2.2 数据结构之 队列与BFS (C语言版)
编程总结
在刷题之前需要反复练习的编程技巧,尤其是手写各类数据结构实现,它们好比就是全真教的上乘武功。
本学习来自 leetcode,整理提炼.
https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/queue-stack/kyozi/
广度优先搜索(BFS)是一种遍历或搜索数据结构(如树或图)的算法。
如前所述,我们可以使用 BFS 在树中执行层序遍历。
我们也可以使用 BFS 遍历图。例如,我们可以使用 BFS 找到从起始结点到目标结点的路径,特别是最短路径。
我们可以在更抽象的情景中使用 BFS 遍历所有可能的状态。在这种情况下,我们可以把状态看作是图中的结点,而以合法的过渡路径作为图中的边。
1. 解释队列和BFS的关系.
广度优先搜索(BFS)的一个常见应用是找出从根结点到目标结点的最短路径。
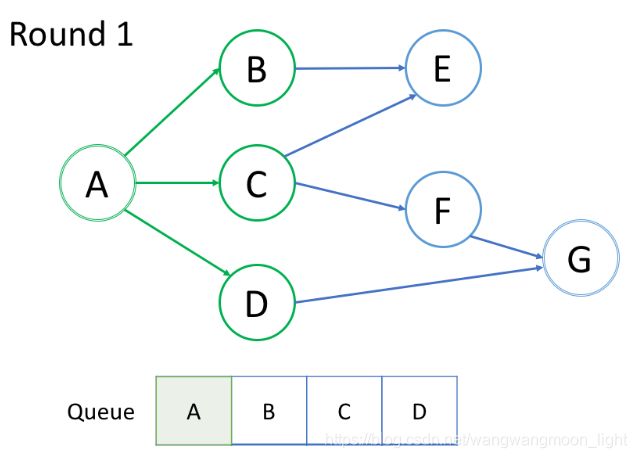
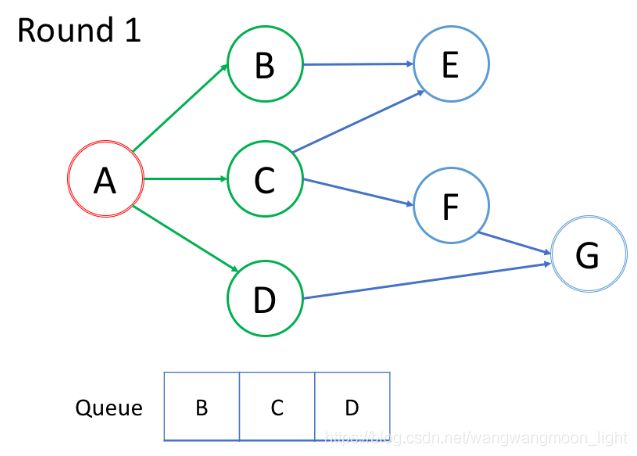
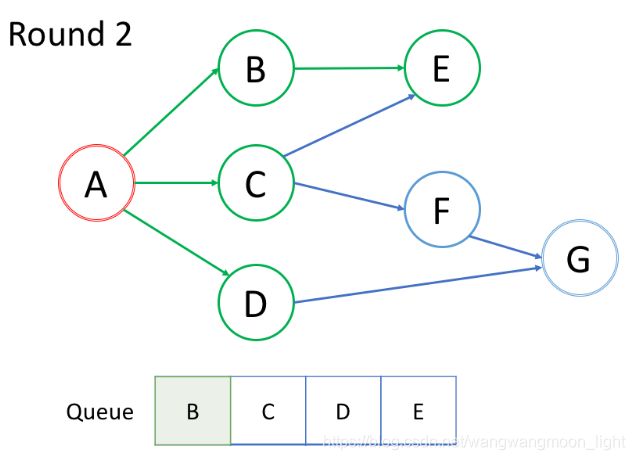
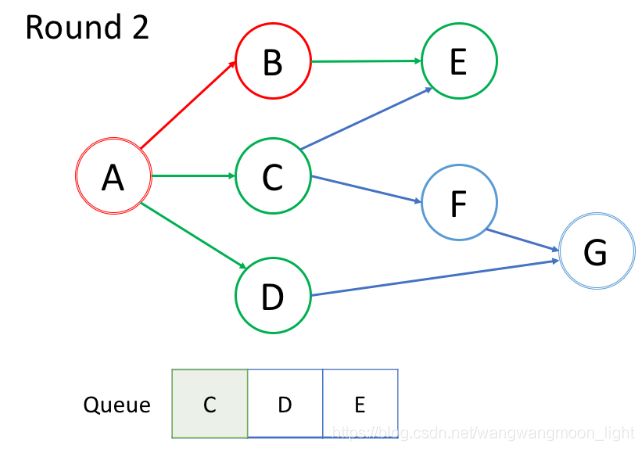
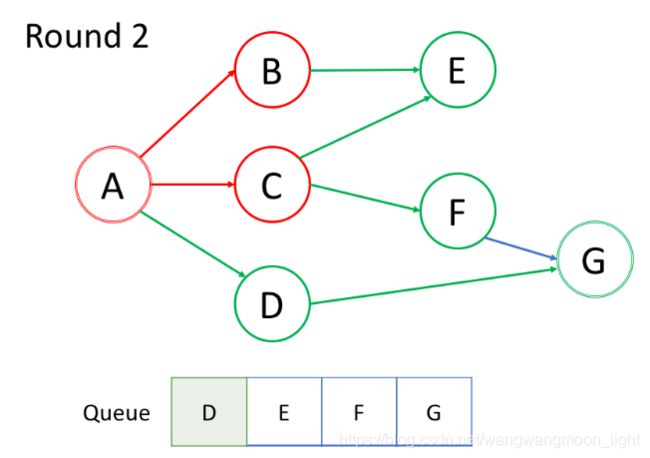
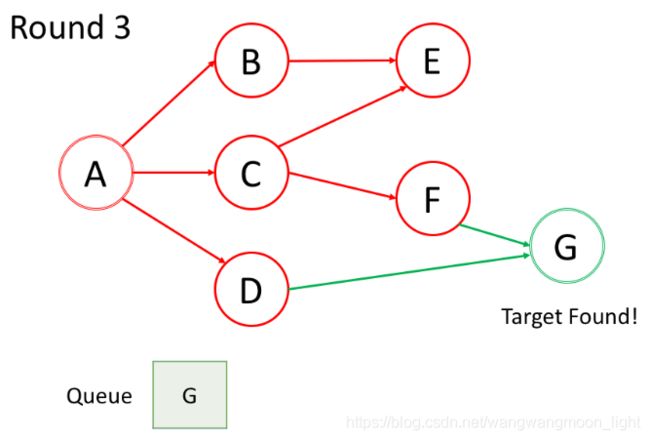
这里我们提供一个示例来说明如何使用 BFS 来找出根结点 A 和目标结点 G 之间的最短路径。
- 结点的处理顺序是什么?
在第一轮中,我们处理根结点。在第二轮中,我们处理根结点旁边的结点;在第三轮中,我们处理距根结点两步的结点;等等等等。
与树的层序遍历类似,越是接近根结点的结点将越早地遍历。
如果在第 k 轮中将结点 X 添加到队列中,则根结点与 X 之间的最短路径的长度恰好是 k。也就是说,第一次找到目标结点时,你已经处于最短路径中。
- 队列的入队和出队顺序是什么?
如上面的动画所示,我们首先将根结点排入队列。然后在每一轮中,我们逐个处理已经在队列中的结点,并将所有邻居添加到队列中。值得注意的是,新添加的节点不会立即遍历,而是在下一轮中处理。
结点的处理顺序与它们添加到队列的顺序是完全相同的顺序,即先进先出(FIFO)。这就是我们在 BFS 中使用队列的原因。
广度优先搜索 - 模板
之前,我们已经介绍了使用 BFS 的两个主要方案:遍历或找出最短路径。通常,这发生在树或图中。正如我们在章节描述中提到的,BFS 也可以用于更抽象的场景中。在本文中,我们将为你提供一个模板。然后,我们在本文后提供一些习题供你练习。在特定问题中执行 BFS 之前确定结点和边缘非常重要。通常,结点将是实际结点或是状态,而边缘将是实际边缘或可能的转换。
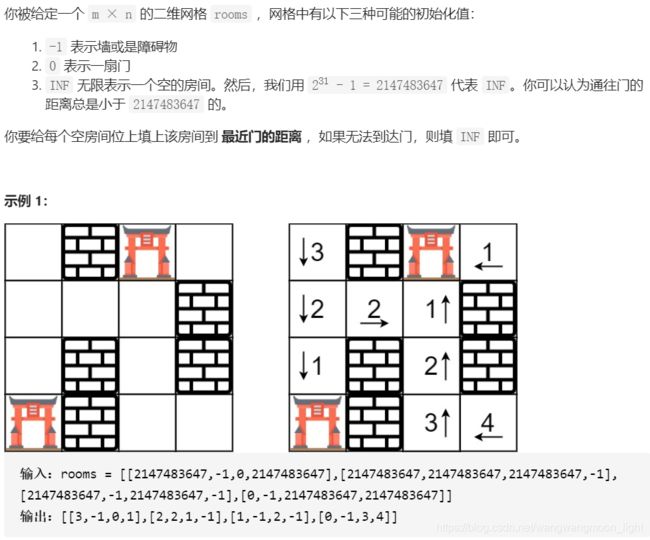
286. 墙与门
// 反向思维,从门开始找
// 反向思维,从门开始找
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
int step;
} Node;
void wallsAndGates(int **rooms, int roomsSize, int *roomsColSize)
{
if ((roomsSize == 0) || (*roomsColSize == 0)) {
return;
}
int row = roomsSize;
int col = roomsColSize[0];
int step[4][2] = {
{
1,0},{
-1,0},{
0,1},{
0,-1} }; // 下上右左
Node *queue = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node) * row * col);
int head = 0;
int tail = 0;
int i, j;
// 找门,门节点都入队列.
for (i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (rooms[i][j] == 0) {
queue[tail].x = i;
queue[tail].y = j;
queue[tail++].step = 0;
}
}
}
// 以门为起点开始BFS,利用该门节点遍历所有“岛”节点(这里借助了第200题岛的概念)
// 循环迭代直到队列为空
while (tail != head) {
int xx = queue[head].x;
int yy = queue[head].y;
int curStep = queue[head++].step; // 门节点出队列
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xNext = xx + step[i][0];
int yNext = yy + step[i][1];
if ((xNext >= 0) && (xNext < row) && (yNext >= 0) && (yNext < col) && (rooms[xNext][yNext] == INT_MAX)) {
rooms[xNext][yNext] = curStep + 1;
queue[tail].x = xNext;
queue[tail].y = yNext;
queue[tail++].step = curStep + 1; // 将当前出队的元素相邻元素入队
}
}
}
}
200. 岛屿数量

BFS : 思路是线性扫描整个二维网络,如果一个节点包含1,则以其为根节点启动BFS. 并将其设为2(FLAG_NUM)以标记访问过该节点,迭代地搜索队列中的每一个节点,直到队列为空 – 凡是能遍历到的都是一个岛上的. 继续此方法遍历二维网络其他点找其他岛,遍历完后就能找到所有“岛”的数量
#include 752.打开转盘锁
#include