2.1 数据结构之 队列 (C语言版)
编程总结
在刷题之前需要反复练习的编程技巧,尤其是手写各类数据结构实现,它们好比就是全真教的上乘武功
顺序为自右往左.

/-------------------------------------------分割线--------------------------------------/
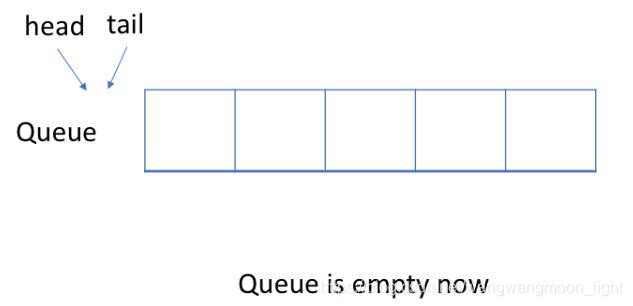
队头统一叫: head.
队尾统一叫: tail.
一. 循环队列的实现
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
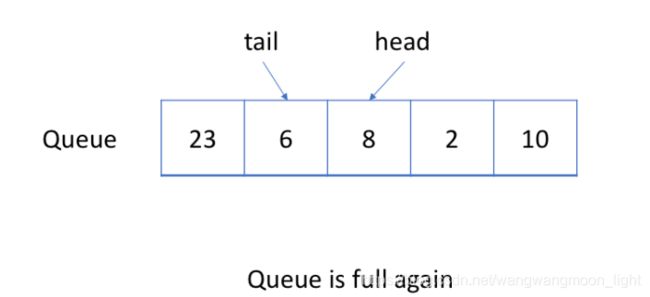
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
- 判断队列是否为空的条件:
/* 检查循环队列是否为空 */
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
return (obj->head == obj->tail);
}
手法1:检查循环队列是否为空,只看 head == tail. 如下特殊情况下,检查队列为空,也是看 head == tail.

/* 检查循环队列是否已满 */
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
return ((obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize == obj->head);
}
通常判断队列是否满,直接判断
(obj->tail + 1) == obj->head 即可。
手法2:但是循环队列,队列一直进,最后head为0,tail+1指向队列最后一个元素时;obj->tail + 1== obj->MaxSize. 此时也是队列满.
所以需要以下条件来判断:
((obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize == obj->head);
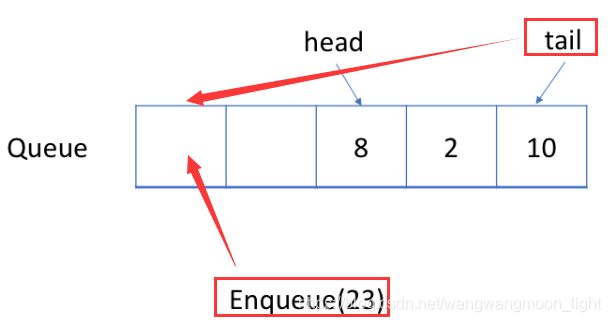
- 进队列的条件:

进队列,队尾动,队尾插入:
obj->base[obj->tail] = value;
如果tail到了队尾要处理下,循环队列到队首.
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
/* 在循环队列中插入元素, 如果操作成功, 则返回true */
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue *obj, int value) {
// 插入之前首先判断队列是否满
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->base[obj->tail] = value;
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
return true;
}
/* 从循环队列中删除元素。如果操作成功,则返回true */
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue *obj) {
// 删除之前先判断队列是否为空
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->head = (obj->head + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
return true;
}
- 获取队首尾元素:
手法1:队尾元素为 obj->base[obj->tail - 1]. 但有个特殊情况:tail为0时,tail-1小于0. tail为0时,其队尾元素为队列的最后一个元素 obj->base[obj->Maxsize-1].
/*从队列中获取 Front 项。*/
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->head];
}
/*从队列中获取最后一项。*/
int myCircularQueueTail(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
int i = (obj->tail - 1 + obj->MaxSize) % obj->MaxSize; // obj->tail -1 可能为0
return obj->base[i];
}
- 释放队列:
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue *obj) {
if (obj->base) {
free(obj->base);
}
obj->base = NULL; // 先释放指针,并赋值NULL
obj->front = 0;
obj->rear = 0;
free(obj);
}
/----------------队列实现完整代码----------------/
typedef struct {
int *base; // 开始地址
int head;
int tail;
int MaxSize;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue *obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue *obj);
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue *obj = (MyCircularQueue *)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->base = (int *)malloc((k + 1) * sizeof(int));
if (obj->base == NULL) {
return false;
}
obj->head = 0;
obj->tail = 0;
obj->MaxSize = k + 1; // 需要维护一个 size+1 的队列.
return obj;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. 插入元素,成功返回true*/
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue *obj, int value) {
// 插入之前首先判断队列是否满
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->base[obj->tail] = value; // 先入队
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize; // tail再移动,队尾元素为tail-1.
return true;
}
/* Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue *obj) {
// 删除之前先判断队列是否为空
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->head = (obj->head + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
return true;
}
/* Get the front item from the queue. */
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->head];
}
/* Get the last item from the queue. */
int myCircularQueueTail(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
int i = (obj->tail - 1 + obj->MaxSize) % obj->MaxSize; // 队尾元素为 obj->base[obj->tail - 1].
// 但有个特殊情况:tail为0时,tail-1小于0.
// tail为0时,其队尾元素为队列的最后一个元素 obj->base[obj->Maxsize-1].
return obj->base[i];
}
/* Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
return (obj->head == obj->tail);
}
/* Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue *obj)
{
return ((obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize == obj->head);
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue *obj) {
if (obj->base) {
free(obj->base);
}
obj->base = NULL; // 先释放指针,并赋值NULL
obj->head = 0;
obj->tail = 0;
free(obj);
}
int main(void)
{
MyCircularQueue *obj = myCircularQueueCreate(3);
int val = 1;
int index = 0;
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 1);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 2);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 3);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 4);
val = myCircularQueueRear(obj);
myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 4);
myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 24);
myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, 25);
val = myCircularQueueRear(obj);
myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
return 0;
}
二. 队列的实现
#define MAX_NUN 10000
typedef struct {
int tail;
int head;
int size; // 计算队列元素个数
int *base;
} RecentCounter;
bool QueueIsEmpty(RecentCounter *obj)
{
return (obj->head == obj->tail);
}
bool QueueIsFull(RecentCounter *obj)
{
return ((obj->tail + 1) == obj->head);
}
bool QueueEnQueue(RecentCounter *obj, int value) {
if (QueueIsFull(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->base[obj->tail] = value; // 先入队
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1); // tail再移动,队尾元素为tail-1.
obj->size++;
return true;
}
int QueueFront(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->head];
}
int QueueTail(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->tail - 1];
}
bool QueueDeQueue(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->head = (obj->head + 1);
obj->size--;
return true;
}
RecentCounter *QueueCreate(void)
{
RecentCounter *obj = (RecentCounter *)malloc(sizeof(RecentCounter));
obj->base = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(MAX_NUN+1));
obj->tail = 0;
obj->head = 0;
obj->size = 0;
if (obj->base == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
memset(obj->base, 0, sizeof(int)*(MAX_NUN+1));
return obj;
}
void QueueFree(RecentCounter* obj)
{
free(obj->base);
obj->base = NULL;
free(obj);
obj = NULL;
}
346. 数据流中的移动平均值
typedef struct {
int *base; // 开始地址
int head;
int tail;
int len; // 需要计算的len长度
int MaxSize; // 队列长度
} MovingAverage;
/* Initialize your data structure here. */
MovingAverage *movingAverageCreate(int size)
{
MovingAverage *obj = (MovingAverage *)malloc(sizeof(MovingAverage));
obj->base = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(size+ 1));
memset(obj->base, 0, sizeof(int)*(size+1));
obj->head = 0;
obj->tail = 0;
obj->MaxSize = size + 1;
obj->len = 0;
return obj;
}
bool movingAverageEmpty(MovingAverage *obj)
{
return (obj->head == obj->tail);
}
bool movingAverageFull(MovingAverage *obj)
{
return (((obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize) == obj->head);
}
// 进队列
bool movingAveragePush(MovingAverage *obj, int num)
{
if (movingAverageFull(obj) == 1) {
return false;
}
// 赋值元素进来
obj->base[obj->tail] = num;
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
obj->len++;
return true;
}
// 出队列
bool movingAveragePop(MovingAverage *obj, int num)
{
if (movingAverageEmpty(obj) == 1) {
return false;
}
obj->head = (obj->head + 1) % obj->MaxSize;
obj->len--;
return true;
}
double movingAverageNext(MovingAverage *obj, int val)
{
double res;
long result = 0;
// 利用循环队列来计算
// 需要计算的 len 超过队列长度时,队头出队列 head前移.
if (obj->len >= obj->MaxSize - 1) {
movingAveragePop(obj, val);
}
movingAveragePush(obj, val);
for (int i = 0; i < obj->len; i++) {
result += obj->base[(obj->head + i) % obj->MaxSize];
}
res = (double) result / (double)obj->len; // 除法的处理
return res;
}
void movingAverageFree(MovingAverage* obj)
{
if (obj->base) {
free(obj->base);
}
obj->base = NULL;
obj->head = 0;
obj->tail = 0;
obj->MaxSize = 0;
obj->len = 0;
free(obj);
obj = NULL;
return ;
}
933. 最近的请求次数
#define MAX_NUN 10000
typedef struct {
int tail;
int head;
int size; // 计算队列元素个数
int *base;
} RecentCounter;
bool QueueIsEmpty(RecentCounter *obj)
{
return (obj->head == obj->tail);
}
bool QueueIsFull(RecentCounter *obj)
{
return ((obj->tail + 1) == obj->head);
}
bool QueueEnQueue(RecentCounter *obj, int value) {
if (QueueIsFull(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->base[obj->tail] = value; // 先入队
obj->tail = (obj->tail + 1); // tail再移动,队尾元素为tail-1.
obj->size++;
return true;
}
int QueueFront(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->head];
}
int QueueTail(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return -1;
}
return obj->base[obj->tail - 1];
}
bool QueueDeQueue(RecentCounter *obj)
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(obj)) {
return false;
}
obj->head = (obj->head + 1);
obj->size--;
return true;
}
RecentCounter *recentCounterCreate(void)
{
RecentCounter *obj = (RecentCounter *)malloc(sizeof(RecentCounter));
obj->base = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(MAX_NUN+1));
obj->tail = 0;
obj->head = 0;
obj->size = 0;
if (obj->base == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
memset(obj->base, 0, sizeof(int)*(MAX_NUN+1));
return obj;
}
int recentCounterPing(RecentCounter *obj, int t)
{
int tailA = 0;
int tailB = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int res = 0;
// 队列满
if (QueueIsFull(obj) == 1) {
return false;
}
// 1. 元素先入队
QueueEnQueue(obj, t);
// 2. 取出队尾元素
while (obj->base[obj->head] < (t - 3000)) {
// 由于队列是单调递增的,所以一旦小于右值,后续也将小于该值,可以出队列.
QueueDeQueue(obj);
}
res = obj->tail - obj->head;
return res;
}
void recentCounterFree(RecentCounter* obj)
{
free(obj->base);
obj->base = NULL;
free(obj);
obj = NULL;
}