Spring系列之事务的控制 注解实现+xml实现
在前面我写过一篇关于事务的文章,大家可以先去看看那一篇再看这一篇,学习起来会更加得心应手
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/pjh88/article/details/107574137
编程式事务控制对象
事务管理器:PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager是事务的管理器,他提供了我们常用的事务操作方法
 为什么PlatformTransactionManager是接口类型?
为什么PlatformTransactionManager是接口类型?
因为不同的dao层技术有不同的实现类
Dao层是jdbc时:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
Dao层是mybatis时:org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager
事务的定义信息对象:TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition
里面的方法
事务的隔离级别
**
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED(读未提交)
实质:一个事务读取另一个事务未提交的数据
例子:老板要给程序员发工资,程序员的工资是3.6万/月。但是发工资时老板不小心按错了数字,按成3.9万/月,该钱已经打到程序员的户口,但是事务还没有提交,就在这时,程序员去查看自己这个月的工资,发现比往常多了3千元,以为涨工资了非常高兴。但是老板及时发现了不对,马上回滚差点就提交了的事务,将数字改成3.6万再提交。
分析:实际程序员这个月的工资还是3.6万,但是程序员看到的是3.9万。他看到的是老板还没提交事务时的数据。这就是脏读。
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED(读已提交)
实质:一个用户读取另一个用户已提交的数据
事例:程序员拿着信用卡去享受生活(卡里当然是只有3.6万),当他埋单时(程序员事务开启),收费系统事先检测到他的卡里有3.6万,就在这个时候!!程序员的妻子要把钱全部转出充当家用,并提交。当收费系统准备扣款时,再检测卡里的金额,发现已经没钱了(第二次检测金额当然要等待妻子转出金额事务提交完)。程序员就会很郁闷,明明卡里是有钱的…
分析:这就是读提交,若有事务对数据进行更新(UPDATE)操作时,读操作事务要等待这个更新操作事务提交后才能读取数据,可以解决脏读问题。但在这个事例中,出现了一个事务范围内两个相同的查询却返回了不同数据,这就是不可重复读。
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ(重复读)
实质:一个事务在读取数据时,其他事务不允许进行修改操作
事例:程序员拿着信用卡去享受生活(卡里当然是只有3.6万),当他埋单时(事务开启,不允许其他事务的UPDATE修改操作),收费系统事先检测到他的卡里有3.6万。这个时候他的妻子不能转出金额了。接下来收费系统就可以扣款了。
分析:重复读可以解决不可重复读问题。写到这里,应该明白的一点就是,不可重复读对应的是修改,即UPDATE操作。但是可能还会有幻读问题。因为幻读问题对应的是插入INSERT操作,而不是UPDATE操作。
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE(幻读)
事例:程序员某一天去消费,花了2千元,然后他的妻子去查看他今天的消费记录(全表扫描FTS,妻子事务开启),看到确实是花了2千元,就在这个时候,程序员花了1万买了一部电脑,即新增INSERT了一条消费记录,并提交。当妻子打印程序员的消费记录清单时(妻子事务提交),发现花了1.2万元,似乎出现了幻觉,这就是幻读。
**
事务的传播行为
**
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作
超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
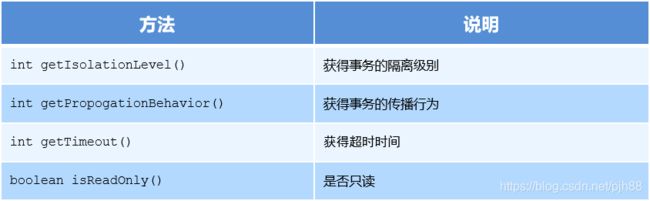
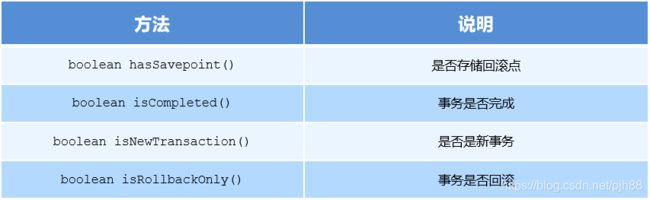
TransactionStatus:事务的具体运行状态
TransactionStatus接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法如下
PlatformTransactionManager
TransactionDefinition
TransactionStatus
基于XML的声明式事务控制
Spring的声明式事务控制顾名思义就是使用声明的方式来处理事务,这里的声明指的是在配置文件中声明,Spring配置文件中的声明式处理来代替代码式的事务处理
声明式事务处理的作用
事务处理是不侵入开发的组件,具体来说,业务逻辑对象不会意识带正在处于事务处理之中,事实上也应该如此,因为事务管理是出于系统层面的职务,而不是业务逻辑处理的一部分,如果要改变事务管理策划的话,也只需要在定义文件中重新配置即可
在不需要事务管理的时候,只要在设定的文件上修改一下,即可移除事务管理服务,不需要改变代码重新编译,这样维护起来更加方便
Spring事务控制的底层就是AOP
声明式事务控制的实现
切点:需要被事务管理的方法,即业务方法
通知/增强:事务增强
切面:二者结合
下面通过一个银行业务转账的案例来方便大家理解
1.创建数据库和实体
表名:account
字段名:moey--钱,Name--客户名
CREATE TABLE account(
NAME VARCHAR(10),
money DOUBLE
);
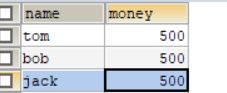
插入三个字段值
INSERT INTO account VALUE('tom',1),('bob',2),('jack',3);
2.需要导入的坐标
4.0.0
org.example
spring-mysql
1.0-SNAPSHOT
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.32
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.10
c3p0
c3p0
0.9.1.2
org.springframework
spring-context
5.0.5.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-tx
5.0.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
5.0.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-test
5.0.5.RELEASE
junit
junit
4.13
org.aspectj
aspectjweaver
1.8.13
org.junit.jupiter
junit-jupiter
RELEASE
compile
3.创建实体类
package com.pjh.account;
public class account {
private double money;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "account{" +
"money=" + money +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
4.dao层(执行语句,与数据库交互)
接口
package com.pjh.dao;
public interface ServiceDao {
public void inman(String inName,double money);
public void outman(String outName,double money);
}
实现类
package com.pjh.dao.imp;
import com.pjh.dao.ServiceDao;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class ServiceDaoImp implements ServiceDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public void inman(String inName, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money-? where name =?",money,inName);
}
public void outman(String outName, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money+? where name =?",money,outName);
}
}
5.service层
接口
package com.pjh.service;
public interface service {
public void trasfer(String inName,String outName,double money);
}
实现类
package com.pjh.service.Imp;
import com.pjh.dao.imp.ServiceDaoImp;
import com.pjh.service.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class serviceImp implements service {
private ServiceDaoImp serviceDaoImp;
public void setServiceDaoImp(ServiceDaoImp serviceDaoImp) {
this.serviceDaoImp = serviceDaoImp;
}
public void trasfer(String inName, String outName, double money) {
serviceDaoImp.inman(inName,money);
serviceDaoImp.outman(outName,money);
}
}
6.applicationContext配置文件
7.主函数
package com.pjh.control;
import com.pjh.service.Imp.serviceImp;
import com.pjh.service.service;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class control2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
service bean1 =(service) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean(service.class);
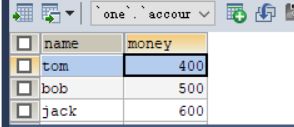
bean1.trasfer("tom","jack",100);
}
}
**
下面我们重点来讲讲切点方法的事务配置
**
这个部分一定要重点掌握这是核心
使用注解的方式进行事务的配置
1.dao层
package com.pjh.dao.imp;
import com.pjh.dao.ServiceDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("ServiceDaoImp")
public class ServiceDaoImp implements ServiceDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void inman(String inName, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money-? where name =?",money,inName);
}
public void outman(String outName, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money+? where name =?",money,outName);
}
}
2.service层
package com.pjh.service.Imp;
import com.pjh.dao.imp.ServiceDaoImp;
import com.pjh.service.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("serviceImp")
@Transactional
public class serviceImp implements service {
@Autowired
private ServiceDaoImp serviceDaoImp;
public void trasfer(String inName, String outName, double money) {
serviceDaoImp.inman(inName,money);
//int a=1/0;
serviceDaoImp.outman(outName,money);
}
}
3.编写applicationContext的内容
小总结
1.使用 @Transactional 在需要进行事务控制的类或是方法上修饰,注解可用的属性同 xml 配置方式,例如隔离级别、传播行为等。
注解使用在类上,那么该类下的所有方法都使用同一套注解参数配置。
使用在方法上,不同的方法可以采用不同的事务参数配置。
2.Xml配置文件中要开启事务的注解驱动