<总结> 设计模式之 开放封闭原则OCP C++示例
原文是C++ VIEW第二期的一篇译文,这里做个总结,便于查阅。
开放封闭原则
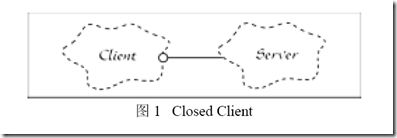
系统在添加新的需求的时候能够尽可能做到,只是添加新的代码 open for extension,而不需要修改原有模块代码 closed for modification
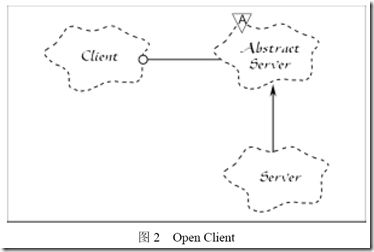
通过提取基类的方法,client 调用server 抽象基类abstract server的抽象接口,从而更换不同sever的时候,client的调用server的代码都不需要改动,接口不变,
只是server内容变化。
例子,
一个绘制函数,要求能够针对输入的不同对象,调用不同的绘制函数,如能够绘制矩形,圆形,适当调用矩形绘制函数,圆形绘制函数。
1.用c语言实现
这个例子其实给出了,c语言模拟c++类继承的方法。利用指针的强制转换,因为指针仅仅是地址可以指向任何对象,利用指针强制转换,告诉编译器具体按什么对象处理指针所指。
Listing 1
/*Procedural Solution to the Square/Circle Problem*/
enum ShapeType {circle, square};
struct Shape
{
ShapeType itsType;
};
struct Circle
{
ShapeType itsType;
double itsRadius;
Point itsCenter;
};
struct Square
{
ShapeType itsType;
double itsSide;
Point itsTopLeft;
};
//
// 下面两个函数的实现定义在别处
//
void DrawSquare(struct Square*)
void DrawCircle(struct Circle*);
typedef struct Shape *ShapePointer;
void DrawAllShapes(ShapePointer list[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
struct Shape* s = list[i];
switch (s->itsType)
{
case square:
DrawSquare((struct Square*)s);
break;
case circle:
DrawCircle((struct Circle*)s);
break;
}
}
}
上面的代码不符合open close法则,因为新加入其它的shape如椭圆, DrawAllShapes函数就需要变化。
2. C++的实现
Listing 2
/*OOD solution to Square/Circle problem.*/
class Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() const = 0;
};
class Square : public Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() const;
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() const;
};
void DrawAllShapes(Set<Shape*>& list)
{
for (Iterator<Shape*>i(list); i; i++)
(*i)->Draw();
}
和上面C语言实现代码对比,显然符合open close 法则,加入新的shape, DrawAllShapes函数可保持不变,只是添加新的shape内容。
但是事实上如果有新的需求变化,DrawAllShapes也无法做到完全不变,任何模块只能是相对封闭,无法完全封闭。
例如我们有新的需求,要求绘制图形列表的时候,一种形状的图形要在另一种图形前面绘制。
解决方法,加入 顺序抽象类
Listing 3
/*Shape with ordering methods.*/
class Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() const = 0;
virtual bool Precedes(const Shape&) const = 0;
bool operator<(const Shape& s) {return Precedes(s);}
};
Listing 4
/*DrawAllShapes with Ordering*/
void DrawAllShapes(Set<Shape*>& list)
{
// copy elements into OrderedSet and then sort.
OrderedSet<Shape*> orderedList = list;
orderedList.Sort();
for (Iterator<Shape*> i(orderedList); i; i++)
(*i)->Draw();
}
Listing 5
/*Ordering a Circle*/
bool Circle::Precedes(const Shape& s) const
{
if (dynamic_cast<Square*>(s))
return true;
else
return false;
}
这里使用的Precedes函数,如果新加入shape需要改变,怎么样才能做到更好呢?
使用数据驱动获得封闭性,利用预先写好的table,我们将各个图形的优先顺序写入table,那么新加入shape只需要更新table加入新的shape。
Listing 6
/*Table driven type ordering mechanism*/
#include <typeinfo.h>
#include <string.h>
enum {false, true};
typedef int bool;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() const = 0;
virtual bool Precedes(const Shape&) const;
bool operator<(const Shape& s) const
{return Precedes(s);}
private:
static char* typeOrderTable[];
};
/*
译者注:由于typeinfo.name没有标准,因此最好直接用typeinfo作为表中的元素类型,而不是用类名字符串。
*/
char* Shape::typeOrderTable[] =
{
“Circle”,
“Square”,
0
};
// This function searches a table for the class names.
// The table defines the order in which the
// shapes are to be drawn. Shapes that are not
// found always precede shapes that are found.
//
bool Shape::Precedes(const Shape& s) const
{
const char* thisType = typeid(*this).name();
const char* argType = typeid(s).name();
bool done = false;
int thisOrd = -1;
int argOrd = -1;
for (int i=0; !done; i++)
{
const char* tableEntry = typeOrderTable[i];
if (tableEntry != 0)
{
if (strcmp(tableEntry, thisType) == 0)
thisOrd = i;
if (strcmp(tableEntry, argType) == 0)
argOrd = i;
if ((argOrd > 0) && (thisOrd > 0))
done = true;
}
else // table entry == 0
done = true;
}
return thisOrd < argOrd;
}
进一步扩展封闭性
故事还没有结束。我们已经设法使得Shape类层次和DrawShapes函数对于依赖于图形类型的画出顺序是封闭的。然而,如果画出顺序与图形类型无关,那么Shape派生类并不对这种顺序的变化封闭。我们似乎需要根据一个更加高层次的结构来决定画出各个shape的顺序。关于这个问题的深入彻底探讨已经超过了本文的范围;然而有兴趣的读者可能会考虑定义一个OrderedObject的抽象类,并从Shape类和OrderedObject类派生一个新的抽象类OrderedShape。
所有成员变量都应该是私有的
永远不要用全局变量
然而,有些情况下全局变量的方便性是很重要的。全局变量cout和cin就是例子。在这种情况下,如果没有破环开放―封闭(open-closed)原则,那么牺牲风格来获得这种方便性是值得的
RTTI是危险的
根据一般的经验,如果使用RTTI不会破坏开放―封闭(open-closed)原则,那么就是安全的