Objective-C 语言尽可能将决策从编译时间、链接时间推迟到运行时。只要有可能,它就会动态地执行任务。这意味着 Objective-C 不仅需要编译器,还需要运行时系统(runtime system)执行编译的代码。Objective-C 的动态性就是由 runtime 来支撑和实现的。
借助 runtime 可以实现很多功能,如字典转模型(MJExtension),查看私有成员变量,替换方法实现(method swizzling),为分类增加属性(associated objects)等。JSPatch热更新也是利用了 runtime,以便实现动态添加、改变方法实现。
关于 Objective-C runtime 的内容有很多,这里将分两篇文章介绍。本篇文章涉及内容如下:
- Runtime 预览
- 对象和类
- 对象 object
- 类 Class
- 元类 meta class
- Method
- 消息发送
1. Runtime 预览
Runtime API 提供的接口基本都是 C 语言的,源码由C、C++、汇编语言编写。Runtime 库为 C 语言添加了动态功能,还添加了使面向对象(object-oriented programming,简称OOP)成为可能所需要的支持。
1.1 动态、静态语言 Dynamic vs Static Language
Objective-C 是一种动态语言(dynamic language),它尽可能将决策从编译时间、链接时间推迟到运行时。
这一点与静态语言(如 C 语言)不同。在 C 语言中,调用函数意味着跳转到内存特定位置,其在编译时已经决定。因此,与诸如 Objective-C 这样的动态语言相比,灵活性要差很多。
先看下面代码:
Engineer *engineer = [[Engineer alloc] initWithName:@"pro648"];
[engineer sayHi];
// compiler translates above line to:
objc_msgSend(engineer, @selector(sayHi));
有一个名称为Engineer的类,调用sayHi方法。sayHi方法的实现并不会立即执行,编译器会将其转换为 C 语言的函数调用。objc_msgSend()函数向engineer实例对象发送消息,Objective-C 对象可能无法处理该消息,当无法处理时,会进入动态方法解析(dynamic method resolution)、消息转发(message forwarding)阶段。
Objective-C 中的方法调用都是转成
objc_msgSend函数调用,给 receiver(方法调用者)发送一条消息(selector方法名)。
1.2 与 Runtime 交互
开发者在没有意识到的情况下已经在使用 runtime 了。从开始编写 iOS、macOS 程序起,我们就被告知需要继承自NSObject。这是因为许多麻烦的功能(如内存管理)都集成在NSObject中。只要使用NSObject的子类,就会自动获得这些基础功能。
第二种与 runtime 交互的情况是调用 runtime 函数。大多数时候,我们不需要使用 runtime 函数,但 runtime 有时可以帮我们解决一些棘手的问题。导入
2. 对象和类
在面向对象的程序中,类(class)是可扩展的代码模版,是逻辑和数据的抽象;对象(object)是 class 的特定实例。下面将介绍 Objective-C 中对象和类的表示方式。
2.1 对象 Object
在objc4源码中,object 定义如下:
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
public:
// ISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object
Class ISA(bool authenticated = false);
// rawISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object or a non pointer ISA
Class rawISA();
// getIsa() allows this to be a tagged pointer object
Class getIsa();
uintptr_t isaBits() const;
// initIsa() should be used to init the isa of new objects only.
// If this object already has an isa, use changeIsa() for correctness.
// initInstanceIsa(): objects with no custom RR/AWZ
// initClassIsa(): class objects
// initProtocolIsa(): protocol objects
// initIsa(): other objects
void initIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=false*/);
void initClassIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initProtocolIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor);
// 省略...
#if DEBUG
bool sidetable_present();
#endif
}
可以看到,Objective-C 中的对象本质上是结构体。
这篇文章使用objc4-818.2版本源码。
实例(instance)对象在内存中存储了以下信息:
- isa指针,指向类(class)对象。
- 成员变量的值,变量类型、名称信息保存在类对象中。
2.2 类 Class
Objective-C 是一个基于类的对象系统。每个 instance 对象都是某个类的实例,instance 对象的isa指针指向 class。
类对象存储信息如下:
- isa指针,指向元类(meta-class)。
- superclass指针。
- 类的属性(@property)、实例方法信息。
- 类的协议信息(protocol)、成员变量信息(描述性信息,如成员变量名称、类型等)。
Class是指向objc_class结构体的指针。
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
objc_class结构体如下:
struct objc_class : objc_object {
objc_class(const objc_class&) = delete;
objc_class(objc_class&&) = delete;
void operator=(const objc_class&) = delete;
void operator=(objc_class&&) = delete;
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
Class getSuperclass() const {
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
# if ISA_SIGNING_AUTH_MODE == ISA_SIGNING_AUTH
if (superclass == Nil)
return Nil;
#if SUPERCLASS_SIGNING_TREAT_UNSIGNED_AS_NIL
void *stripped = ptrauth_strip((void *)superclass, ISA_SIGNING_KEY);
if ((void *)superclass == stripped) {
void *resigned = ptrauth_sign_unauthenticated(stripped, ISA_SIGNING_KEY, ptrauth_blend_discriminator(&superclass, ISA_SIGNING_DISCRIMINATOR_CLASS_SUPERCLASS));
if ((void *)superclass != resigned)
return Nil;
}
#endif
void *result = ptrauth_auth_data((void *)superclass, ISA_SIGNING_KEY, ptrauth_blend_discriminator(&superclass, ISA_SIGNING_DISCRIMINATOR_CLASS_SUPERCLASS));
return (Class)result;
# else
return (Class)ptrauth_strip((void *)superclass, ISA_SIGNING_KEY);
# endif
#else
return superclass;
#endif
}
void setSuperclass(Class newSuperclass) {
#if ISA_SIGNING_SIGN_MODE == ISA_SIGNING_SIGN_ALL
superclass = (Class)ptrauth_sign_unauthenticated((void *)newSuperclass, ISA_SIGNING_KEY, ptrauth_blend_discriminator(&superclass, ISA_SIGNING_DISCRIMINATOR_CLASS_SUPERCLASS));
#else
superclass = newSuperclass;
#endif
}
class_rw_t *data() const {
return bits.data();
}
// 省略部分...
unsigned classArrayIndex() {
return bits.classArrayIndex();
}
}
2.2.1 isa
objc_class继承自objc_object。因此,objc_class结构体第一个成员也是isa_t,这表明 Objective-C 中类本质上也是一个对象。
这意味着可以将消息发送给类对象,就像发送给实例对象一样。当给实例对象发送消息时,runtime 会查询其类对象是否可以响应该消息。objc_class结构体中的class_data_bits_t bits;包含了方法列表,这使添加、移除、交换方法得以实现。
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
isa_t共用体结构如下:
union isa_t {
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
uintptr_t bits;
private:
// Accessing the class requires custom ptrauth operations, so
// force clients to go through setClass/getClass by making this
// private.
Class cls;
public:
#if defined(ISA_BITFIELD)
struct {
ISA_BITFIELD; // defined in isa.h
};
bool isDeallocating() {
return extra_rc == 0 && has_sidetable_rc == 0;
}
void setDeallocating() {
extra_rc = 0;
has_sidetable_rc = 0;
}
#endif
void setClass(Class cls, objc_object *obj);
Class getClass(bool authenticated);
Class getDecodedClass(bool authenticated);
};
在arm64架构之前,isa就是普通指针,直接存储类对象、元类对象地址值。arm64架构开始,对isa进行了优化,变成了共用体(union)结构,使用位域来存储更多的信息。
2.2.2 superclass
superclass指针指向父类。如果它已经是最顶级的类(如NSObject、NSProxy),则superclass指针为NULL。
在消息传递时,如果在当前类找不到该方法,会根据superclass指针进入父类查找。
2.2.3 cache_t
向实例对象发送消息时,runtime 根据isa指针找到类对象,然后在类对象class_rw_t中查找;如果找不到方法,继续在父类class_rw_t中查找,直到找到方法或查找失败。如果每次都需要进行这样的查找,会非常耗时。
为了提高查找性能,runtime 使用哈希表存储了当前类已经查找过的方法。使用selector & mask做为 key,将selector存储到buckets中。不同方法 & mask 后可能产生相同 key。如果遇到已经被占用,其会减一再次尝试,直到循环到初次计算出的位置。取方法时,取出后会先比较selector。如果不同,key减一再次比较。哈希表用空间换时间,牺牲内存提高效率。
最终,发送消息时,类会先查找cache_t是否存在该方法。如果存在,则直接调用;如果不存在,首先进入objc_method_list查找;如果找到,调用该方法并添加到当前类的cache_t;如果找不到,则根据super_class指针,进入父类查找,这里也会先在cache_t查找。如果找到,调用该方法并添加到消息接受者类的cache_t(不是父类的cache_t)。依此类推,直到找到该方法,或根类也找不到,进入方法动态解析阶段。
2.3 元类 meta class
Objective-C 的 class 也是一个对象,有isa指针和其他数据,可以响应 selector。当调用[NSObject alloc]类似的类方法时,本质上是向类对象发送消息。
类是元类(metaclass)的实例。metaclass 是类对象的描述,就像类是对实例对象的描述。类对象的isa指针指向元类。metaclass 的 method list 包含类方法,当向类对象发送消息时,objc_msgSend()根据 metaclass(和其父类) 的 method list 查找方法实现。
类对象、元类对象都是 Class 类型。因此,内存结构是一样的,但用途不同。meta class 在内存中存储信息如下:
- isa 指针,所有元类的isa都指向
NSObject基类的元类。 - superclass指针。
- 类方法信息。
类对象描述实例对象的行为,元类描述类对象的行为。
将变量值存储在实例对象,可以满足不同实例有不同值的需求。而实例方法、变量描述(类型、名称)信息、协议信息等,不同实例间没有区别,放到类对象中可以减少实例对象内存占用。否则,每个实例都要存储一份实例方法、变量信息等。
内存中,只有一个类对象、元类对象,可能有多个实例对象。
meta-meta class?
你或许会想 meta class 的isa指针指向哪里?是否有元类的元类?
为避免这种无限递归,Objective-C 的创建者让所有元类的isa指针指向根元类,根元类的isa指针指向自身。
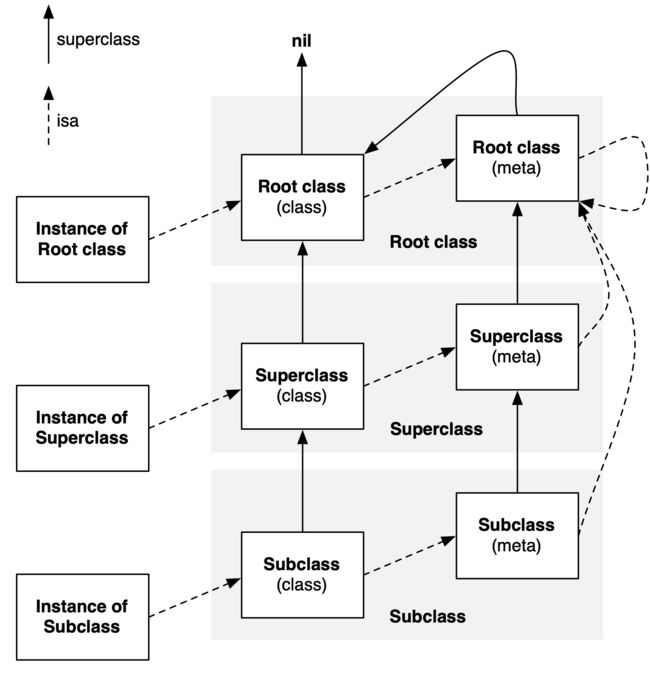
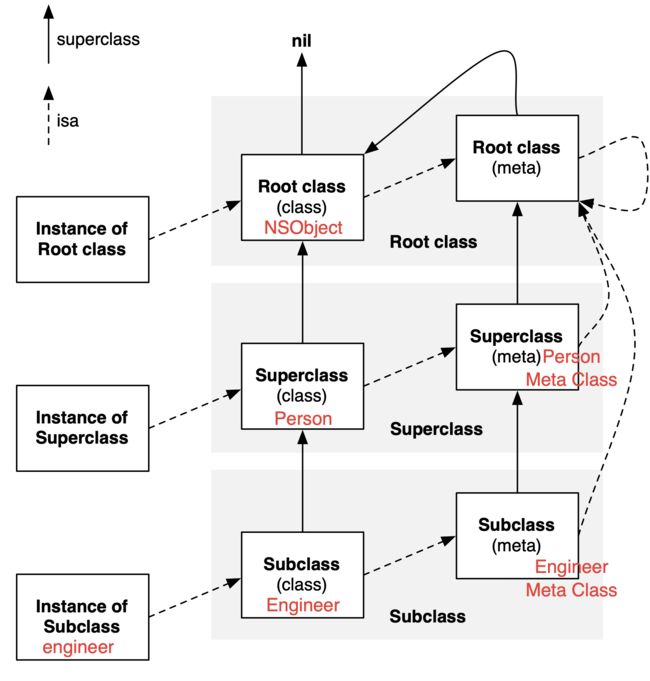
现在,已经对类结构有了完整的了解。Runtime 工程师 Greg Parker 在他的博客贴了张非常清晰的图表,如下:
metaclass 的父类与类的父类链条平行。因此,查找类方法与查找实例方法类似。
root meta class 的父类是 root class。因此,层级结构中的所有实例、类、元类都将继承自基类,root class 的实例方法对所有实例、类、元类均有效。root class 的类方法对所有类、元类都有效。
下面是两个简单的类,Person继承自NSObject,Engineer继承自Person。在Engineer类实现了一些方法,testMetaClass方法查找isa指针指向并输出;testSuperClass方法查找super_class指针指向并输出:
- (void)testMetaClass {
NSLog(@"----- %s -----", __func__);
NSLog(@"This object is %p", self);
NSLog(@"Class is %@, and super is %@.", [self class], [self superclass]);
Class currentClass = [self class];
for (int i=0; i<4; ++i) {
NSLog(@"Following the isa pointer %d times gives %p", i+1, currentClass);
currentClass = object_getClass(currentClass);
}
// 不能通过[Person class]获得元类
NSLog(@"NSObject's meta class is %p", object_getClass([NSObject class]));
}
- (void)testSuperClass {
NSLog(@"----- %s -----", __func__);
NSLog(@"This object is %p.", self);
NSLog(@"Class is %@, and super is %@.", [self class], [self superclass]);
Class currentClass = [self class];
Class currentMetaClass = object_getClass(currentClass);
for (int i=0; i<4; ++i) {
NSLog(@"Following the super pointer %d times gives %p", i+1, currentClass);
currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass);
}
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i) {
NSLog(@"Following the meta class super pointer %d times gives %p", i+1, currentMetaClass);
currentMetaClass = class_getSuperclass(currentMetaClass);
}
NSLog(@"NSObject's meta class is %p", object_getClass([NSObject class]));
}
执行以下代码:
Engineer *engineer = [[Engineer alloc] initWithName:@"pro648"];
[engineer testMetaClass];
[engineer testSuperClass];
输出如下:
----- -[Engineer testMetaClass] -----
This object is 0x6000037b7950
Class is Engineer, and super is Person.
Following the isa pointer 1 times gives 0x10f7956c0
Following the isa pointer 2 times gives 0x10f7956e8
Following the isa pointer 3 times gives 0x1100de1d8
Following the isa pointer 4 times gives 0x1100de1d8
NSObject's meta class is 0x1100de1d8
----- -[Engineer testSuperClass] -----
This object is 0x6000037b7950.
Class is Engineer, and super is Person.
Following the super pointer 1 times gives 0x10f7956c0
Following the super pointer 2 times gives 0x10f795648
Following the super pointer 3 times gives 0x1100de200
Following the super pointer 4 times gives 0x0
Following the meta class super pointer 1 times gives 0x10f7956e8
Following the meta class super pointer 2 times gives 0x10f795620
Following the meta class super pointer 3 times gives 0x1100de1d8
Following the meta class super pointer 4 times gives 0x1100de200
Following the meta class super pointer 5 times gives 0x0
NSObject's meta class is 0x1100de1d8
指针指向的具体地址并不重要,但可跟踪isa指向。
engineer实例内存地址是0x6000037b7950,它的类对象地址是0x10f7956c0,它的元类地址是0x10f7956e8,root meta class 地址是0x1100de1d8,root meta class 的isa指针指向自身。
通过testSuperClass方法的输出,可以跟踪super_class层级结构。root meta class 的 super class 是0x1100de200,也就是NSObject类对象。NSObject的父类是NULL。
3. Method
类的方法列表是实例对象方法的集合。当向实例对象发送消息时,objc_msgSend()在其类对象(和类对象的父类)的method_array_t中查找方法。
class_rw_t里面的methods、properties、protocols数组是二维的,是可读可写的。源码如下:
struct class_rw_t {
// Be warned that Symbolication knows the layout of this structure.
uint32_t flags;
uint16_t witness;
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
uint16_t index;
#endif
// 省略...
const class_ro_t *ro() const {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (slowpath(v.is())) {
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->ro;
}
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext);
}
void set_ro(const class_ro_t *ro) {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (v.is()) {
v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->ro = ro;
} else {
set_ro_or_rwe(ro);
}
}
const method_array_t methods() const {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (v.is()) {
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->methods;
} else {
return method_array_t{v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseMethods()};
}
}
const property_array_t properties() const {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (v.is()) {
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->properties;
} else {
return property_array_t{v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseProperties};
}
}
const protocol_array_t protocols() const {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (v.is()) {
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->protocols;
} else {
return protocol_array_t{v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseProtocols};
}
}
}
method_array_t源码如下:
class method_array_t :
public list_array_tt
{
typedef list_array_tt Super;
public:
method_array_t() : Super() { }
method_array_t(method_list_t *l) : Super(l) { }
const method_list_t_authed_ptr *beginCategoryMethodLists() const {
return beginLists();
}
const method_list_t_authed_ptr *endCategoryMethodLists(Class cls) const;
};
method_array_t里包含method_list_t,method_list_t里包含method_t,method_t源码如下:
struct method_t {
static const uint32_t smallMethodListFlag = 0x80000000;
method_t(const method_t &other) = delete;
// The representation of a "big" method. This is the traditional
// representation of three pointers storing the selector, types
// and implementation.
struct big {
SEL name;
const char *types;
MethodListIMP imp;
};
// 省略...
SEL name() const {
if (isSmall()) {
return (small().inSharedCache()
? (SEL)small().name.get()
: *(SEL *)small().name.get());
} else {
return big().name;
}
}
const char *types() const {
return isSmall() ? small().types.get() : big().types;
}
// 省略...
void setName(SEL name) {
if (isSmall()) {
ASSERT(!small().inSharedCache());
*(SEL *)small().name.get() = name;
} else {
big().name = name;
}
}
void setImp(IMP imp) {
if (isSmall()) {
remapImp(imp);
} else {
big().imp = imp;
}
}
};
method_t包含SEL、types、MethodListIMP。
3.1 SEL
在 Objective-C 中,selector 是一个 C 的数据结构,可以把它看作是方法的 id。在 runtime 中定义如下:
/// An opaque type that represents a method selector.
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
object_selector是不透明类型,可以把它当作方法名称,但 runtime 不是直接存储方法名称,而是将其映射为层级结构中唯一的字符串。这也是为什么类中不能有名称相同、参数类型不同的方法。
3.2 IMP
IMP指针指向函数的实现:
typedef id _Nullable (*IMP)(id _Nonnull, SEL _Nonnull, ...);
如果将 signature 与objc_msgSend进行比较,会发现其实际上是相同的。其参数都包含一个对象、一个 selector,外加可变数量的参数。按照约定,runtime 将self作为第一个参数传递,将当前 selector 作为第二个参数传递。
这就是为什么可以在方法内调用self和_cmd,以及添加 C 函数时,需要添加self、_cmd参数。
3.3 Method Type
method_types存储方法返回值类型、参数类型,runtime 将这些信息编码为一个字符串。具体规则可以查看Type Encodings文档。
也可以通过@encode指令获取编码后的字符。例如:
char *intTypeCode = @encode(int);
char *voidTypeCode = @encode(void);
NSLog(@"int: %s, void:%s",intTypeCode, voidTypeCode);
输出如下:
int: i, void:v
3. 消息发送
结合前面的介绍,我们已经知道 runtime 如何发送消息:
根据实例对象的
isa指针找到类对象。-
类对象的消息解析:
- 查看类对象的
cache是否存在该方法。如果存在,直接调用;如果不存在,进入下一步。 - 查看类对象
class_rw_t是否有该方法。如果存在,调用并添加到cache;如果不存在,进入下一步。 - 查看父类的
cache是否存在该方法。如果存在,调用并添加到消息接收者的cache;如果不存在,进入下一步。 - 查看父类
class_rw_t是否有该方法。如果存在,调用并添加到消息接收者cache;如果不存在,进入下一步。 - 以此类推,直到找到根类。
如果在3、4及其它父类中找到该方法,会将其添加到消息接收者的
cache,即 receiver 的cache。 - 查看类对象的
动态方法解析。
消息转发。
下一篇文章Runtime从入门到进阶二将介绍动态方法解析、消息转发,以及runtime在项目中的具体应用。
Demo名称:Runtime
源码地址:https://github.com/pro648/BasicDemos-iOS/tree/master/Runtime
参考资料:
- [objc explain] - Non-pointer isa
- [objc explain] - Classes and metaclasses
- Greg Parker objc
- Digging Into the Objective-C Runtime - Part I
- Understanding the Objective-C Runtime
- 从 NSObject 的初始化了解 isa
欢迎更多指正:https://github.com/pro648/tips
本文地址:https://github.com/pro648/tips/blob/master/sources/Runtime%E4%BB%8E%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%88%B0%E8%BF%9B%E9%98%B6%E4%B8%80.md