
}
}
int ans=tmp.sumv+mp[p][tmp.st]+mp[tmp.ed][p];
node judge = q.top();
/*如果当前的路径和比所有的目标函数值都小则跳出*/
if(ans <= judge.lb)
{
ret=min(ans,ret);
break;
}
/*否则继续求其他可能的路径和,并更新上界*/
else
{
up = min(up,ans);
ret=min(ret,ans);
continue;
}
}
/*当前点可以向下扩展的点入优先级队列*/
node next;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(tmp.visp[i]==0)
{
next.st=tmp.st;
/*更新路径和*/
next.sumv=tmp.sumv+mp[tmp.ed][i];
/*更新最后一个点*/
next.ed=i;
/*更新顶点数*/
next.k=tmp.k+1;
/*更新经过的顶点*/
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) next.visp[j]=tmp.visp[j];
next.visp[i]=1;
/*求目标函数*/
next.lb=get_lb(next);
/*如果大于上界就不加入队列*/
if(next.lb>up) continue;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
in();
printf("%d\n",solve());
return 0;
} References. :
- [ 1 ]. Coursera | Java程序设计 | PKU
- [ 2 ]. http://www.cnblogs.com/chinazhangjie/archive/2010/11/01/
1866136.html - [ 3 ]. http://blog.csdn.net/lovesummerforever/article/details/18622127
- [ 4 ]. http://blog.csdn.net/yake827/article/details/52119469