参考资料
- keras中文文档(官方)
- keras中文文档(非官方)
- 莫烦keras教程代码
- 莫烦keras视频教程
- 一些keras的例子
- Keras开发者的github
- keras在
imagenet以及VGG19上的应用 - 一个不负责任的Keras介绍(上)
- 一个不负责任的Keras介绍(中)
- 一个不负责任的Keras介绍(下)
- 使用keras构建流行的深度学习模型
- Keras FAQ: Frequently Asked Keras Questions
- GPU并行训练
- 常见CNN结构的keras实现
Keras框架介绍
在用了一段时间的Keras后感觉真的很爽,所以特意祭出此文与我们公众号的粉丝分享。
Keras是一个非常方便的深度学习框架,它以TensorFlow或Theano为后端。用它可以快速地搭建深度网络,灵活地选取训练参数来进行网路训练。总之就是:灵活+快速!
安装Keras
首先你需要有一个Python开发环境,直接点就用Anaconda,然后在CMD命令行中安装:
# GPU 版本
>>> pip install --upgrade tensorflow-gpu
# CPU 版本
>>> pip install --upgrade tensorflow
# Keras 安装
>>> pip install keras -U --pre
第一个例子:回归模型
首先我们在Keras中定义一个单层全连接网络,进行线性回归模型的训练:
# Regressor example
# Code: https://github.com/keloli/KerasPractise/edit/master/Regressor.py
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1337)
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 创建数据集
X = np.linspace(-1, 1, 200)
np.random.shuffle(X) # 将数据集随机化
Y = 0.5 * X + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, (200, )) # 假设我们真实模型为:Y=0.5X+2
# 绘制数据集plt.scatter(X, Y)
plt.show()
X_train, Y_train = X[:160], Y[:160] # 把前160个数据放到训练集
X_test, Y_test = X[160:], Y[160:] # 把后40个点放到测试集
# 定义一个model,
model = Sequential () # Keras有两种类型的模型,序贯模型(Sequential)和函数式模型
# 比较常用的是Sequential,它是单输入单输出的
model.add(Dense(output_dim=1, input_dim=1)) # 通过add()方法一层层添加模型
# Dense是全连接层,第一层需要定义输入,
# 第二层无需指定输入,一般第二层把第一层的输出作为输入
# 定义完模型就需要训练了,不过训练之前我们需要指定一些训练参数
# 通过compile()方法选择损失函数和优化器
# 这里我们用均方误差作为损失函数,随机梯度下降作为优化方法
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='sgd')
# 开始训练
print('Training -----------')
for step in range(301):
cost = model.train_on_batch(X_train, Y_train) # Keras有很多开始训练的函数,这里用train_on_batch()
if step % 100 == 0:
print('train cost: ', cost)
# 测试训练好的模型
print('\nTesting ------------')
cost = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test, batch_size=40)
print('test cost:', cost)
W, b = model.layers[0].get_weights() # 查看训练出的网络参数
# 由于我们网络只有一层,且每次训练的输入只有一个,输出只有一个
# 因此第一层训练出Y=WX+B这个模型,其中W,b为训练出的参数
print('Weights=', W, '\nbiases=', b)
# plotting the prediction
Y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
plt.scatter(X_test, Y_test)
plt.plot(X_test, Y_pred)
plt.show()
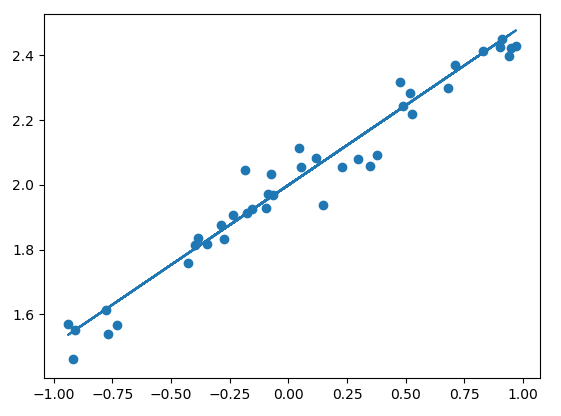
训练结果:
最终的测试cost为:0.00313670327887,可视化结果如下图:
第二个例子:手写数字识别
MNIST数据集可以说是在业内被搞过次数最多的数据集了,毕竟各个框架的“hello world”都用它。这里我们也简单说一下在Keras下如何训练这个数据集:
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
# Classifier mnist
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1337)
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
# 下载数据集
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处处理
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], -1) / 255.
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], -1) / 255.
y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=10)
y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes=10)
# 不使用model.add(),用以下方式也可以构建网络
model = Sequential([
Dense(400, input_dim=784),
Activation('relu'),
Dense(10),
Activation('softmax'),
])
# 定义优化器
rmsprop = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9, epsilon=1e-08, decay=0.0)
model.compile(optimizer=rmsprop,
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']) # metrics赋值为'accuracy',会在训练过程中输出正确率
# 这次我们用fit()来训练网路
print('Training ------------')
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=4, batch_size=32)
print('\nTesting ------------')
# 评价训练出的网络
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print('test loss: ', loss)
print('test accuracy: ', accuracy)
简单训练后得到:test loss: 0.0970609934615,test accuracy: 0.9743
第三个例子:加经典网络的预训练模型(以VGG16为例)
预训练模型Application
https://gist.github.com/baraldilorenzo/07d7802847aaad0a35d3
https://github.com/keras-team/keras/issues/4465
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/43386463/keras-vgg16-fine-tuning
1.当服务器不能联网时,需要把模型*.h5文件下载到用户目录下的~/.keras/model,模型的预训练权重在载入模型时自动载入
- 通过以下代码加载VGG16:
# 使用VGG16模型
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
print('Start build VGG16 -------')
# 获取vgg16的卷积部分,如果要获取整个vgg16网络需要设置:include_top=True
model_vgg16_conv = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False)
model_vgg16_conv.summary()
# 创建自己的输入格式
# if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
# input_shape = (3, img_width, img_height)
# else:
# input_shape = (img_width, img_height, 3)
input = Input(input_shape, name = 'image_input') # 注意,Keras有个层就是Input层
# 将vgg16模型原始输入转换成自己的输入
output_vgg16_conv = model_vgg16_conv(input)
# output_vgg16_conv是包含了vgg16的卷积层,下面我需要做二分类任务,所以需要添加自己的全连接层
x = Flatten(name='flatten')(output_vgg16_conv)
x = Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc1')(x)
x = Dense(512, activation='relu', name='fc2')(x)
x = Dense(128, activation='relu', name='fc3')(x)
x = Dense(1, activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x)
# 最终创建出自己的vgg16模型
my_model = Model(input=input, output=x)
# 下面的模型输出中,vgg16的层和参数不会显示出,但是这些参数在训练的时候会更改
print('\nThis is my vgg16 model for the task')
my_model.summary()
其他Keras使用细节
指定占用的GPU以及多GPU并行
参考:
keras指定运行时显卡及限制GPU用量
Tensorflow中指定使用设备
-
查看GPU使用情况语句(Linux)
# 1秒钟刷新一次 watch -n 1 nvidia-smi -
指定显卡
import os os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "2"这里指定了使用编号为2的GPU,大家可以根据需要和实际情况来指定使用的GPU
GPU并行
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/db0ba022936f
from model import unet
G = 3 # 同时使用3个GPU
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
M = unet(input_rows, input_cols, 1)
model = keras.utils.training_utils.multi_gpu_model(M, gpus=G)
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-5), loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
model.fit(X_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size*G, epochs=nb_epoch, verbose=0, shuffle=True,
validation_data=(X_valid, y_valid))
model.save_weights('/path/to/save/model.h5')
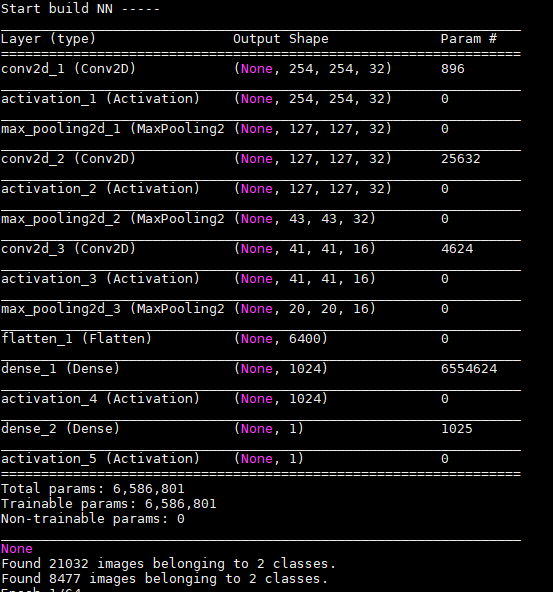
查看网络结构的命令
- 查看搭建的网络
print (model.summary())
- 保存网络结构图
# 你还可以用plot_model()来讲网络保存为图片 plot_model(my_model, to_file='my_vgg16_model.png')
训练集与测试集图像的处理:
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
print('Lodaing data -----------')
train_datagen=ImageDataGenerator()
test_datagen=ImageDataGenerator()
写在最后
本文介绍了一个灵活快速的深度学习框架,并且通过三个例子讲解了如何利用Keras搭建深度网络进行训练、如何使用预训练模型,还介绍了在使用Keras训练网络中的一些tricks。
最后,祝各位炼丹师玩的愉快~
PS:
欢迎follow我的GitHub:https://github.com/keloli
还有我的博客:https://www.jianshu.com/u/d055ee434e59