随着现在研究的不断深入,越来越多的情况需要我们对多种数据的联合分析,其中在单细胞没有出来之前,普通转录组(bulk-seq)的测序结果是非常多的,也解决了我们很多的生物学问题,单细胞技术的出现,更高分辨率的同时,与普通转录组的联合分析也是现在分析的一个关注点。
在文章《Distinct and temporary-restricted epigenetic mechanisms regulate human αβ and γδ T cell development》中就提到了单细胞和bulk数据的联合我们,在这里,我们来深入解读一下联合的方法。(当然,这篇文章也做了单细胞ATAC与单细胞转录组的联合分析)
我们首先来看文章中对于联合分析的结果
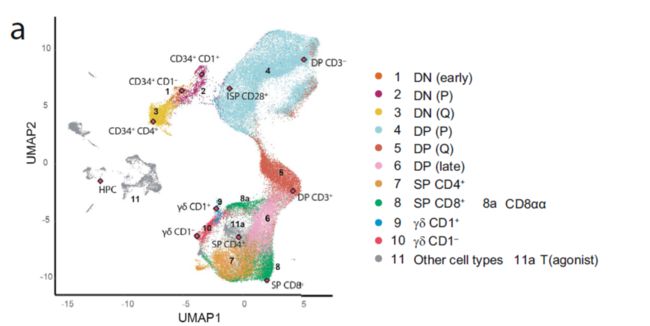
Integration of our bulk RNA-seq with single-cell RNA-seq data from pediatric thymus samples30 confirmed that our subsets reflect the continuum of human postnatal T cell development and revealed with high confidence that most thymocytes are represented by our bulk subsets。结果内容的这里提到了单细胞与普通转录组的联合分析,得到如下结果:
图例中的解释为:Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of the single cell RNAseq dataset available from with integration of our 11 bulk RNAseq subsets (red diamonds). DN: CD4 CD8 double negative; DP: CD4+ CD8+; P: proliferative; Q: quiescent; T(agonist): agonist selected T cells; DP (late): Positively selected DP T cells。从这个结果来看,从这个结果来看,实点代表一个普通转录组的数据,通过一定的计算方法映射到了单细胞数据的UMAP图上(单细胞数据也做了详细的定义划分)。
我们首先来看单细胞的数据来源。
单细胞数据的来源是文章《A cell atlas of human thymic development defines T cell repertoire formation》
这里我们不展开讨论,我们关注一下文章对于数据的处理,Cells with fewer than 2000 UMI counts and 500 detected genes were considered as empty droplets and removed from the dataset. Cells with more than 7000 detected genes were considered as potential doublets and removed from the dataset.Scanpy (version 1.3.4) python package was used to load the cell-gene count matrix and perform downstream analysis. Doublet detection, clustering, annotation, batch alignment, trajectory analysis, cell-cell interaction, and repertoire analysis is performed using the tools in Scanpy package complemented with some custom codes.Scanpy用于后续分析,scanpy1.3.4版本的时候没有多样本整合的能力,也就是说,作者采用的是cellramger aggr的方式整合得到矩阵,然后用scanpy做后续分析,批次矫正采用线性回归的方式。(这个地方我只是猜测,并不是十分的确定)。
再来看bulk的数据
bulk数据是不同发育阶段的前体细胞和T细胞(磁珠分选),如下图:
接下里就是bulk和单细胞数据的联合
bulk和单细胞数据的联合
第一步,Bulk thymic RNA-seq samples were downsampled 50 times ranging from 100% to 2.5% sequencing depth, using the downsampleMatrix from the DropletUtils library。bulk的数据处理采用的是“downsample”的方式,这是一个术语,这里就是不同的测序深度。
第二步,From the publicly available scRNA-seq data30,pediatric samples were retained after loading publicly available scRNA-seq data into R using Scanpy43 via Reticulate.单细胞数据就是文献来源。
第三步,Genes present in both the scRNA-seq and the bulk RNA-seq data were retained and both datasets were merged(merge数据)。
第四步,ed. Using Seurat each scRNA-seq donor or bulk RNA-seq run was processed separately during normalization, with highly variable gene selection, data scaling and PCA generation. Batch correction of the scRNA-seq data and bulk RNA-seq data was done separately using the FindIntegrationAnchors and IntegrateData functions.样本之间先单独预处理,然后scRNA数据与bulk的数据分开整合,specifying reference samples and implementing the reciprocal PCA method这个seurat方法大家可以多借鉴,值得一试。
第五步,联合,k.anchors was set to 15 for the bulk RNA-seq data. The scRNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq data were integrated using the FindTransferAnchors and TransferData functions with canonical correlation analysis.关于k.anchors等参数的功能我之前介绍过,可以看我的文章《单细胞数据整合分析之寻找最近邻(k.anchor、k.filter、k.score、MNN)》.这个地方有了label转换,After integration the data were scaled, PCA was performed and a UMAP was generated.
第六步,Using the integrated data, the single cells were classified according to their bulk RNA-seq counterparts, using the LogisticRegression function, specifying the liblinear solver, from the sklearn module in R via Reticulate.依据bulk的数据对单细胞进行数据划分(也就是定义),这里涉及到一些算法,python的模块sklearn,大家感兴趣多学习一下。
第七步,The non-T cell-lineage cells present in the dataset were used to specify cutoffs (mean + s.d.) for each bulk RNA-seq dataset, allowing filtering of less probable classifications.
通过这些过程,实现了单细胞与bulk的联合分析,方法值得大家借鉴,尤其是依据bulk对单细胞数据进行的定义。
请保持愤怒,让王多鱼倾家荡产,看完了,点赞呐~~~