matlab基础(2):进阶
MATLAB编程习惯与风格
变量的命名规则
Cell Mode
程序发布(Publish)
MATLAB程序调试
1. 闻道有先后,术业有专攻
所谓高手,就是他们比你更早经历了那些bug,比你经历了更多bug,仅此而已
2. 错误信息的阅读
– Index must be a positive integer or logical.
– Undefined function or variable “B”.
– Inner matrix dimensions must agree.
– Function definitions are not permitted at the prompt or in scripts.
– Index out of bounds because numel(A)=5.
– In an assignment A(I) = B, the number of elements in B and I must be the same.
– Expression or statement is incorrect–possibly unbalanced (, {, or [.
– Too many input arguments.
– ……
3. 断点调试
– 设置/清除断点
– 进入/退出调试模式
– 循环体的调试
4. 如何充分地利用网络资源?
– www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/
– www.matlabsky.com
– www.ilovematlab.cn
– Some Tips:
• 再现问题(完整的错误信息、源程序文件、数据等)
• 帖子标题(应简要说明问题的本质,勿出现“跪求”、“ **大神/大侠” …)
5. 如何查看、编辑MATLAB自带的工具箱函数?
– edit
– varargin/varargout/nargin/nargout
• varargin: Variable length input argument list.
• varargout: Variable length output argument list.
• nargin: Number of input arguments specified for a function.
• nargout: Number of output arguments specified for a function.
MATLAB的内存优化配置
memory/feature memstats
禁用Java虚拟机
增加虚拟内存数量
打开系统3GB开关(32位系统)(推荐)
– “我的电脑” →“属性” →“高级” →“启动和故障恢复” →“设置” →“编辑”

向量化编程
1. 及时清除不用的变量
使用变量前,预分配内存空间
选择恰当的数据类型
循环与向量化
– 按列优先循环
– 循环次数多的变量安排在内层
给一些函数“瘦身”
……
2. 图像对象和句柄
图形对象:用于界面制作和数据可视的基本绘图元素。
图形对象是图形系统中最基本、最底层的单元。
图形对象的属性由属性名和属性值两部分组成。
句柄是图形对象的标识代码,句柄含有图形对象的各种必要的属性信息。
根屏幕的句柄为0,图形窗口的句柄为整数,其他对象的句柄为浮点数

%% I. 清空环境变量及命令
% clear all
clc
%% II. MATLAB编程习惯与风格
x_coordinate = rand(1,10);
y_coordinate = rand(1,10);
figure
plot(x_coordinate,y_coordinate,'r-*')
%% III. MATLAB程序调试
% %%
% % 1. Index must be a positive integer or logical.
% A = [1 2 3 4 5];
% A(0)
% A(3.5)
% A(-2)
%
% %%
% % 2. Undefined function or variable 'B'.
% B
%
% %%
% % 3. Inner matrix dimensions must agree.
% B = [1 2 3];
% A * B
%
% %%
% % 4. Function definitions are not permitted at the prompt or in scripts.
% function c = add(a,b)
% c = a + b;
%
% %%
% % 5. Index out of bounds because numel(A)=5.
% A(6)
%
% %%
% % 6. In an assignment A(I) = B, the number of elements in B and I must be the same.
% A(3) = B;
%
% %%
% % 7. Expression or statement is incorrect--possibly unbalanced (, {, or [.
% mean(A(1:3)
%
% %%
% % 8. Too many input arguments.
% mean(A,1,2)
%%
% 9. 循环体的调试
a = 1:100;
b = [];
for i = 21:21
index = 105 - 5*i;
b = [b a(index)];
end
%%
% 10. 查看、编辑MATLAB自带的工具箱函数
edit mean
edit newff
%% III. MATLAB内存优化配置
feature memstats
%
%% IV. 向量化编程
%%
% 1. 及时清除不用的变量
a = rand(10000);
b = rand(10000);
clear a
b = rand(10000);
%%
% 2. 使用变量前,预分配内存空间
clear all
clc
n = 30000;
tic;
for k = 1:n
a(k) = 1;
end
time = toc;
disp(['未预分配内存下动态赋值长为',num2str(n),'的数组时间是:',num2str(time),'秒!'])
tic
b = zeros(1,n);
for k = 1:n
b(k) = 1;
end
time = toc;
disp(['预分配内存下动态赋值长为',num2str(n),'的数组时间是:',num2str(time),'秒!'])
%%
未预分配内存下动态赋值长为30000的数组时间是:0.47359秒!
预分配内存下动态赋值长为30000的数组时间是:0.0031263秒!
%
%%c
% 3. 选择恰当的数据类型
clear all
clc
n = 300000;
a = 8;
b{1} = 8;
c.data = 8;
tic
for k = 1:n;
a;
end
time = toc;
disp(['访问',num2str(n),'次double型数组时间是:',num2str(time),'秒!'])
tic
for k = 1:n;
b{1};
end
time = toc;
disp(['访问',num2str(n),'次cell型数组时间是:',num2str(time),'秒!'])
tic
for k = 1:n;
c.data;
end
time = toc;
disp(['访问',num2str(n),'次struct型数组时间是:',num2str(time),'秒!'])
%%
访问300000次double型数组时间是:0.13秒!
访问300000次cell型数组时间是:0.046659秒!
访问300000次struct型数组时间是:0.20081秒!
%
%%
% 4. 按列优先循环
clear all
clc
n = 1000;
a = rand(n);
tic
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
a(i,j);
end
end
toc
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
a(j,i);
end
end
toc
%%
Elapsed time is 0.045155 seconds.
Elapsed time is 0.081694 seconds.
%
%%
% 5. 循环次数多的变量安排在内层
clear all
clc
tic
a = 0;
for i = 1:1000
for j = 50000
a = a + 1;
end
end
toc
tic
a = 0;
for i = 1:50000
for j = 1:1000
a = a + 1;
end
end
toc
%%
Elapsed time is 0.005826 seconds.
Elapsed time is 0.214452 seconds.
%
%%
% 6. 给一些函数“瘦身”
edit mean
clear all
clc
a = rand(1,10000);
tic
b = mean(a)
toc
tic
c = sum(a)/length(a)
toc
%%
b = 0.5012
Elapsed time is 0.022365 seconds.
c = 0.5012
Elapsed time is 0.002307 seconds.
%
%% V. 图像对象和句柄
%%
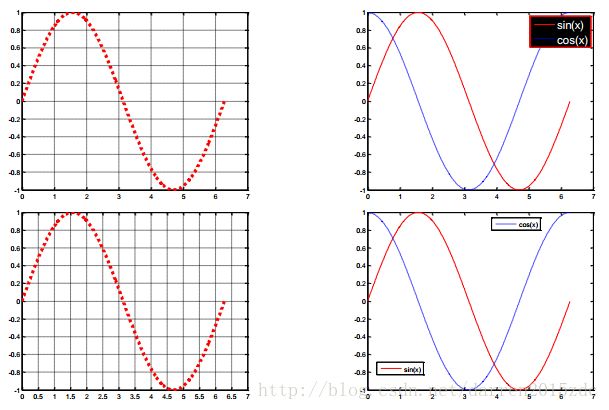
% 1. 如何设置线条的属性呢?
x = 0:0.01:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
h = plot(x,y);
grid on
get(h)
set(h,'linestyle','-','linewidth',2,'color','k')
%%
% 2. 如何修改网格的间隔呢?
set(gca,'xtick',0:0.5:7)
set(gca,'ytick',-1:0.1:1)
%%
% 3. 如何设置图例的字体及大小呢?
x = 0:0.01:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
plot(x,y1,'r')
hold on
plot(x,y2,'-.b')
h = legend('sin(x)','cos(x)');
set(h,'fontsize',16,'color','k','edgecolor','r','textcolor','w')
%%
% 4. 如何拆分图例呢?
x = 0:0.01:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
h1 = plot(x,y1,'r');
hold on
h2 = plot(x,y2,'-.b');
ax1 = axes('position',get(gca,'position'),'visible','off');
legend(ax1,h1,'sin(x)','location','northwest')
ax2 = axes('position',get(gca,'position'),'visible','off');
legend(ax2,h2,'cos(x)','location','northeast')