使用JWT进行身份验证
应用程序的Github存储库:https://github.com/OmarElGabry/microservices-spring-boot
身份验证工作流程
身份验证流程很简单:
- 用户发送请求以获取传递其凭据的令牌(token)。
- 服务器验证凭据并发回令牌。
- 对于每个请求,用户必须提供令牌,服务器将验证该令牌。
我们将引入另一项称为“auth service”的服务,用于验证用户凭据和颁发令牌。
验证令牌怎么样?好吧,它可以在auth service本身中实现,并且网关必须在允许请求转到任何服务之前调用auth service来验证令牌。
相反,我们可以在网关级别验证令牌,并让auth service验证用户凭据,并发出令牌。这就是我们要在这里做的事情。
在这两种方式中,我们都会阻止请求,除非它经过身份验证(生成令牌的请求除外)。
基于JSON的令牌(JWT)
令牌是一个编码字符串,由我们的应用程序生成(经过身份验证后),并由用户沿每个请求发送,以允许访问我们的应用程序公开的资源。
基于JSON的令牌(JWT)是一种基于JSON的开放标准,用于创建访问令牌。它由三部分组成; 标头(header),有效负载(payload)和签名(signature)。
标头包含散列算法
{type: “JWT”, hash: “HS256”}
有效负载包含属性(用户名,电子邮件等)及其值。
{username: "Omar", email: "[email protected]", admin: true }
签名是哈希: Header + “.” + Payload + Secret key
网关
在网关中,我们需要做两件事:(1)针对每个请求验证令牌,以及(2)阻止对我们的服务的所有未经身份验证的请求。
在pom.xml添加spring安全性和JWT依赖项中。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
io.jsonwebtoken
jjwt
0.9.0
在application.properties添加路径AUTH服务(我们将在稍后创建它)。
# Map path to auth service
zuul.routes.auth-service.path=/auth/**
zuul.routes.auth-service.service-id=AUTH-SERVICE
# By default, all requests to gallery service for example will start with: "/gallery/"
# What will be sent to the gallery service is what comes after the path defined,
# So, if request is "/gallery/view/1", gallery service will get "/view/1".
# In case of auth, we need to pass the "/auth/" in the path to auth service. So, set strip-prefix to false
zuul.routes.auth-service.strip-prefix=false
# Exclude authorization from sensitive headers
zuul.routes.auth-service.sensitive-headers=Cookie,Set-Cookie
要定义我们的安全性配置,创建一个类,并使用注释@EnableWebSecurity,并使用extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类来覆盖并提供我们自己的自定义安全性配置。
package com.eureka.zuul.security;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import com.eureka.zuul.security.JwtConfig;
@EnableWebSecurity // Enable security config. This annotation denotes config for spring security.
public class SecurityTokenConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private JwtConfig jwtConfig;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
// make sure we use stateless session; session won't be used to store user's state.
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
// handle an authorized attempts
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint((req, rsp, e) -> rsp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED))
.and()
// Add a filter to validate the tokens with every request
.addFilterAfter(new JwtTokenAuthenticationFilter(jwtConfig), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
// authorization requests config
.authorizeRequests()
// allow all who are accessing "auth" service
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, jwtConfig.getUri()).permitAll()
// must be an admin if trying to access admin area (authentication is also required here)
.antMatchers("/gallery" + "/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
// Any other request must be authenticated
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
@Bean
public JwtConfig jwtConfig() {
return new JwtConfig();
}
}
Spring具有将在请求的生命周期(过滤器链)内执行的过滤器。要启用和使用这些过滤器,我们需要扩展任何这些过滤器的类。
默认情况下,spring会尝试确定何时应该执行过滤器。否则,我们还可以定义何时应该执行(在另一个过滤器之后或之前)。
这JwtConfig只是一个包含配置变量的类。
public class JwtConfig {
@Value("${security.jwt.uri:/auth/**}")
private String Uri;
@Value("${security.jwt.header:Authorization}")
private String header;
@Value("${security.jwt.prefix:Bearer }")
private String prefix;
@Value("${security.jwt.expiration:#{24*60*60}}")
private int expiration;
@Value("${security.jwt.secret:JwtSecretKey}")
private String secret;
// getters ...
}
最后一步是实现验证令牌的过滤器。我们正在使用OncePerRequestFilter。它保证每个请求单次执行(因为您可以在过滤器链上多次使用过滤器)。
package com.eureka.zuul.security;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import com.eureka.zuul.security.JwtConfig;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
public class JwtTokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private final JwtConfig jwtConfig;
public JwtTokenAuthenticationFilter(JwtConfig jwtConfig) {
this.jwtConfig = jwtConfig;
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. get the authentication header. Tokens are supposed to be passed in the authentication header
String header = request.getHeader(jwtConfig.getHeader());
// 2. validate the header and check the prefix
if(header == null || !header.startsWith(jwtConfig.getPrefix())) {
chain.doFilter(request, response); // If not valid, go to the next filter.
return;
}
// If there is no token provided and hence the user won't be authenticated.
// It's Ok. Maybe the user accessing a public path or asking for a token.
// All secured paths that needs a token are already defined and secured in config class.
// And If user tried to access without access token, then he won't be authenticated and an exception will be thrown.
// 3. Get the token
String token = header.replace(jwtConfig.getPrefix(), "");
try { // exceptions might be thrown in creating the claims if for example the token is expired
// 4. Validate the token
Claims claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(jwtConfig.getSecret().getBytes())
.parseClaimsJws(token)
.getBody();
String username = claims.getSubject();
if(username != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List authorities = (List) claims.get("authorities");
// 5. Create auth object
// UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken: A built-in object, used by spring to represent the current authenticated / being authenticated user.
// It needs a list of authorities, which has type of GrantedAuthority interface, where SimpleGrantedAuthority is an implementation of that interface
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken auth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, null, authorities.stream().map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new).collect(Collectors.toList()));
// 6. Authenticate the user
// Now, user is authenticated
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// In case of failure. Make sure it's clear; so guarantee user won't be authenticated
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
// go to the next filter in the filter chain
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
验证服务(Auth Service)
在Auth Service中,我们需要(1)验证用户凭证,如果有效,(2)生成令牌,否则抛出异常。
在pom.xml添加以下依赖项:Web,Eureka Client,Spring Security和JWT。
....
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
io.jsonwebtoken
jjwt
0.9.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
....
在里面 application.properties
spring.application.name=auth-service
server.port=9100
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eureka
正如我们在Gateway中进行安全配置所做的那样,创建一个带有注释@EnableWebSecurity和扩展的类WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
package com.eureka.auth.security;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import com.eureka.auth.security.JwtConfig;
@EnableWebSecurity // Enable security config. This annotation denotes config for spring security.
public class SecurityCredentialsConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private JwtConfig jwtConfig;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
// make sure we use stateless session; session won't be used to store user's state.
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
// handle an authorized attempts
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint((req, rsp, e) -> rsp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED))
.and()
// Add a filter to validate user credentials and add token in the response header
// What's the authenticationManager()?
// An object provided by WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter, used to authenticate the user passing user's credentials
// The filter needs this auth manager to authenticate the user.
.addFilter(new JwtUsernameAndPasswordAuthenticationFilter(authenticationManager(), jwtConfig))
.authorizeRequests()
// allow all POST requests
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, jwtConfig.getUri()).permitAll()
// any other requests must be authenticated
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
// Spring has UserDetailsService interface, which can be overriden to provide our implementation for fetching user from database (or any other source).
// The UserDetailsService object is used by the auth manager to load the user from database.
// In addition, we need to define the password encoder also. So, auth manager can compare and verify passwords.
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Bean
public JwtConfig jwtConfig() {
return new JwtConfig();
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
正如您在上面的代码中看到的,我们需要实现UserDetailsService接口。
该类充当用户的提供者; 意味着它从数据库(或任何数据源)加载用户。它不进行身份验证。它只是加载用户的用户名。
package com.eureka.auth.security;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service // It has to be annotated with @Service.
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// hard coding the users. All passwords must be encoded.
final List users = Arrays.asList(
new AppUser(1, "omar", encoder.encode("12345"), "USER"),
new AppUser(2, "admin", encoder.encode("12345"), "ADMIN")
);
for(AppUser appUser: users) {
if(appUser.getUsername().equals(username)) {
// Remember that Spring needs roles to be in this format: "ROLE_" + userRole (i.e. "ROLE_ADMIN")
// So, we need to set it to that format, so we can verify and compare roles (i.e. hasRole("ADMIN")).
List grantedAuthorities = AuthorityUtils
.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_" + appUser.getRole());
// The "User" class is provided by Spring and represents a model class for user to be returned by UserDetailsService
// And used by auth manager to verify and check user authentication.
return new User(appUser.getUsername(), appUser.getPassword(), grantedAuthorities);
}
}
// If user not found. Throw this exception.
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Username: " + username + " not found");
}
// A (temporary) class represent the user saved in the database.
private static class AppUser {
private Integer id;
private String username, password;
private String role;
public AppUser(Integer id, String username, String password, String role) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.role = role;
}
// getters and setters ....
}
}
这是最后一步; 过滤器。
我们正在使用JwtUsernameAndPasswordAuthenticationFilter。它用于验证用户凭据并生成令牌。必须在POST请求中发送用户名和密码。
package com.eureka.auth.security;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
import com.eureka.auth.security.JwtConfig;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
public class JwtUsernameAndPasswordAuthenticationFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
// We use auth manager to validate the user credentials
private AuthenticationManager authManager;
private final JwtConfig jwtConfig;
public JwtUsernameAndPasswordAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationManager authManager, JwtConfig jwtConfig) {
this.authManager = authManager;
this.jwtConfig = jwtConfig;
// By default, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter listens to "/login" path.
// In our case, we use "/auth". So, we need to override the defaults.
this.setRequiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher(jwtConfig.getUri(), "POST"));
}
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
try {
// 1. Get credentials from request
UserCredentials creds = new ObjectMapper().readValue(request.getInputStream(), UserCredentials.class);
// 2. Create auth object (contains credentials) which will be used by auth manager
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
creds.getUsername(), creds.getPassword(), Collections.emptyList());
// 3. Authentication manager authenticate the user, and use UserDetialsServiceImpl::loadUserByUsername() method to load the user.
return authManager.authenticate(authToken);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// Upon successful authentication, generate a token.
// The 'auth' passed to successfulAuthentication() is the current authenticated user.
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication auth) throws IOException, ServletException {
Long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
String token = Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(auth.getName())
// Convert to list of strings.
// This is important because it affects the way we get them back in the Gateway.
.claim("authorities", auth.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority).collect(Collectors.toList()))
.setIssuedAt(new Date(now))
.setExpiration(new Date(now + jwtConfig.getExpiration() * 1000)) // in milliseconds
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, jwtConfig.getSecret().getBytes())
.compact();
// Add token to header
response.addHeader(jwtConfig.getHeader(), jwtConfig.getPrefix() + token);
}
// A (temporary) class just to represent the user credentials
private static class UserCredentials {
private String username, password;
// getters and setters ...
}
}
共同事务
如果您有多个服务使用的公共配置变量,枚举类或逻辑,就像我们拥有的那样JwtConfig。我们将其放在一个单独的服务中,而不是复制代码,该服务可以包含在其他服务中并作为依赖项使用。
为此,只需创建一个新项目(服务),将其命名为“common”,然后按照与图像服务相同的步骤操作。所以,在pom.xml文件中
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
在里面 application.properties
spring.application.name=common-service
server.port=9200
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eureka
在spring boot主应用程序类中
package com.eureka.common;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class SpringEurekaCommonApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringEurekaCommonApp.class, args);
}
}
然后,复制JwtConfig我们之前在Gateway中创建的公共服务类。
package com.eureka.common.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
public class JwtConfig {
// ...
}
现在,为了能够JwtConfig从其他服务(如auth和gateway)调用类,我们只需要将公共服务添加pom.xml为依赖项。
com.eureka.common
spring-eureka-common
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
在我们的身份验证和网关服务中......
// change these lines of code
import com.eureka.zuul.security.JwtConfig;
import com.eureka.auth.security.JwtConfig;
// to reference the class in common service instead
import com.eureka.common.security.JwtConfig;
测试我们的微服务
现在我们插入了身份验证逻辑,我们可以无缝地验证凭据,发放令牌和验证用户身份。
所以,运行我们的Eureka服务器。然后,运行其他服务:image,gallery,common,auth,最后是网关。
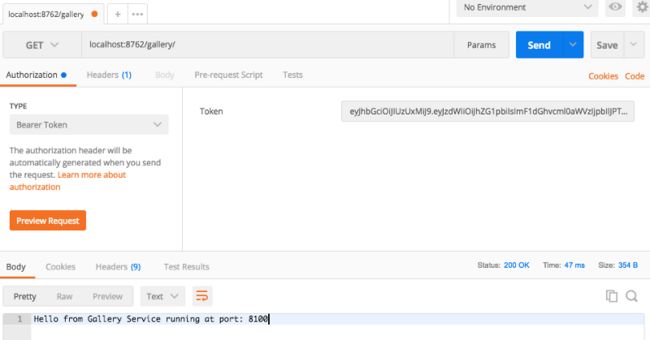
首先,让我们尝试在localhost:8762/gallery没有令牌的情况下访问图库服务。你应该得到Unauthorized错误。
{
"timestamp": "...",
"status": 401,
"error": "Unauthorized",
"message": "No message available",
"path": "/gallery/"
}
要获取令牌,请将用户凭据发送给localhost:8762/auth(我们在UserDetailsServiceImpl上面的类中硬编码了两个用户),并确保Content-Type将头中的用户分配给application/json
现在,我们可以向标头中的令牌传递令牌服务请求。
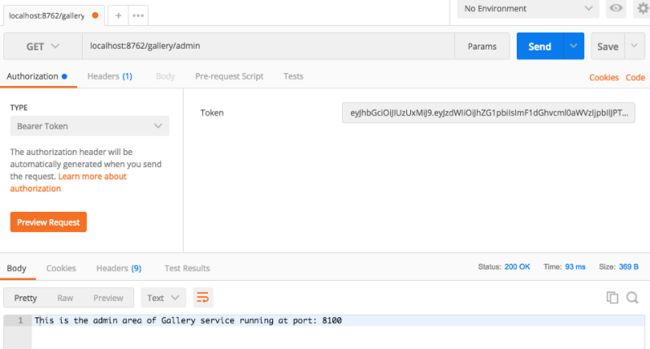
如果为管理员用户创建了令牌,那么您应该能够访问图库服务的管理区域。
同样,如果您正在运行多个gallery服务实例,每个实例都在不同的端口运行,那么请求将在它们之间平均分配。