导语:
CJMethodLog 对于Objective-C中的任意类、任意方法,均可实时根据用户的操作行为,监控还原对应的函数调用日志,而且能够自定义记录当前函数的参数类型、返回类型、执行时间……
CJMethodLog
上一篇介绍了 Runtime 原理
CJMethodLog(一)Runtime原理:从监控还原APP运行的每一行代码说起
这里就来讲讲 CJMethodLog 的具体实现。
上图展示了CJMethodLog的文件结构,其中CJMethodLog.h CJMethodLog.m是核心部分
/**
* 初始化类名监听配置
* 注意!!!所有设置的hook类不能存在继承关系
*
* @param classNameList 需要hook的类名
* @param options 日志选项
* @param value 是否打印监听日志,(设置为YES,会输出方法监听的log信息,该值只在 DEBUG 环境有效)
*/
+ (void)forwardingClasses:(NSArray *)classNameList logOptions:(CJLogOptions)options logEnabled:(BOOL)value;
/**
* 获取日志文件
*
* @param finishBlock 获取日志文件回调block
*/
+ (void)syncLogData:(SyncDataBlock)finishBlock;
/**
* 删除日志数据
*/
+ (void)clearLogData;
CJMethodLog.h 暂时提供三个方法:初始化配置、获取日志文件、删除日志数据。
使用
在 main.m 文件中设置需要监听的类名配置,理论上任意时刻都可以重设监听配置,但不建议这么做!!因为每次重设监听配置都会修改监听类的方法链表(methodLists)中方法的IMP实现,随意修改可能会出现替换指定IMP的同时刚好调用了该IMP的实现,造成不可预知错误。另外在 main.m中初始化配置可以确保所有的hook类都生效,比如如果你hook的是 AppDelegate 类。
#import
#import "AppDelegate.h"
#import "CJMethodLog.h"
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
/*
* 利用消息转发,hook指定类的调用方法
*/
[CJMethodLog forwardingClasses:@[
@"AppDelegate",
@"TestViewController"
]
logOptions:CJLogDefault
logEnabled:NO];
return UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]));
}
}
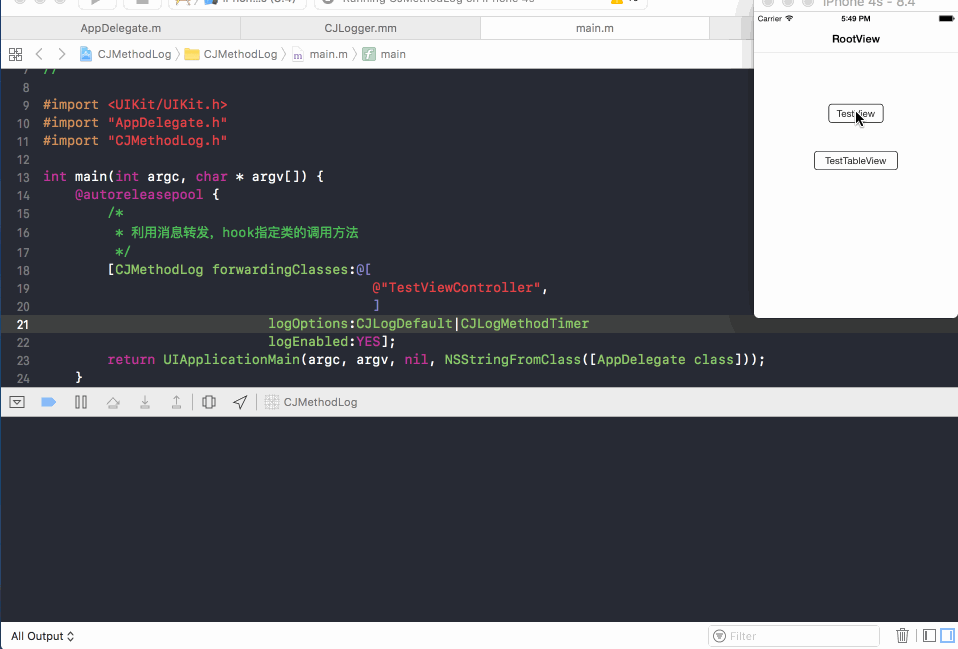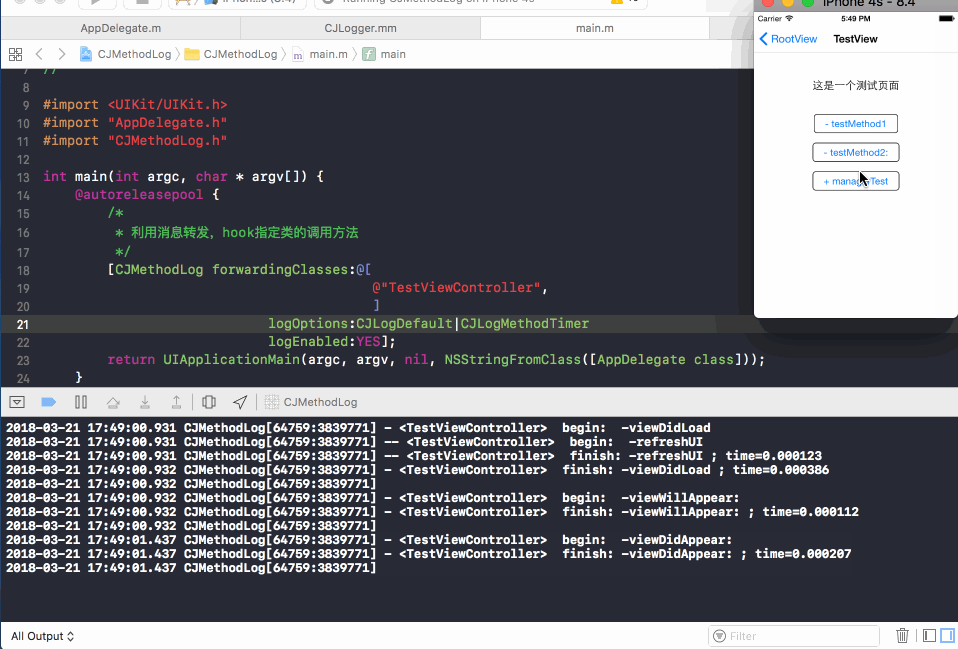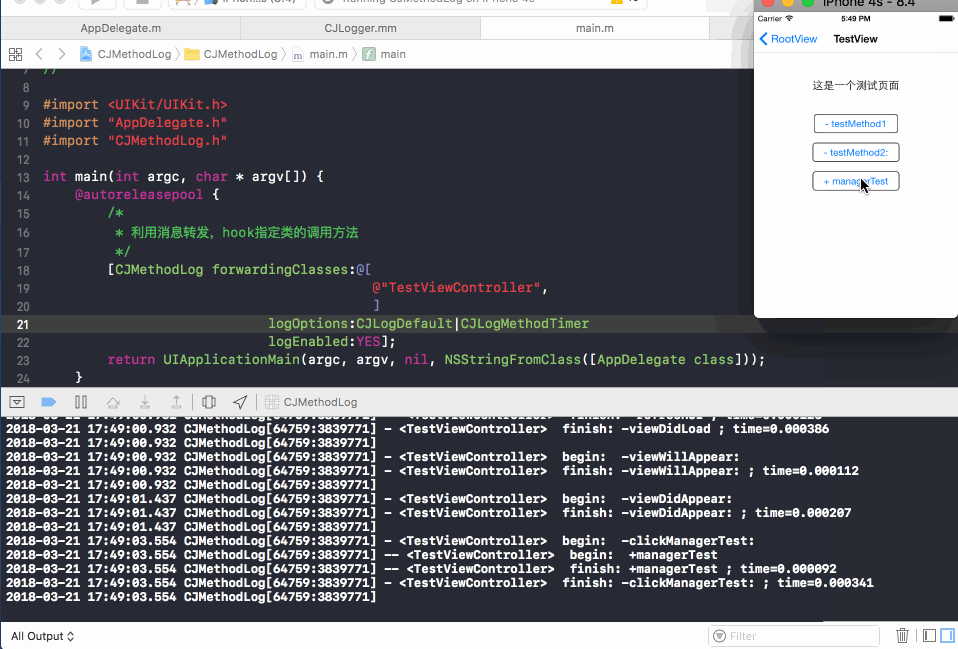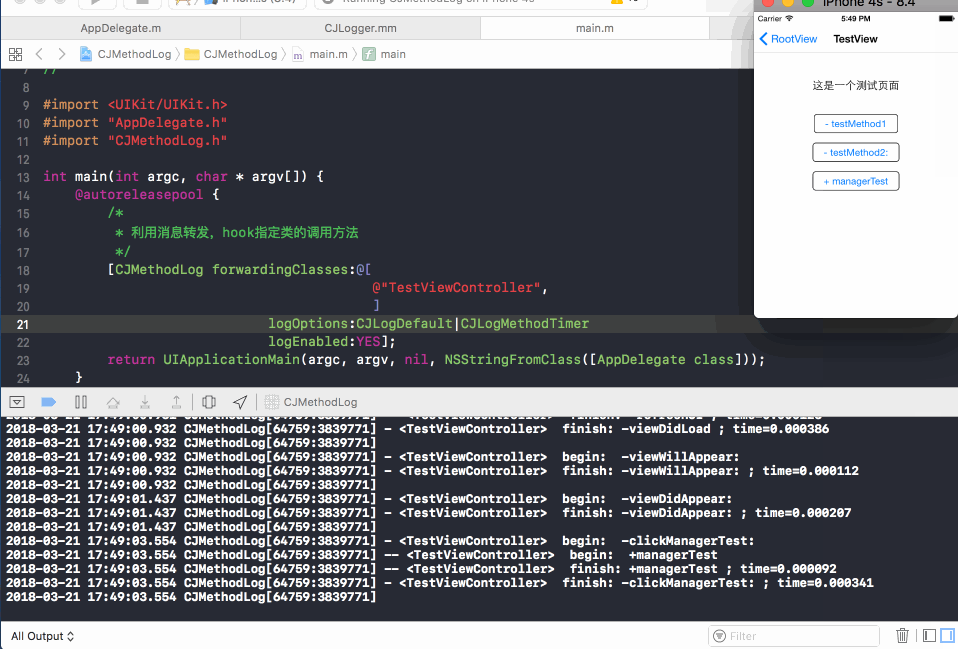
下图展示了hook TestViewController类之后的函数调用情况:
日志格式说明:
- begin: -clickManagerTest:
-- begin: +managerTest
-- finish: +managerTest ; time=0.000110
- finish: -clickManagerTest: ; time=0.000416
- 最开始的
-表示函数调用层级; -
-
begin:finish:分别表示函数执行起始阶段(只会在设置了CJLogMethodTimer选项的时候出现); -
-clickManagerTest:表示执行的是实例方法,+managerTest表示执行的是类方法; -
time=0.000110表示函数耗时 - 之后会补充函数参数以及返回结果说明
日志数据
获取日志数据使用+ (void)syncLogData:(SyncDataBlock)finishBlock ,你可以根据需要获取。比如这里在app启动的时候获取,判断当数据量大于10*1024的时候上传服务器并删除客户端数据。
- (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application {
[CJMethodLog syncLogData:^void(NSData *logData) {
NSLog(@"CJMethodLog: logData = %@",@([logData length]));
if ([logData length] > 10*1024) {
// TODO: 上传到服务器等自定义处理
// 删除日志数据
[CJMethodLog clearLogData];
}
}];
}
其他
CJLogger.h CJLogger.mm 是日志数据存储与获取的实现类,这是一个由OC和C++混编实现的类。
CJMethodLog+CJMessage.h 是处理一些通用设置的分类。
实现原理
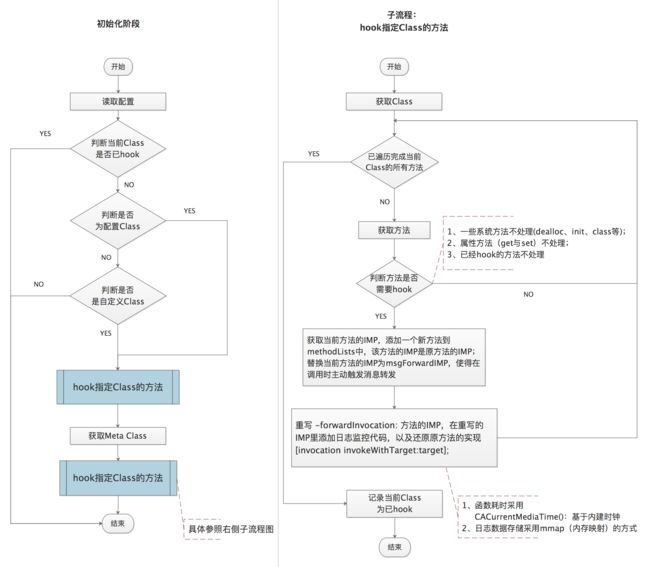
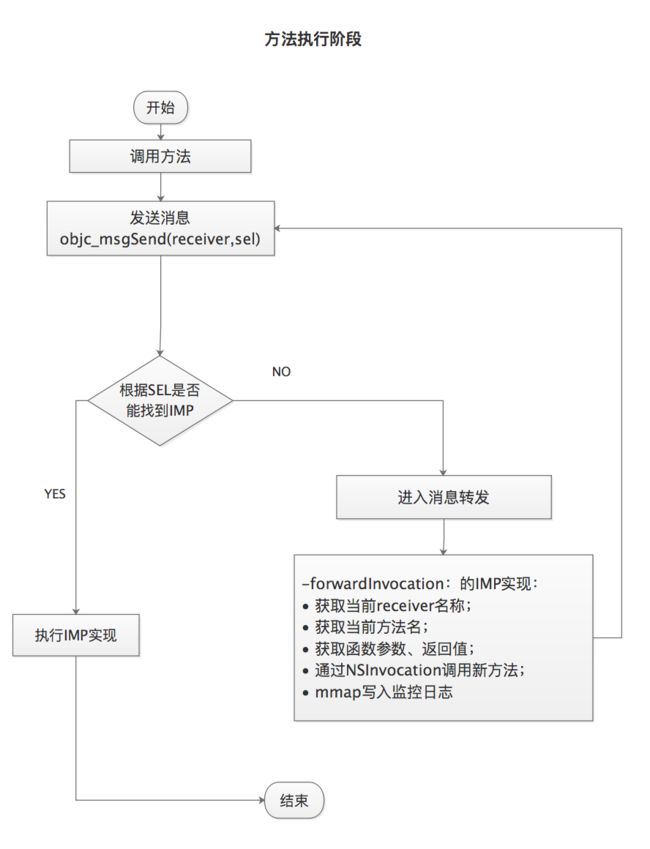
CJMethodLog 借助 Runtime 的消息转发机制,在调用方法的时候主动触发消息转发,然后在 - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation 方法中还原当前selector的实现,同时记录监控日志信息。下面是具体的实现流程图:
初始设置阶段:
方法执行阶段:
一些关键点
-
默认不 hook 系统类。CJMethodLog 理论上可以 hook 记录任意类、任意类的任意方法的执行日志,但实际上很少会这样做;我们关注的应该是基于具体的业务需求对应到代码层面是怎样的函数执行逻辑,而且这里的函数执行逻辑信息一般只需要到达app层级的逻辑实现就可以了,没必要更进一步去关注系统层级的实现。当然我也不介意你在初始阶段设置指定系统类或三方类,分析其内部的逻辑实现,然后做些坏坏的事。
附:设置不 hook 系统类的另一个原因是,hook 某个类,准确的做法应该要将该类的方法、它的父类的方法、父类的父类的方法……全都 hook 上,这样才能完整的还原出它在整个生命周期内的函数调用日志。那如果将父类方法也 hook,这时就需要一个出口了,不然会导致继承链的判断过长。我的做法是判断当父类为系统类时则停止。
其实 hook 父类方法部分还未实现,因为遇到了难题,具体后面会讲到判断是否为自定义类:
BOOL inMainBundle(Class hookClass) { NSBundle *currentBundle = [NSBundle bundleForClass:hookClass]; return [currentBundle.bundlePath hasPrefix:[NSBundle mainBundle].bundlePath]; } -
过滤属性的setter和getter方法。属性的setter和getter方法不hook,不然每调用一次
self.语法就产生一条监控日志,造成太多没必要的干扰信息。注意默认过滤规则:getter方法(属性名),setter方法(setXXX:),其他自定义的setter和getter方法无法过滤。+ (void)enumerateClassMethods:(Class)hookClass forwardMsg:(BOOL)forwardMsg logOptions:(CJLogOptions)options { NSString *hookClassName = NSStringFromClass(hookClass); // hookClass中已经被hook过的方法 NSArray *hookClassMethodList = [_hookClassMethodDic objectForKey:hookClassName]; NSMutableArray *methodList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:hookClassMethodList]; //属性的 setter 与 getter 方法不hook NSMutableArray *propertyMethodList = [NSMutableArray array]; unsigned int propertyCount = 0; objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(hookClass, &propertyCount); for (int i = 0; i < propertyCount; i++) { objc_property_t property = properties[i]; // getter 方法 NSString *propertyName = [[NSString alloc]initWithCString:property_getName(property) encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; [propertyMethodList addObject:propertyName]; // setter 方法 NSString *firstCharacter = [propertyName substringToIndex:1]; firstCharacter = [firstCharacter uppercaseString]; NSString *endCharacter = [propertyName substringFromIndex:1]; NSMutableString *propertySetName = [[NSMutableString alloc]initWithString:@"set"]; [propertySetName appendString:firstCharacter]; [propertySetName appendString:endCharacter]; [propertySetName appendString:@":"]; [propertyMethodList addObject:propertySetName]; } unsigned int outCount; Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(hookClass,&outCount); for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i ++) { // Method tempMethod = *(methods + i); Method tempMethod = methods[i]; SEL selector = method_getName(tempMethod); BOOL needHook = YES; for (NSString *selStr in propertyMethodList) { SEL propertySel = NSSelectorFromString(selStr); if (sel_isEqual(selector, propertySel)) { needHook = NO; break; } } if (needHook) { if (forwardMsg) { /* * 方案一:利用消息转发,hook forwardInvocation: 方法 */ BOOL canHook = enableHook(tempMethod); if (canHook) { forwardInvocationReplaceMethod(hookClass, selector, options); } }else{ // char *returnType = method_copyReturnType(tempMethod); // /* // * 方案二:hook每一个方法(未实现) // */ // cjlHookMethod(hookClass, selector, returnType); // free(returnType); } [methodList addObject:NSStringFromSelector(selector)]; } } free(methods); [_hookedClassList addObject:hookClassName]; [_hookClassMethodDic setObject:methodList forKey:hookClassName]; } -
一些系统方法不应该 hook。具体如下:
@[ /*UIViewController的:*/ @".cxx_destruct", @"dealloc", @"_isDeallocating", @"release", @"autorelease", @"retain", @"Retain", @"_tryRetain", @"copy", /*UIView的:*/ @"nsis_descriptionOfVariable:", /*NSObject的:*/ @"respondsToSelector:", @"class", @"allowsWeakReference", @"retainWeakReference", @"init", @"resolveInstanceMethod:", @"resolveClassMethod:", @"forwardingTargetForSelector:", @"methodSignatureForSelector:", @"forwardInvocation:", @"doesNotRecognizeSelector:", @"description", @"debugDescription", @"self", @"lockFocus", @"lockFocusIfCanDraw", @"lockFocusIfCanDraw" ]; CACurrentMediaTime() 。如果选择了日志选项
CJLogMethodTimer,那么在计算函数执行时间时采用CACurrentMediaTime()计算,CACurrentMediaTime()是基于内建时钟的,能够更精确更原子化地测量,并且不会因为外部时间变化而变化(例如时区变化、夏时制、秒突变等),可以最小化的减少性能损耗。mmap。日志数据采用
mmap内存映射的方式存储,具体请看CJLogger.mm中的相关实现。
引用自—— 认真分析mmap:是什么 为什么 怎么用
mmap是一种内存映射文件的方法,即将一个文件或者其它对象映射到进程的地址空间,实现文件磁盘地址和进程虚拟地址空间中一段虚拟地址的一一对映关系。实现这样的映射关系后,进程就可以采用指针的方式读写操作这一段内存,而系统会自动回写脏页面到对应的文件磁盘上,即完成了对文件的操作而不必再调用read,write等系统调用函数。相反,内核空间对这段区域的修改也直接反映用户空间,从而可以实现不同进程间的文件共享。
-
forwardInvocationReplaceMethod 这个方法是实现 CJMethodLog 的核心部分:
BOOL forwardInvocationReplaceMethod(Class cls, SEL originSelector, CJLogOptions options) { Method originMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, originSelector); if (originMethod == nil) { return NO; } const char *originTypes = method_getTypeEncoding(originMethod); IMP msgForwardIMP = _objc_msgForward; #if !defined(__arm64__) if (isStructType(originTypes)) { //Reference JSPatch: //In some cases that returns struct, we should use the '_stret' API: //http://sealiesoftware.com/blog/archive/2008/10/30/objc_explain_objc_msgSend_stret.html //NSMethodSignature knows the detail but has no API to return, we can only get the info from debugDescription. NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:originTypes]; if ([methodSignature.debugDescription rangeOfString:@"is special struct return? YES"].location != NSNotFound) { msgForwardIMP = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_stret; } } #endif IMP originIMP = method_getImplementation(originMethod); if (originIMP == nil || originIMP == msgForwardIMP) { return NO; } //添加一个新方法,该方法的IMP是原方法的IMP,并且在hook到的forwardInvocation里调用新方法 SEL newSelecotr = createNewSelector(originSelector); BOOL addSucess = class_addMethod(cls, newSelecotr, originIMP, originTypes); if (!addSucess) { NSString *str = NSStringFromSelector(newSelecotr); CJLNSLog(@"CJMethodLog: Class addMethod fail : %@,%@",cls,str); return NO; } //替换当前方法的IMP为msgForwardIMP,从而在调用时候触发消息转发 class_replaceMethod(cls, originSelector, msgForwardIMP, originTypes); Method forwardInvocationMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:)); _VIMP originMethod_IMP = (_VIMP)method_getImplementation(forwardInvocationMethod); method_setImplementation(forwardInvocationMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id target, NSInvocation *invocation){ SEL originSelector = invocation.selector; BOOL isInstance = isInstanceType(target); Class targetClass = isInstance?[target class]:object_getClass(target); if (class_respondsToSelector(targetClass, originSelector)) { _CJDeep ++; NSString *originSelectorStr = NSStringFromSelector(originSelector); NSMutableString *methodlog = [[NSMutableString alloc]initWithCapacity:3]; for (NSInteger deepLevel = 0; deepLevel <= _CJDeep; deepLevel ++) { [methodlog appendString:@"-"]; } [methodlog appendFormat:@" <%@> ",targetClass]; CFTimeInterval startTimeInterval = 0; BOOL beginAndEnd = NO; if ((options & CJLogMethodTimer) || (options & CJLogMethodArgs)) { [methodlog appendFormat:@" begin: "]; if (options & CJLogMethodTimer) { startTimeInterval = CACurrentMediaTime(); } beginAndEnd = YES; } if (isInstance) { [methodlog appendFormat:@" -%@",originSelectorStr]; }else{ [methodlog appendFormat:@" +%@",originSelectorStr]; } if (options & CJLogMethodArgs) { NSDictionary *methodArguments = CJMethodArguments(invocation); NSArray *argumentArray = methodArguments[_CJMethodArgsListKey]; NSMutableString *argStr = [[NSMutableString alloc]initWithCapacity:3]; for (NSInteger i = 0; i < argumentArray.count; i++) { id arg = argumentArray[i]; if (i == 0) { [argStr appendFormat:@" ; args=[ argIndex:%@ argValue:%@",@(i),[arg description]]; }else{ [argStr appendFormat:@", argIndex:%@ argValue:%@",@(i),[arg description]]; } } if (argumentArray.count > 0) { [argStr appendString:@" ]"]; } [methodlog appendString:argStr]; } if (_logEnable) { CJLNSLog(@"%@",methodlog); } [_logger flushAllocationStack:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@\n",methodlog]]; [invocation setSelector:createNewSelector(originSelector)]; [invocation setTarget:target]; [invocation invoke]; if (beginAndEnd) { [methodlog setString:[methodlog stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"begin: " withString:@"finish:"]]; if (options & CJLogMethodTimer) { CFTimeInterval endTimeInterval = CACurrentMediaTime(); [methodlog appendFormat:@" ; time=%f",(endTimeInterval-startTimeInterval)]; } if (options & CJLogMethodReturnValue) { id returnValue = getReturnValue(invocation); [methodlog appendFormat:@" ; return= %@",[returnValue description]]; } if (_logEnable) { CJLNSLog(@"%@",methodlog); } [_logger flushAllocationStack:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@\n",methodlog]]; } _CJDeep --; } //如果target本身已经实现了对无法执行的方法的消息转发(forwardInvocation:),则这里要还原其本来的实现 else { originMethod_IMP(target,@selector(forwardInvocation:),invocation); } if (_CJDeep == -1) { if (_logEnable) { CJLNSLog(@"\n"); } [_logger flushAllocationStack:@"\n"]; } })); return YES; }
首先判断SEL对应的Method是否存在
然后获取消息转发IMP (
msgForwardIMP),注意_objc_msgForward与_objc_msgForward_stret的判断判断当前方法的IMP(
originIMP)不为nil,并且不等于msgForwardIMP添加一个指定前缀(
"cjlMethod_")开头的新方法,该方法的IMP是原方法的IMP替换当前方法的IMP为
msgForwardIMP,从而在调用时候触发消息转发获取记录当前class的
@selector(forwardInvocation:)对应的IMP,然后重写其IMP实现,这里直接使用了imp_implementationWithBlock(id _Nonnull block)生成IMP-
调用方法,触发消息转发,进入
@selector(forwardInvocation:)对应的IMP内。
首先判断当前Class是否可执行原来方法,这里注意一下实例方法以及类方法的判断,如果是类方法,取的是object_getClass():SEL originSelector = invocation.selector; BOOL isInstance = isInstanceType(target); Class targetClass = isInstance?[target class]:object_getClass(target); if (class_respondsToSelector(targetClass, originSelector)) { //TODO:写入日志以及还原原方法的执行 } //如果target本身已经实现了对无法执行的方法的消息转发(forwardInvocation:),则这里要还原其本来的实现 else { originMethod_IMP(target,@selector(forwardInvocation:),invocation); }当判断到当前方法需要执行日志监听时,拼装日志信息(
_CJDeep记录了方法执行的层级关系),然后执行一次日志写入操作:[_logger flushAllocationStack:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@\n",methodlog]];再接着还原实际调用方法的实现:
[invocation setSelector:createNewSelector(originSelector)]; [invocation setTarget:target]; [invocation invoke];紧接着如果存在
CJLogMethodTimer选项,则计算当前函数执行时间,同时写入日志信息。
最后将_CJDeep- 1,从而完成本次hook方法的执行。
-
CJMethodLog 无法同时 hook super方法
是否还记得上篇文章讲到,Objective-C中执行方法,其实底层调用的是objc_msgSend(receiver,SEL);如果是super方法,会调用objc_msgSendSuper(objc_super,SEL),再往下会转换成objc_msgSend(objc_super->receiver, SEL),此时的receiver和 objc_super->receiver 表示的是同一个接收者。
比如下面例子:- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; } 底层对应的是 objc_msgSend(self,@selector(viewDidLoad)) objc_msgSend(objc_super->receiver, @selector(viewDidLoad))当CJMethodLog都hook了父子类的 viewDidLoad 方法后,调用会触发消息转发,最终由以下代码还原其实现
[invocation setSelector:createNewSelector(@selector(viewDidLoad))]; [invocation setTarget:target]; [invocation invoke];子类方法 target=self,父类方法 target=objc_super->receiver,其中self = objc_super->receiver,到此为止你是否发现了问题所在?问题就是这里的方法调用其实是一个死循环!!!伪代码如下:
objc_msgSend(receiver,@selector(viewDidLoad)) { objc_msgSend(receiver, @selector(viewDidLoad)); }要破解这一难题只能想办法区分父子类调用方法时候的不同上下文,可惜这一块我还没找到好的解决方案。
更多
- 解决
selfsuper上下文调用的问题 - 欢迎各位大神
starissue,帮忙解决难题
项目地址: CJMethodLog