vue 获取url地址的参数_手把手教你的Vue项目实战
1. 接口模块处理
1.1 axios二次封装
这里封装的依据是后台传的JWT,已封装好的请跳过。
import axios from 'axios'import router from '../router'import {MessageBox, Message} from 'element-ui'let loginUrl = '/login'// 根据环境切换接口地址axios.defaults.baseURL = process.env.VUE_APP_APIaxios.defaults.headers = {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'}axios.defaults.timeout = 60000// 请求拦截器axios.interceptors.request.use( config => { if (router.history.current.path !== loginUrl) { let token = window.sessionStorage.getItem('token') if (token == null) { router.replace({path: loginUrl, query: {redirect: router.currentRoute.fullPath}}) return false } else { config.headers['Authorization'] = 'JWT ' + token } } return config }, error => { Message.warning(error) return Promise.reject(error) })复制代码紧接着的是响应拦截器(即异常处理)
axios.interceptors.response.use( response => { return response.data }, error => { if (error.response !== undefined) { switch (error.response.status) { case 400: MessageBox.alert(error.response.data) break case 401: if (window.sessionStorage.getItem('out') === null) { window.sessionStorage.setItem('out', 1) MessageBox.confirm('会话已失效! 请重新登录', '提示', {confirmButtonText: '重新登录', cancelButtonText: '取消', type: 'warning'}).then(() => { router.replace({path: loginUrl, query: {redirect: router.currentRoute.fullPath}}) }).catch(action => { window.sessionStorage.clear() window.localStorage.clear() }) } break case 402: MessageBox.confirm('登陆超时 !', '提示', {confirmButtonText: '重新登录', cancelButtonText: '取消', type: 'warning'}).then(() => { router.replace({path: loginUrl, query: {redirect: router.currentRoute.fullPath}}) }) break case 403: MessageBox.alert('没有权限!') break // ...忽略 default: MessageBox.alert(`连接错误${error.response.status}`) } return Promise.resolve(error.response) } return Promise.resolve(error)})复制代码这里做的处理分别是会话已失效和登陆超时,具体的需要根据业务来作变更。
最后是导出基础请求类型封装。
export default { get (url, param) { if (param !== undefined) { Object.assign(param, {_t: (new Date()).getTime()}) } else { param = {_t: (new Date()).getTime()} } return axios({method: 'get', url, params: param}) }, // 不常更新的数据用这个 getData (url, param) { return axios({method: 'get', url, params: param}) }, post (url, param, config) { return axios.post(url, param, config) }, put: axios.put, _delete: axios.delete}复制代码其中给get请求加上时间戳参数,避免从缓存中拿数据。 除了基础请求类型,还有很多类似下载、上传这种,需要特殊的的请求头,此时可以根据自身需求进行封装。
浏览器缓存是基于url进行缓存的,如果页面允许缓存,则在一定时间内(缓存时效时间前)再次访问相同的URL,浏览器就不会再次发送请求到服务器端,而是直接从缓存中获取指定资源。
1.2 请求按模块合并
模块的请求:
import http from '@/utils/request'export default { A (param) { return http.get('/api/', param) }, B (param) { return http.post('/api/', param) } C (param) { return http.put('/api/', param) }, D (param) { return http._delete('/api/', {data: param}) },}复制代码utils/api/index.js:
import http from '@/utils/request'import account from './account'// 忽略...const api = Object.assign({}, http, account, *...其它模块*)export default api复制代码1.3 global.js中的处理
在global.js中引入:
import Vue from 'vue'import api from './api/index'// 略...const errorHandler = (error, vm) => { console.error(vm) console.error(error)}Vue.config.errorHandler = errorHandlerexport default { install (Vue) { // 添加组件 // 添加过滤器 }) // 全局报错处理 Vue.prototype.$throw = (error) => errorHandler(error, this) Vue.prototype.$http = api // 其它配置 }}复制代码写接口的时候就可以简化为:
async getData () { const params = {/*...key : value...*/} let res = await this.$http.A(params) res.code === 4000 ? (this.aSata = res.data) : this.$message.warning(res.msg)}复制代码2. 基础组件自动化全局注册
来自 @SHERlocked93:Vue 使用中的小技巧
官方文档:基础组件的自动化全局注册
我们写组件的时候通常需要引入另外的组件:
复制代码写小项目这么引入还好,但等项目一臃肿起来...啧啧。 这里是借助webpack,使用 require.context() 方法来创建自己的模块上下文,从而实现自动动态require组件。
这个方法需要3个参数:
- 要搜索的文件夹目录
- 是否还应该搜索它的子目录
- 一个匹配文件的正则表达式。
在你放基础组件的文件夹根目录下新建componentRegister.js:
import Vue from 'vue'/** * 首字母大写 * @param str 字符串 * @example heheHaha * @return {string} HeheHaha */function capitalizeFirstLetter (str) { return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + str.slice(1)}/** * 对符合'xx/xx.vue'组件格式的组件取组件名 * @param str fileName * @example abc/bcd/def/basicTable.vue * @return {string} BasicTable */function validateFileName (str) { return /^S+.vue$/.test(str) && str.replace(/^S+/(w+).vue$/, (rs, $1) => capitalizeFirstLetter($1))}const requireComponent = require.context('./', true, /.vue$/)// 找到组件文件夹下以.vue命名的文件,如果文件名为index,那么取组件中的name作为注册的组件名requireComponent.keys().forEach(filePath => { const componentConfig = requireComponent(filePath) const fileName = validateFileName(filePath) const componentName = fileName.toLowerCase() === 'index' ? capitalizeFirstLetter(componentConfig.default.name) : fileName Vue.component(componentName, componentConfig.default || componentConfig)})复制代码最后我们在main.js中
import 'components/componentRegister.js'
我们就可以随时随地使用这些基础组件,无需手动引入了。
3. 页面性能调试:Hiper
我们写单页面应用,想看页面修改后性能变更其实挺繁琐的。有时想知道是「正优化」还是「负优化」只能靠手动刷新查看network。而Hiper很好解决了这一痛点(其实Hiper是后台静默运行Chromium来实现无感调试)。
Hiper官方文档
https://github.com/pod4g/hiper/blob/master/README.zh-CN.md
我们开发完一个项目或者给一个项目做完性能优化以后,如何来衡量这个项目的性能是否达标?
我们的常见方式是在Dev Tool中的performance和network中看数据,记录下几个关键的性能指标,然后刷新几次再看这些性能指标。
有时候我们发现,由于样本太少,受当前「网络」、「CPU」、「内存」的繁忙程度的影响很重,有时优化后的项目反而比优化前更慢。
如果有一个工具,一次性地请求N次网页,然后把各个性能指标取出来求平均值,我们就能非常准确地知道这个优化是「正优化」还是「负优化」。
并且,也可以做对比,拿到「具体优化了多少」的准确数据。这个工具就是为了解决这个痛点的。
全局安装
sudo npm install hiper -g# 或者使用 yarn:# sudo yarn global add hiper复制代码性能指标
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/PerformanceTiming
用例配置
# 当我们省略协议头时,默认会在url前添加`https://` # 最简单的用法 hiper baidu.com # 如何url中含有任何参数,请使用双引号括起来 hiper "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" # 加载指定页面100次 hiper -n 100 "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" # 禁用缓存加载指定页面100次 hiper -n 100 "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" --no-cache # 禁JavaScript加载指定页面100次 hiper -n 100 "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" --no-javascript # 使用GUI形式加载指定页面100次 hiper -n 100 "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" -H false # 使用指定useragent加载网页100次 hiper -n 100 "baidu.com?a=1&b=2" -u "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_13_4) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.181 Safari/537.36"复制代码此外,还可以配置Cookie访问
module.exports = { .... cookies: [{ name: 'token', value: process.env.authtoken, domain: 'example.com', path: '/', httpOnly: true }], ....}复制代码# 载入上述配置文件(假设配置文件在/home/下)hiper -c /home/config.json# 或者你也可以使用js文件作为配置文件hiper -c /home/config.js复制代码4. Vue高阶组件封装
我们常用的和就是一个高阶(抽象)组件。
export default { name: 'keep-alive', abstract: true, ...}复制代码所有的高阶(抽象)组件是通过定义abstract选项来声明的。高阶(抽象)组件不渲染真实DOM。 一个常规的抽象组件是这么写的:
import { xxx } from 'xxx'const A = () => { .....}export default { name: 'xxx', abstract: true, props: ['...', '...'], // 生命周期钩子函数 created () { .... }, .... destroyed () { .... }, render() { const vnode = this.$slots.default .... return vnode },})复制代码4.1 防抖/节流 抽象组件
关于防抖和节流是啥就不赘述了。这里贴出组件代码:
改编自:Vue实现函数防抖组件
const throttle = function(fn, wait=50, isDebounce, ctx) { let timer let lastCall = 0 return function (...params) { if (isDebounce) { if (timer) clearTimeout(timer) timer = setTimeout(() => { fn.apply(ctx, params) }, wait) } else { const now = new Date().getTime() if (now - lastCall < wait) return lastCall = now fn.apply(ctx, params) } }}export default { name: 'Throttle', abstract: true, props: { time: Number, events: String, isDebounce: { type: Boolean, default: false }, }, created () { this.eventKeys = this.events.split(',') this.originMap = {} this.throttledMap = {} }, render() { const vnode = this.$slots.default[0] this.eventKeys.forEach((key) => { const target = vnode.data.on[key] if (target === this.originMap[key] && this.throttledMap[key]) { vnode.data.on[key] = this.throttledMap[key] } else if (target) { this.originMap[key] = target this.throttledMap[key] = throttle(target, this.time, this.isDebounce, vnode) vnode.data.on[key] = this.throttledMap[key] } }) return vnode },})复制代码通过第三个参数isDebounce来控制切换防抖节流。 最后在main.js里引用:
import Throttle from '../Throttle'....Vue.component('Throttle', Throttle)复制代码使用方式
click+1 { {val}} click+3 { {val}} click+3 { {val}}
复制代码
const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data () { return { val: 0 } }, methods: { onClick ($ev, val) { this.val += val }, onAdd () { this.val += 3 } }})复制代码抽象组件是一个接替Mixin实现抽象组件公共功能的好方法,不会因为组件的使用而污染DOM(添加并不想要的div标签等)、可以包裹任意的单一子元素等等
至于用不用抽象组件,就见仁见智了。
5. 性能优化:eventBus封装
中央事件总线eventBus的实质就是创建一个vue实例,通过一个空的vue实例作为桥梁实现vue组件间的通信。它是实现非父子组件通信的一种解决方案。
而eventBus实现也非常简单
import Vue from 'Vue'export default new Vue复制代码我们在使用中经常最容易忽视,又必然不能忘记的东西,那就是:清除事件总线eventBus。
不手动清除,它是一直会存在,这样当前执行时,会反复进入到接受数据的组件内操作获取数据,原本只执行一次的获取的操作将会有多次操作。本来只会触发并只执行一次,变成了多次,这个问题就非常严重。
当不断进行操作几分钟后,页面就会卡顿,并占用大量内存。
所以一般在vue生命周期beforeDestroy或者destroyed中,需要用vue实例的$off方法清除eventBus
beforeDestroy(){ bus.$off('click') }复制代码可当你有多个eventBus时,就需要重复性劳动$off销毁这件事儿。 这时候封装一个 eventBus就是更优的解决方案。
5.1 拥有生命周期的 eventBus
我们从Vue源码Vue.init中可以得知:
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { const vm: Component = this // a uid vm实例唯一标识 vm._uid = uid++ // .... }复制代码每个Vue实例有自己的_uid作为唯一标识,因此我们让EventBus和_uid关联起来,并将其改造:
实现来自:让在Vue中使用的EventBus也有生命周期
class EventBus { constructor (vue) { if (!this.handles) { Object.defineProperty(this, 'handles', { value: {}, enumerable: false }) } this.Vue = vue // _uid和EventName的映射 this.eventMapUid = {} } setEventMapUid (uid, eventName) { if (!this.eventMapUid[uid]) this.eventMapUid[uid] = [] this.eventMapUid[uid].push(eventName) // 把每个_uid订阅的事件名字push到各自uid所属的数组里 } $on (eventName, callback, vm) { // vm是在组件内部使用时组件当前的this用于取_uid if (!this.handles[eventName]) this.handles[eventName] = [] this.handles[eventName].push(callback) if (vm instanceof this.Vue) this.setEventMapUid(vm._uid, eventName) } $emit () { let args = [...arguments] let eventName = args[0] let params = args.slice(1) if (this.handles[eventName]) { let len = this.handles[eventName].length for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { this.handles[eventName][i](...params) } } } $offVmEvent (uid) { let currentEvents = this.eventMapUid[uid] || [] currentEvents.forEach(event => { this.$off(event) }) } $off (eventName) { delete this.handles[eventName] }}// 写成Vue插件形式,直接引入然后Vue.use($EventBus)进行使用let $EventBus = {}$EventBus.install = (Vue, option) => { Vue.prototype.$eventBus = new EventBus(Vue) Vue.mixin({ beforeDestroy () { // 拦截beforeDestroy钩子自动销毁自身所有订阅的事件 this.$eventBus.$offVmEvent(this._uid) } })}export default $EventBus复制代码使用:
// main.js中...import EventBus from './eventBus.js'Vue.use(EnemtBus)...复制代码组件中使用:
created () { let text = Array(1000000).fill('xxx').join(',') this.$eventBus.$on('home-on', (...args) => { console.log('home $on====>>>', ...args) this.text = text }, this) // 注意第三个参数需要传当前组件的this,如果不传则需要手动销毁 }, mounted () { setTimeout(() => { this.$eventBus.$emit('home-on', '这是home $emit参数', 'ee') }, 1000) }, beforeDestroy () { // 这里就不需要手动的off销毁eventBus订阅的事件了 }复制代码6. webpack插件:真香
6.1 取代uglifyjs 的Terser Plugin
在二月初项目升级Vue-cli3时遇到了一个问题:uglifyjs不再支持webpack4.0。找了一圈,在Google搜索里查到Terser Plugin这个插件。
我主要用到了其中这几个功能:
- cache,启用文件缓存。
- parallel,使用多进程并行来提高构建速度。
- sourceMap,将错误消息位置映射到模块(储存着位置信息)。
- drop_console,打包时剔除所有的console语句
- drop_debugger,打包时剔除所有的debugger语句
作为一个管小组前端的懒B,很多时候写页面会遗留console.log,影响性能。设置个drop_console就非常香。以下配置亲测有效。
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin')....new TerserPlugin({cache: true,parallel: true,sourceMap: true, // Must be set to true if using source-maps in productionterserOptions: { compress: { drop_console: true, drop_debugger: true }}})复制代码更多的配置请看Terser Plugin
6.2 双端开启 gzip
开启gzip压缩的好处是什么?
可以减小文件体积,传输速度更快。gzip是节省带宽和加快站点速度的有效方法。
- 服务端发送数据时可以配置 Content-Encoding:gzip,用户说明数据的压缩方式
- 客户端接受到数据后去检查对应字段的信息,就可以根据相应的格式去解码。
- 客户端请求时,可以用 Accept-Encoding:gzip,用户说明接受哪些压缩方法。
6.2.1 Webpack开启gzip
这里使用的插件为:CompressionWebpackPlugin
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')module.exports = { “plugins”:[new CompressionWebpackPlugin] }复制代码具体配置:
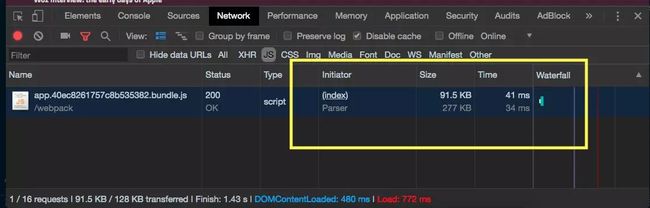
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin');webpackConfig.plugins.push( new CompressionWebpackPlugin({ asset: '[path].gz[query]', algorithm: 'gzip', test: new RegExp('.(js|css)$'), // 只处理大于xx字节 的文件,默认:0 threshold: 10240, // 示例:一个1024b大小的文件,压缩后大小为768b,minRatio : 0.75 minRatio: 0.8 // 默认: 0.8 // 是否删除源文件,默认: false deleteOriginalAssets: false }))复制代码开启gzip前
开启gzip后 gzip后的大小从277KB到只有~91.2KB!
6.2.2 扩展知识:Nginx的gzip设置
打开/etc/nginx/conf.d编写以下配置。
server { gzip on; gzip_static on; gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript; gzip_proxied any; gzip_vary on; gzip_comp_level 6; gzip_buffers 16 8k; gzip_http_version 1.1; ...}复制代码Nginx尝试查找并发送文件/path/to/bundle.js.gz。如果该文件不存在,或者客户端不支持 gzip,Nginx则会发送该文件的未压缩版本。
保存配置后,重新启动Nginx:
$ sudo service nginx restart复制代码开启gzip前
开启gzip后
6.2.3 如何验证gzip?
通过使用curl测试每个资源的请求响应,并检查Content-Encoding:
显示 Content-Encoding: gzip,即为配置成功。
6.2.4 双端Gzip区别及其意义
不同之处在于:
- Webpack压缩会在构建运行期间一次压缩文件,然后将这些压缩版本保存到磁盘。
- nginx在请求时压缩文件时,某些包可能内置了缓存,因此性能损失只发生一次(或不经常),但通常不同之处在于,这将在响应 HTTP请求时发生。
- 对于实时压缩,让上游代理(例如 Nginx)处理 gzip和缓存通常更高效,因为它们是专门为此而构建的,并且不会遭受服务端程序运行时的开销(许多都是用C语言编写的) 。
- 使用 Webpack的好处是, Nginx每次请求服务端都要压缩很久才回返回信息回来,不仅服务器开销会增大很多,请求方也会等的不耐烦。我们在 Webpack打包时就直接生成高压缩等级的文件,作为静态资源放在服务器上,这时将 Nginx作为二重保障就会高效很多(请求其它目录资源时)。
- 注:具体是在请求时实时压缩,或在构建时去生成压缩文件,就要看项目业务情况。
原链接:https://juejin.im/post/5cab64ce5188251b19486041