1、init程序的类型
SysV: init, CentOS 5之前
配置文件:/etc/inittab
Upstart: init,CentOS6
配置文件:/etc/inittab, /etc/init/*.conf
Systemd:systemd, CentOS 7
配置文件:/usr/lib/systemd/system
/etc/systemd/system
[root@station1 ~]# rpm -qf /sbin/init ---centos5
SysVinit-2.86-15.el5
[root@centos6 sbin]#rpm -qf /sbin/init ---centos6
upstart-0.6.5-16.el6.x86_64
[root@redhat7 sbin]#rpm -qf /sbin/init ----centos7
systemd-219-42.el7.x86_64
2、cents6的之前的inint程序的配置文件/etc/inittab文件
init读取其初始化文件:/etc/inittab
初始运行级别(RUN LEVEL)
系统初始化脚本
对应运行级别的脚本目录
捕获某个关键字顺序
定义UPS电源终端/恢复脚本
在虚拟控制台生成getty
在运行级别5初始化X
[root@station1 ~]# cat /etc/inittab
#
# inittab This file describes how the INIT process should set up
# the system in a certain run-level.
#
# Author: Miquel van Smoorenburg,
# Modified for RHS Linux by Marc Ewing and Donnie Barnes
#
# Default runlevel. The runlevels used by RHS are:
# 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
0:关机
# 1 - Single user mode
1:单用户模式(root自动登录), single, 维护模式
# 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking)
2: 多用户模式,启动网络功能,但不会启动NFS;维护模式,实际上是有网络功能的,即使不启动NFS
# 3 - Full multiuser mode
3:多用户模式,正常模式;文本界面
# 4 - unused
4:预留级别;可同3级别
# 5 - X11
5:多用户模式,正常模式;图形界面
# 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
6:重启
默认级别:3, 5
切换级别:init#
查看级别:runlevel; who -r
#
id:5:initdefault: ----设定默认运行级别,每一行定义一种action以及与之对应的process
id:runlevel:action:process
action:
wait: 切换至此级别运行一次
respawn:此process终止,就重新启动之
initdefault:设定默认运行级别;process省略
sysinit:设定系统初始化方式,此处一般为指定
# System initialization.
si::sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit ---系统启动时执行的第一个脚本,也叫系统初始化脚本,完成系统初始化,这个脚本和运行模式无关,无论什么模式都会运行。
l0:0:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 0
l1:1:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 1
l2:2:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 2
l3:3:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 3
l4:4:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 4
l5:5:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 5
l6:6:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 6
定义了各种运行模式下开机启动和关闭的服务脚本,例如在3模式下运行时,就执行/etc/rc.d/rc这个脚本,使/etc/rc.d/rc3.d目录中以S打头的文件服务在开机的时候就启动,以K打头的文件服务在开机的时候就不启动。
# Trap CTRL-ALT-DELETE
ca::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/shutdown -t3 -r now
表示在本机操作时按ctrl+alt+del就重启
# When our UPS tells us power has failed, assume we have a few minutes
# of power left. Schedule a shutdown for 2 minutes from now.
# This does, of course, assume you have powerd installed and your
# UPS connected and working correctly.
pf::powerfail:/sbin/shutdown -f -h +2 "Power Failure; System Shutting Down"
表示停电之后2分钟之后关机,要配合UPS并且UPS是正常的
# If power was restored before the shutdown kicked in, cancel it.
pr:12345:powerokwait:/sbin/shutdown -c "Power Restored; Shutdown Cancelled"
如果两分钟之内又来电了,还可以取消关机
# Run gettys in standard runlevels
1:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty1
2:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty2 ---respawn表示此程序终止就重新
启动,mingetty这个程序用killall命令是杀不死的,杀死了就又复活,并
且换了新的进程编号pid,即使用killall -9 都杀不死
3:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty3
4:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty4
5:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty5
6:2345:respawn:/sbin/mingetty tty6
如果在下面加一行,tty10,再重启,在本机操作时按ctrl+alt+F10也可以登陆,否则在本机只能按6次。
# Run xdm in runlevel 5
x:5:respawn:/etc/X11/prefdm -nodaemon
表示在5运行模式下会开启图形,如果把5改成3,重启电脑。在登陆时
按a ,修改内核参数,按3,表示以3模式登陆,发现也会开启图形,这
一行的作用就是在哪种模式下开启图形。注意,不能在下面加一行,只
能把5修改为3或者其他的运行模式。
3、CentOS 6 /etc/inittab和相关文件
/etc/inittab
设置系统默认的运行级别
id:3:initdefault:
/etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf
/etc/init/tty.conf
/etc/init/start-ttys.conf
/etc/init/rc.conf
/etc/init/prefdm.conf ---相当于在哪个运行模式下开启图形
4、单用户模式下破解root口令
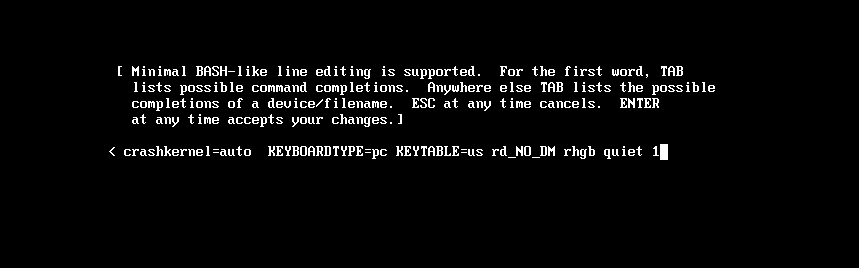
在如下界面输入a,修改内核参数
在如下界面输入1,进入单用户模式
单用户模式会自动以root身份登录,不需要输入密码,这样就可以对root账号用passwd命令进行修改密码
5、/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit: 系统初始化脚本
(1) 设置主机名
(2) 设置欢迎信息
(3) 激活udev和selinux
(4) 挂载/etc/fstab文件中定义的文件系统
(5) 检测根文件系统,并以读写方式重新挂载根文件系统
(6) 设置系统时钟
(7) 激活swap设备
(8) 根据/etc/sysctl.conf文件设置内核参数
(9) 激活lvm及software raid设备
(10) 加载额外设备的驱动程序
(11) 清理操作
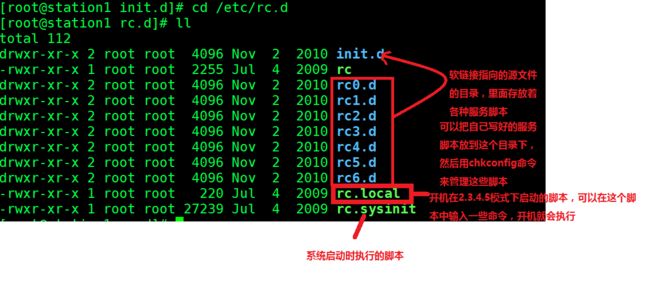
6、/etc/rc.d/rcN.d/文件说明
这个文件定义了各种服务脚本,在各种运行模式下开机启动的服务和关闭的服务。以S打头的服务开机的时候启动,以K打头的服务开机的时候不启动,以S打头的文件数字越小的服务,越优先运行,说明是最基本的服务,后面大的服务要依赖于前面小的基本的服务才能启动。以K打头的服务,数字越小,越优先关闭,说明是大的服务,大的服务先关闭,小的基本的服务最后关闭。
以/etc/rc.d/rc5.d为例
[root@station1 rc.d]# cd /etc/rc.d/rc5.d/ ---进入这个目录
[root@station1 rc5.d]# ls ---我们发现有很多以K和S打头的服务
K01dnsmasq K85mdmpd S12restorecond S50hplip
K02avahi-dnsconfd K87multipathd S12syslog S55sshd
K02NetworkManager K88wpa_supplicant S13irqbalance S56cups
K05conman K89dund S13portmap S56rawdevices
K05saslauthd K89netplugd S14nfslock S56xinetd
K05wdaemon K89pand S15mdmonitor S80sendmail
K10psacct K89rdisc S18rpcidmapd S85gpm
K20nfs K91capi S19rpcgssd S90crond
K24irda S02lvm2-monitor S22messagebus S90xfs
K35vncserver S04readahead_early S23setroubleshoot S95anacron
K35winbind S05kudzu S25bluetooth S95atd
K50netconsole S06cpuspeed S25netfs S96readahead_later
K69rpcsvcgssd S08ip6tables S25pcscd S97rhnsd
K73ypbind S08iptables S26acpid S97yum-updatesd
K74ipmi S08mcstrans S26apmd S98avahi-daemon
K74nscd S09isdn S26haldaemon S99firstboot
K74ntpd S10network S26hidd S99local
K80kdump S11auditd S28autofs S99smartd
[root@station1 rc5.d]# ll ---这些服务在这个目录下都是软连接,指向的是/etc/rc.d/init.d这个目录下的各种服务脚本
total 288
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Nov 2 2010 K01dnsmasq -> ../init.d/dnsmasq ---软链接的相对路径是相对于软链接的目录
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 Nov 2 2010 K02avahi-dnsconfd -> ../init.d/avahi-dnsconfd
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 Nov 2 2010 K02NetworkManager -> ../init.d/NetworkManager
[root@station1 rc.d]# cd init.d/ ---进入这个目录
[root@station1 init.d]# ls ---可以看到各种服务脚本
acpid dund krb524 nscd sendmail
anacron firstboot kudzu ntpd setroubleshoot
apmd functions lvm2-monitor pand single
atd gpm mcstrans pcscd smartd
auditd haldaemon mdmonitor portmap sshd
autofs halt mdmpd psacct syslog
avahi-daemon hidd messagebus rawdevices vncserver
avahi-dnsconfd hplip microcode_ctl rdisc wdaemon
bluetooth ip6tables multipathd readahead_early winbind
capi ipmi netconsole readahead_later wpa_supplicant
conman iptables netfs restorecond xfs
cpuspeed irda netplugd rhnsd xinetd
crond irqbalance network rpcgssd ypbind
cups isdn NetworkManager rpcidmapd yum-updatesd
cups-config-daemon kdump nfs rpcsvcgssd
dnsmasq killall nfslock saslauthd
7、/etc/rc.d目录介绍
8、服务管理
[root@station1 init.d]# service atd restart
Stopping atd: [ OK ]
Starting atd: [ OK ]
[root@station1 init.d]# ./atd restart ---执行这条命令和上面的命令结果是一样的,说明用service启动服务的时候就是执行/etc/rc.d/init.d/atd这个脚本
Stopping atd: [ OK ]
Starting atd: [ OK ]
[root@station1 init.d]# chkconfig --list ---可以查看各种服务在各种运行
模式下开机是启动还是关闭的状态
NetworkManager 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
acpid 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
anacron 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
apmd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off ---比如atd服务,在
计算机启动时,只要是3.4.5模式,这个服务就启动
.
.
[root@station1 init.d]# runlevel ---当前运行在5模式也就是图形界面
N 5
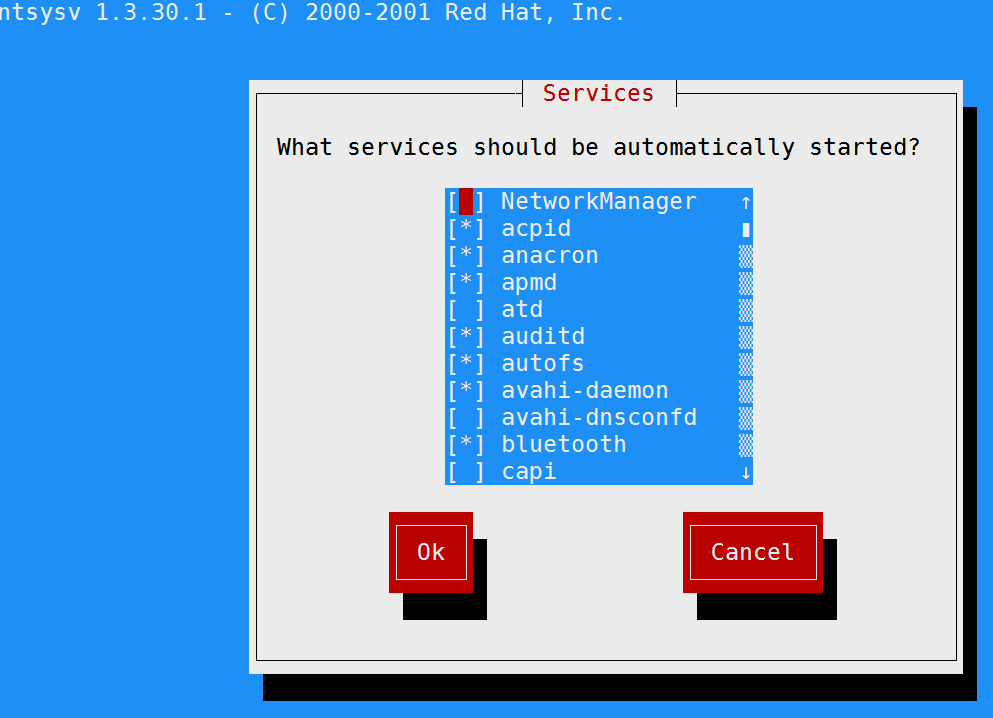
[root@station1 init.d]# ntsysv ----输入这条命令,可以修改当前模式下对应的服务是否开机启动还是关闭
按空格键可以把对应的*去掉,表示开机的时候在这个模式下不启动这个服务,然后按tab键可以退出。
[root@station1 ~]# chkconfig --list
NetworkManager 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
acpid 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
anacron 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
apmd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:off 6:off ---发现在5模式下已经不启动了。
[root@station1 ~]# ntsysv --level=2 ---也可以指定更改哪个模式
[root@station1 ~]# chkconfig --list atd
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:off 6:off
[root@station1 ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 atd off ---这种方法用起来比较方便,可以更改任何的运行模式
[root@station1 ~]# chkconfig --list atd
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
[root@station1 rc5.d]# chkconfig --level 234 atd on
[root@station1 rc5.d]# chkconfig --list atd ---3模式对于这个服务已经打开
atd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:off 6:off
[root@station1 rc5.d]# cd /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/
[root@station1 rc3.d]# ls S* ---用chkconfig命令修改运行模式,实际上就是修改/etc/rc.d/rc*.d目录下对应的软链接文件,把它变成以S打头的
S02lvm2-monitor S11auditd S22messagebus S28autofs S90xfs
S04readahead_early S12restorecond S23setroubleshoot S50hplip S95anacron
S05kudzu S12syslog S25bluetooth S55sshd S95atd
S06cpuspeed S13irqbalance S25netfs S56cups S97rhnsd
S08ip6tables S13portmap S25pcscd S56rawdevices S97yum-updatesd
S08iptables S14nfslock S26acpid S56xinetd S98avahi-daemon
S08mcstrans S15mdmonitor S26apmd S80sendmail S99firstboot
S09isdn S18rpcidmapd S26haldaemon S85gpm S99local
S10network S19rpcgssd S26hidd S90crond S99smartd
[root@station1 rc3.d]# chkconfig --level 3 atd off ---关闭3模式下的atd服务
[root@station1 rc3.d]# ls K* ---发现变成以K打头的了
K01dnsmasq K05wdaemon K50netconsole K80kdump K89pand
K02avahi-dnsconfd K10psacct K69rpcsvcgssd K85mdmpd K89rdisc
K02NetworkManager K20nfs K73ypbind K87multipathd K91capi
K05atd K24irda K74ipmi K88wpa_supplicant K99readahead_later
K05conman K35vncserver K74nscd K89dund
K05saslauthd K35winbind K74ntpd K89netplugd
[root@station1 rc3.d]# rm -f K05
K05atd K05conman K05saslauthd K05wdaemon
[root@station1 rc3.d]# rm -f K05atd ---删除这个文件
[root@station1 rc3.d]# ln -s ../init.d/atd S95atd ---创建一个软链接以S打头
[root@station1 rc3.d]# chkconfig --list atd ---这样3模式下就变成开机
自动启动这个服务了,说明看一个服务是否开机启动就看这个服务在这
个目录下是以S打头还是以K打头
atd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:off 6:off
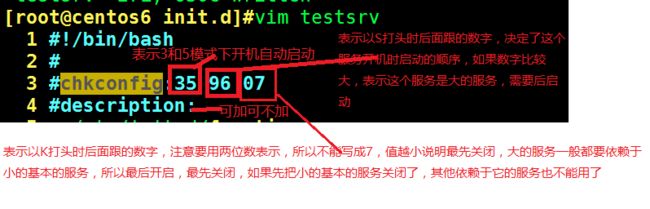
[root@centos6 init.d]#vim testsrv ---在/etc/rc.d/init.d目录下创建一个服务脚本,就可以用service 命令来启动和关闭服务了
#!/bin/bash
#
. /etc/init.d/functions
case $1 in
start)
touch /var/lock/subsys/testsrv
action "testsrv is start ..." true
;;
stop)
rm /var/lock/subsys/testsrv
action "testsrv is stopped" true
;;
restart)
rm /var/lock/subsys/testsrv
action "testsrv is stopped" true
touch /var/lock/subsys/testsrv
action "testsrv is start ..." true
;;
status)
[ -f /var/lock/subsys/testsrv ]&&echo "testsrv is running..."||echo "testsrv is
stopped"
;;
*)
echo "usage:testsrv start|stop|restart|status"
;;
esac
[root@centos6 init.d]#service testsrv start ---可以用service命令来开启和关闭服务
testsrv is start ... [ OK ]
[root@centos6 init.d]#service testsrv stop
testsrv is stopped [ OK ]
[root@centos6 init.d]#./testsrv restart ---相当于执行这个脚本,restart是这个脚本的参数
testsrv is stopped [ OK ]
testsrv is start ... [ OK ]
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv ---此时这个服务脚本还
不能被chkconfig命令控制,因为还没有在/etc/rc.d/rc*.d这个目录下创
建软链接,因为chkconfig命令是修改/etc/rc.d/rc*.d下的软链接文件,
把它变成以S或K打头,要想使其受到chkconfig控制,需要在脚本中加
上一行,如下图
service testsrv does not support chkconfig
注意:#description:在centos5上必须要加这条。35如果写成-,表示所有模式下开机都是off的。
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv ---发现还不在这个列表中
service testsrv supports chkconfig, but is not referenced in any runlevel (run 'chkconfig --add testsrv')
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --add testsrv ---把这个服务加到列表中
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv ---发现已经在列表中,并且 3和5运行模式下这个服务是自动开启的
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
[root@centos6 init.d]#ls /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S* ---看这个目录下也可以看到这个服务变成以S打头的了,并且是我们规定的S后面跟96数字
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S01sysstat /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S26udev-post
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S02lvm2-monitor /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S28autofs
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S05rdma /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S50kdump
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S08ip6tables /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S55sshd
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S10network /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S80postfix
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S11auditd /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S90crond
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S12rsyslog /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S95atd
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S15mdmonitor /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S96testsrv
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S25blk-availability /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S99local
/etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S25netfs
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig testsrv off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig testsrv on ---我们发现不指定运行模式
时,默认修改的是2.3.4.5运行模式
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list testsrv
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[root@centos6 subsys]#chkconfig --del testsrv ---相当于删除挼链接里面的以S打头或者以K打头的文件
[root@centos6 subsys]#chkconfig --list testsrv ---此时就不在列表里了
service testsrv supports chkconfig, but is not referenced in any runlevel (run 'chkconfig --add testsrv')
[root@centos6 subsys]#chkconfig --add testsrv ---加回来又在列表里了
[root@centos6 subsys]#chkconfig --list testsrv
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list nfs ---我们发现nfs服务默认的情
况下所有的模式下都是关闭的,并不只是/etc/inittab文件中说的只有2
模式下才是关闭的
nfs 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list network ---网络服务默认1运行模
式下开机是不启动的,但也可以通过chkconfig --level 1 network on 命
令将其设定为开机自动启动
network 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
总结:这样这个脚本就变成服务脚本,就可以用service和chkconfig命令来管理这个服务了。通过以上可以看出,所有的服务开机启动和不启动不是固定的,可以通过chkconfig命令来修改开机在哪个模式下是否启动和关闭。
9、xinetd管理的服务
xinetd用于管理非独立服务,相当于一个代理人,如果有人访问非独立服务,就激活非独立服务。非独立服务不能独立运行,要依赖于xinetd服务,对于访问量不多的服务,如果都设成独立服务,比较浪费,可以设置非独立服务,让xinetd服务来监管这些服务。xinetd服务是个独立的服务,并且在开机时3.4.5模式是开启的
[root@station1 ~]# chkconfig --list
NetworkManager 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
acpid 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
anacron 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
apmd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
atd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:off 6:off
xinetd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
xinetd based services: ---这些就是非独立服务
chargen-dgram: off
chargen-stream: off
daytime-dgram: off
daytime-stream: off
discard-dgram: off
discard-stream: off
echo-dgram: off
[root@centos6 init.d]#yum install telnet-server ---在centos6上安装一
个非独立服务 telnet-server,安装的时候会把xinetd服务也一起安装
了,因为它会依赖于xinetd服务
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list
saslauthd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
sshd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
sysstat 0:off 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
testsrv 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
udev-post 0:off 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
xinetd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
xinetd based services:
chargen-dgram: off
chargen-stream: off
daytime-dgram: off
daytime-stream: off
discard-dgram: off
discard-stream: off
echo-dgram: off
echo-stream: off
tcpmux-server: off
telnet: off ---目前这个非独立服务处于off状态,表示它不支持xinetd服务的唤醒,
time-dgram: off
time-stream: off
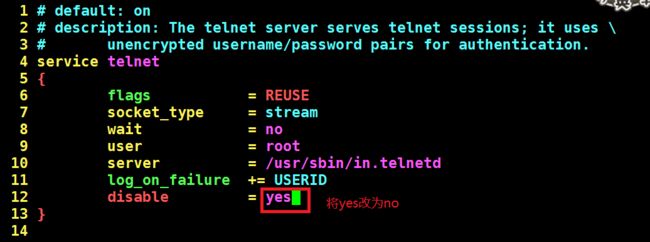
要想将其唤醒,需要修改 /etc/xinetd.d/telnet 文件
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list telnet ---发现这个服务被唤醒
telnet on
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig telnet off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list telnet
telnet off
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig telnet on ---用这个命令也可以唤醒非
独立服务,相当于修改上图的配置文件中的yes和no
[root@centos6 init.d]#chkconfig --list telnet
telnet on
[root@centos6 init.d]#service xinetd start ---启动xinetd服务,这个服
务又被称为超级守护服务,注意,一旦非独立服务的状态发生更改,都
要重启xinetd服务。
Starting xinetd: [ OK ]
[root@centos6 init.d]#ss -ntlp
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* users:(("sshd",1645,4))
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:(("sshd",1645,3))
LISTEN 0 64 :::23 :::* users:(("xinetd",3359,5))
我们发现xinetd服务在帮我们监听telnet服务,telnet服务开启的端口是
tcp下的23端口
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* users:(("master",1724,13))
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* users:(("master",1724,12))
[root@redhat7 script]#telnet 172.18.21.6 ---我们用centos7当客户端去连接centos6
[root@centos6 init.d]#ss -ntp ---发现处于连接状态的是telnet服务,表
示xinetd服务只是帮你去代理监听,真正有人访问的时候还是要自己上
场
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
ESTAB 24 0 172.18.21.6:23 172.18.21.7:38616 users:(("in.telnetd",3409,0),("in.telnetd",3409,1),("in.telnetd",3409,2))
ESTAB 0 64 172.18.21.6:22 172.18.252.32:50807 users:(("sshd",1812,3))
非独立服务的配置文件有两个
[root@centos6 init.d]#cd /etc/xinetd.d/ ---一个是在这个目录下,这个服务有各自的配置文件
[root@centos6 xinetd.d]#ls
chargen-dgram daytime-stream echo-dgram telnet
chargen-stream discard-dgram echo-stream time-dgram
daytime-dgram discard-stream tcpmux-server time-stream
[root@centos6 xinetd.d]#vim /etc/xinetd.conf ---这个是总的配置文件,可以影响所有非独立文件
1 #
2 # This is the master xinetd configuration file. Settings in the
3 # default section will be inherited by all service configurations
4 # unless explicitly overridden in the service configuration. See
5 # xinetd.conf in the man pages for a more detailed explanation of
6 # these attributes.
7
8 defaults
9 {
10 # The next two items are intended to be a quick access place to
11 # temporarily enable or disable services.
12 #
13 # enabled =
14 # disabled =
15
16 # Define general logging characteristics.
17 log_type = SYSLOG daemon info
18 log_on_failure = HOST
19 log_on_success = PID HOST DURATION EXIT
20
21 # Define access restriction defaults
22 #
23 # no_access = ---表示限制谁访问,谁不能访问,比如增加个172.18.21.7,表示拒绝这个机器访问所有的非独立服务
24 # only_from = ----表示只允许谁访问,这两个相当于一个黑名单,一个白名单
25 # max_load = 0
26 cps = 50 10
9、最后启动一个服务S99local
[root@centos6 rc3.d]#ll S99local
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 Aug 15 20:21 S99local -> ../rc.local
这个服务并没有指向/etc/rc.d/init.d这个目录下的服务脚本文件
注意:正常级别下,最后启动一个服务S99local没有链接至/etc/rc.d/init.d一个服务脚本,而是指向了/etc/rc.d/rc.local脚本,不便或不需写为服务脚本放置于/etc/rc.d/init.d/目录,且又想开机时自动运行的命令,可直接放置于/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件中,写到这个文件中的命令,在2.3.4.5运行模式下都会开机自动启动,被称为开机启动脚本。
•/etc/rc.d/rc.local在前面的服务脚本运行后执行。
•可以根据情况,进行自定义修改
10、启动过程总结
总结:/sbin/init--> (/etc/inittab) --> 设置默认运行级别--> 运行系统初始脚本、完成系统初始化--> (关闭对应下需要关闭的服务)启动需要启动服务--> 设置登录终端