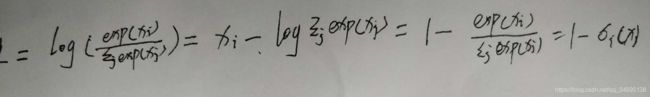nn.Softmax()与nn.LogSoftmax()与F.softmax()
nn.Softmax()与nn.LogSoftmax()与F.softmax()
nn.Softmax()
计算出来的值,其和为1,也就是输出的是概率分布,具体公式如下:
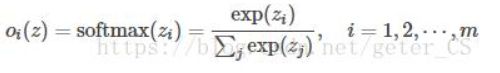
这保证输出值都大于0,在0,1范围内。
nn.LogSoftmax()
公式如下:
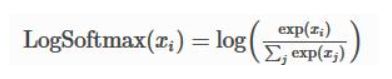
由于softmax输出都是0-1之间的,因此logsofmax输出的是小于0的数,
softmax求导:
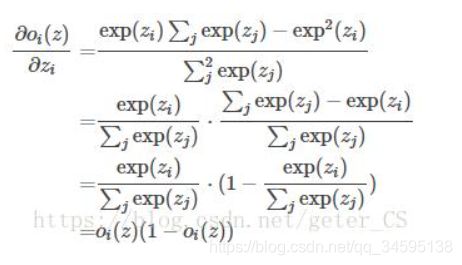
例子:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import numpy as np
layer1=nn.Softmax()
layer2=nn.LogSoftmax()
input=np.asarray([2,3])
input=Variable(torch.Tensor(input))
output1=layer1(input)
output2=layer2(input)
print('output1:',output1)
print('output2:',output2)
输出:
output1: Variable containing:
0.2689
0.7311
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2]
output2: Variable containing:
-1.3133
-0.3133
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2]
F.softmax()的用法:按照行来一行一行做归一化的
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
logits = torch.rand(2,2)
pred = F.softmax(logits, dim=1)
print(logits)
print(pred)
输出结果:
tensor([[0.4140, 0.4571],
[0.9392, 0.6504]])
tensor([[0.4892, 0.5108],
[0.5717, 0.4283]])
关于F.softmax(), nn.Logsoftmax()的坑是什么?
- 1: F.softmax() + nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), 只有一个log操作, 放前面或者放后面.
F.softmax() 是和nn.CrossEntropyLoss()连着用的,softmax后再进行算交叉熵损失,用nn.CrossEntropyLoss()算完损失,有一个log操作 - 2: nn.log_softmax() + nn.NLLLoss(), log操作前置.
nn.log_softmax() 将log进行前置,接下来算损失时,用 nn.NLLLoss()只算交叉熵的熵,不进行log操作了
用法上的两种组合方法,用哪个都可以,一般都习惯用第1种
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/105722023
当使用Softmax函数作为输出节点的激活函数的时候,一般使用交叉熵作为损失函数。由于Softmax函数的数值计算过程中,很容易因为输出节点的输出值比较大而发生数值溢出的现象,在计算交叉熵的时候也可能会出现数值溢出的问题。为了数值计算的稳定性,TensorFlow提供了一个统一的接口,将Softmax与交叉熵损失函数同时实现,同时也处理了数值不稳定的异常,使用TensorFlow深度学习框架的时候,一般推荐使用这个统一的接口,避免分开使用Softmax函数与交叉熵损失函数
TensorFlow提供的统一函数式接口为:
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.version) # 2.0.0
tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, from_logits = False)
其中y_true代表了One-hot编码后的真实标签,y_pred表示网络的实际预测值:
当from_logits设置为True时,y_pred表示未经Softmax函数的输出值;
当from_logits设置为False时,y_pred表示为经过Softmax函数后的输出值;
为了在计算Softmax函数时候数值的稳定,一般将from_logits设置为True,此时tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy将在内部进行Softmax的计算,所以在不需要在输出节点上添加Softmax激活函数。
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.__version__)
z = tf.random.normal([2, 10]) # 构造2个样本的10类别输出的输出值
y = tf.constant([1, 3]) # 两个样本的真是样本标签是1和3
y_true = tf.one_hot(y, depth = 10) # 构造onehot编码
# 输出层未经过Softmax激活函数,因此讲from_logits设置为True
loss1 = tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true, z, from_logits = True)
loss1 = tf.reduce_mean(loss1)
print(loss1) # tf.Tensor(2.6680193, shape=(), dtype=float32)
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(z)
# 输出层经过Softmax激活函数,因此讲from_logits设置为False
loss2 = tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred, from_logits = False)
loss2 = tf.reduce_mean(loss2)
print(loss2) # tf.Tensor(2.668019, shape=(), dtype=float32)
虽然上面两个过程结果差不多,但是当遇到一些不正常的数值时,将from_logits设置为True时TensorFlow会启用一些优化机制。因此推荐使用将from_logits参数设置为True的统一接口