linux命令总结及感悟
一、find命令
作用:查找文件
[root@server ~]# find / -name elasticsearch
/var/log/elasticsearch
/var/run/elasticsearch
/var/lock/subsys/elasticsearch
/var/lib/elasticsearch
/var/lib/elasticsearch/elasticsearch
/usr/share/elasticsearch
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch
/etc/rc.d/init.d/elasticsearch
/etc/elasticsearch
/etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
/opt/kibana/src/plugins/elasticsearch/opt/kibana/node_modules/elasticsearch
二、tar 打包压缩与解压命令
[root@template ~]# cd /tmp
#进入目录打包文件
[root@template tmp]# tar czvf passwd.tar.gz passwd
passwd
#指定解压目录
[root@template tmp]# tar xzvf passwd.tar.gz -C /tmp
passwd
[root@template tmp]# ll
total 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1138 Apr 16 04:12 passwd
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 618 Apr 16 04:13 passwd.tar.gz
用脚本对文件进行打包
[root@template tmp]# ll
总用量 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 4月 28 18:07 nulige
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 4月 28 18:24 tar_backup.sh
[root@template tmp]# sh tar_backup.sh
ok
[root@template tmp]# ll
总用量 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 4月 28 18:07 nulige
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 190 4月 28 18:24 nulige.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 75 4月 28 18:24 tar_backup.sh
[root@template tmp]# cat tar_backup.sh
#!/bin/sbin
cd /tmp
tar zcf nulige.tar.gz ./nulige
[ $? -eq 0 ] && echo ok
三、grep命令
示例:过滤出带有/sbin/nologin的内容
[root@template tmp]# grep /sbin/nologin /etc/passwd
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
avahi-autoipd:x:170:170:Avahi IPv4LL Stack:/var/lib/avahi-autoipd:/sbin/nologin
systemd-bus-proxy:x:999:997:systemd Bus Proxy:/:/sbin/nologin
systemd-network:x:998:996:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
polkitd:x:997:995:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
abrt:x:173:173::/etc/abrt:/sbin/nologin
tss:x:59:59:Account used by the trousers package to sandbox the tcsd daemon:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
mysql:x:27:27:MariaDB Server:/var/lib/mysql:/sbin/nologin
四、stat命令
作用:用于查看文件的具体存储信息和时间
[root@template tmp]# stat passwd
File: ‘passwd’
Size: 1138 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 102426465 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0
Access: 2017-04-16 04:14:47.442943634 +0800
Modify: 2017-04-16 04:12:48.000000000 +0800
Change: 2017-04-16 04:14:47.442943634 +0800
Birth: -
五、cut命令
作用:用来按列提取文本字条
参数:
-f 参数:用来设置要看的列数
-d参数:设置间隔符号
示例:提取出passwd文件中的用户名
[root@template tmp]# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd
root
bin
daemon
adm
lp
sync
shutdown
halt
mail
operator
games
ftp
nobody
avahi-autoipd
systemd-bus-proxy
systemd-network
dbus
polkitd
abrt
tss
postfix
sshd
mysql
六、head命令
作用:用来查看文本文档
示例:显示前10行
[root@template tmp]# head -n 10 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
七、history
作用:查看历史记录命令
[root@template tmp]# history
1 ip a
2 shutdown -h now
3 ip addr
4 systemctl restart network
5 ip addr
清空历史记录
[root@template tmp]# history -c
八、sosreport
sosreport命令用于收集系统配置并诊断信息后输出结论文档,格式为:“sosreport”。
当咱们的Linux系统出现故障需要联系红帽厂商或其他技术支持时,大多数时候都要先使用这个SOS功能来简单收集计算机的状态和配置信息,以便让技术支持公司能够通过远程就解决了一些小问题,又或者让他们能对复杂问题能提前有些了解:
[root@template tmp]# sosreport
sosreport (version 3.2)
This command will collect diagnostic and configuration information from
this CentOS Linux system and installed applications.
An archive containing the collected information will be generated in
/var/tmp and may be provided to a CentOS support representative.
Any information provided to CentOS will be treated in accordance with
the published support policies at:
https://www.centos.org/
The generated archive may contain data considered sensitive and its
content should be reviewed by the originating organization before being
passed to any third party.
No changes will be made to system configuration.
Press ENTER to continue, or CTRL-C to quit. #此处敲击回车来确认收集信息
Please enter your first initial and last name [template]: #此处敲击回车,来确认主机名称
Please enter the case id that you are generating this report for []: #此处敲击回车,生成报告
Setting up archive ...
Setting up plugins ...
Running plugins. Please wait ...
Running 77/77: yum...
Creating compressed archive...
Your sosreport has been generated and saved in:
/var/tmp/sosreport-template-20170416043251.tar.xz
The checksum is: 9f5d08f6373e35985213ab8001f7a078
Please send this file to your support representative.
#此压缩包文件和这段校验值就是要发送给对方的内容。
#查看生成的报告
[root@template tmp]# ll /var/tmp/
-rw-------. 1 root root 5543652 Apr 16 04:34 sosreport-template-20170416043251.tar.xz
九、free命令
作用:显示当前系统中内存的使用量信息
[root@linux~]# free -h
| 总计内存量 | 已用量 | 可用量 | 进程共享的内存量 | 磁盘缓存的内存量 | 缓存的内存量 | |
| total | used | free | shared | buffers | cached | |
| Mem: | 1.8G | 1.3G | 542M | 9.8M | 1.6M | 413M |
| -/+ buffers/cache: | 869M | 957M | ||||
| Swap: | 2.0G | 0B | 2.0G |
十、w和who命令
作用:查看当前登入主机的用户信息
[root@template tmp]# w
04:40:12 up 1:04, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.12, 0.12
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root tty1 03:36 55:00 0.15s 0.15s -bash
root pts/0 192.168.30.1 03:46 4.00s 0.67s 0.02s w
[root@template tmp]# who
root tty1 2017-04-16 03:36
root pts/0 2017-04-16 03:46 (192.168.30.1)
十一、uptime命令
作用:用于查看系统的负载信息,
格式为:“uptime”。
这个命令真的很棒,它可以为您显示当前系统时间、系统已运行时间、当前在线用户以及平均负载值等信息数据。平均负载值指的是最近1分钟、5分钟、15分钟的系统压力情况,负载值越低越好,尽量不要长期超过1。另外您还可以结合搭配用"watch -n 1 uptime"命令来每秒刷新一次来获得当前的系统负载情况。
[root@linux~]# uptime
22:49:55 up 10 min, 2 users, load average: 0.01, 0.19, 0.18
十二、查看系统详细版本和内核版本
[root@template tmp]# uname -a
Linux template 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Nov 19 22:10:57 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
[root@template tmp]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core)
十三、pidof命令
作用:查看指定服务的进程pid值
[root@template tmp]# pidof sshd
2956 1538
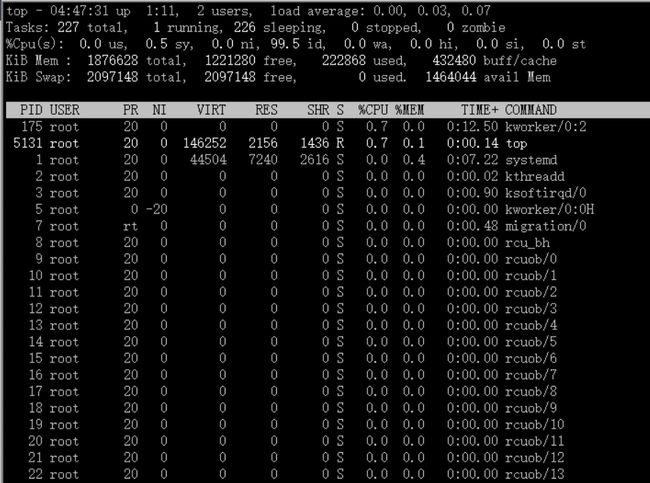
十四、top命令
作用:用于动态的监视进程活动与系统负载等信息
功能类似于windows系统中的任务管理器
前面的五行为系统整体的统计信息,下面咱们来逐行的讲解:
第 1行:系统时间,运行时间,登录用户数,系统负载(分别为1分钟、5分钟、15分钟的平均值)。第 2行:进程总数,运行中的,睡眠中的,停止的,僵死的。第 3行:用户占用资源,系统内核占用资源,改变过优先级的进程,空闲的资源,等待输入输出的时间。此行数据均为CPU数据并以百分比格式显示,例如"99.2 id"意味着有99.2%的CPU资源正在空闲中。第 4行:物理内存总量,使用量,空闲量,作为内核缓存的内存量。第 5行:虚拟内存总量,使用量,空闲量,已被提前加载的内存数据。
十五、ps命令
作用:用于查看系统中的进程状态
| 参数 | 作用 |
| -a | 显示所有的进程(包括其他用户的) |
| -u | 用户以及其他详细信息 |
| -x | 显示没有控制终端的进程 |
Linux系统中时刻运行着许许多多的进程,如果能够合理的管理它们,绝对有益于系统的性能优化,Linux系统中进程最常见的5种不同的状态是运行、中断、不可中断、僵死与停止,它们的特性分别是:
R(运行):正在运行或在运行队列中等待。 S(中断):休眠中, 在等待某个条件的形成或接收到信号。 D(不可中断):收到信号不唤醒和不可运行, 进程必须等待直到有中断发生。 Z:(僵死):进程已终止, 但进程描述符存在, 直到父进程调用wait4()系统调用后释放。 T:(停止):进程收到SIGSTOP, SIGSTP, SIGTIN, SIGTOU信号后停止运行。
当执行"ps aux"命令后通常会看到下面格式的进程状态,表格中只是列举了部分输出值,而且正常的输出值中不包括中文注释部分:
| USER | PID | %CPU | %MEM | VSZ | RSS | TTY | STAT | START | TIME | COMMAND |
| 进程的所有者 | 进程ID号 | 运算器占用率 | 内存占用率 | 虚拟内存使用量(单位是KB) | 占用的固定内存量(单位是KB) | 所在终端 | 进程状态 | 被启动的时间 | 实际使用CPU的时间 | 命令名称与参数 |
| root | 1 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 53684 | 7628 | ? | Ss | 07:22 | 0:02 | /usr/lib/systemd/systemd |
| root | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S | 07:22 | 0:00 | [kthreadd] |
| root | 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S | 07:22 | 0:00 | [ksoftirqd/0] |
| root | 5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S< | 07:22 | 0:00 | [kworker/0:0H] |
| root | 7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S | 07:22 | 0:00 | [migration/0] |
十六、date命令
date命令用于显示及设置系统的时间或日期,格式为:"date [选项] [+指定的格式]"。
强大的date命令只需键入以"+"号开头的参数即可按照指定格式来输出系统的时间或日期,这样日常工作时咱们便可以将打包数据的备份命令与指定格式输出的时间信息结合到一起,使得咱们可以更加便捷的区分每个文件的备份时间啦,date命令常见的格式如下:
| 参数 | 作用 |
| %t | 跳格[TAB键] |
| %H | 小时(00-23) |
| %I | 小时(00-12) |
| %M | 分钟(00-59) |
| %S | 秒(00-59) |
| %X | 相当于%H:%M:%S |
| %Z | 显示时区 |
| %p | 显示本地AM或PM |
| %A | 星期几 (Sunday-Saturday) |
| %a | 星期几 (Sun-Sat) |
| %B | 完整月份 (January-December) |
| %b | 缩写月份 (Jan-Dec) |
| %d | 日(01-31) |
| %j | 一年中的第几天(001-366) |
| %m | 月份(01-12) |
| %Y | 完整的年份 |
按照默认的格式查看当前的系统时间:
[root@linux ~]# date Mon Aug 24 16:11:23 CST 2016
按照"年-月-日 小时:分钟:秒"的格式查看当前的系统时间:
[root@linux ~]# date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" 2016-08-24 16:29:12
设置当前的系统时间为2016年9月1日8点30分:
[root@linux ~]# date -s "20160901 8:30:00" Tue Sep 1 08:30:00 CST 2016
再次按照默认的格式查看当前的系统时间:
[root@linux ~]# date Tue Sep 1 08:30:01 CST 2016
查看今天是一年中的第几天:
[root@linux ~]# date "+%j" 245
十七、dd命令
作用:用于指定大小的拷贝文件或指定转换文件
dd命令:是个比较重要且具有特色的一个命令,它能够让用户指定数据块的大小和个数来复制一个文件的内容,当然如果您愿意的话还可以在复制过程中转换其中的数据。Linux系统中有一个叫做/dev/zero的设备文件,每次讲课解释起来都感觉有点哲学理论的色彩,因为它不会占用您的系统存储空间,但里面却可以保存有无穷无尽的数据,一般用来搭配dd命令来生成出来一个指定大小的文件是再好不过的了。
| 参数 | 作用 |
| if | 输入的文件名称。 |
| of | 输出的文件名称。 |
| bs | 设置每个“块”的大小。 |
| count | 设置要拷贝“块”的个数。 |