神经风格迁移
- 前言
- 正文
-
- 库、包、模板
- 图像预处理
- 构建神经风格迁移模型
-
- 代价函数
-
- 训练模型
- 结果展示
- 总结
- 源码
- 参考
前言
- 本次搭建的卷积神经网络使用了VGG19预训练模型搭建神经风格迁移模型,所以使用CPU整个训练过程也很快。
- 环境和库:
windows10+pycharm+tensorflow+keras+python+CPU
- 使用
tensorflow_hub可以快速体验神经风格迁移,不过需要VPN
import tensorflow_hub as hub
hub_module = hub.load('https://tfhub.dev/google/magenta/arbitrary-image-stylization-v1-256/1')
stylized_image = hub_module(tf.constant(content_image), tf.constant(style_image))[0]
tensor_to_image(stylized_image)
正文
库、包、模板
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import keras.preprocessing.image as process_im
from keras.applications import vgg19
from keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.python.keras import models
from tensorflow.python.keras import losses
from tensorflow.python.keras import layers
from tensorflow.python.keras import backend as k
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import functools
import IPython.display
图像预处理
- PIL中的image对象调用
resize方法,此处将图像进行缩放为某高宽的高质量图像
img_to_array转换前后类型都是一样的,唯一区别是转换前元素类型是整型,转换后元素类型是浮点型(和keras等机器学习框架相适应的图像类型。Keras introduced a special function called img_to_array which accepts an input image and then orders the channels correctly based on the image_data_format setting)expand_dims在数组中增加一个维度,reshape能够达到相同的效果- 作用:加载图像;将图像等比例缩放,最长边为512;并返回图像对应三维数组
- 源码:
def load_img(img_path):
"""
:param img_path:
:return:
"""
max_dim = 512
img = tf.io.read_file(img_path)
img = tf.image.decode_image(img, channels=3)
img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img, tf.float32)
shape = tf.cast(tf.shape(img)[:-1], tf.float32)
long_dim = max(shape)
scale = max_dim / long_dim
new_shape = tf.cast(shape * scale, tf.int32)
img = tf.image.resize(img, new_shape)
img = img[tf.newaxis, :]
return img
构建神经风格迁移模型
VGG19预训练模型
keras.applications.vgg19.VGG19(include_top=True,
weights='imagenet',
input_tensor=None,
input_shape=None,
pooling=None,
classes=1000)
- 有点儿不理解include_top的用法,文档中说:是否包括顶层的全连接层,但是还是有点儿不清楚,所以直接调用
model.summary()来一探究竟,结果是:是否删去所有的全连接层
- 还有对于pooling的用法,实验说明:表示在include_top=False时,最后一层是否要加上一层什么样的池化层。注意:最后一块的最后一层本来就有一层最大池化层
- 此处我们使用VGG19预训练模型对于VGG19的需求如下:不需要最后的全连接层(include_top=False)、需要预训练权重(weights=‘imagenet’)、其他为默认值。
基于VGG19自定义模型
- 整个模型的输入即为VGG19的输入,而输出则需要根据神经风格迁移网络的代价函数来定,我们需要提取内容图像中的内容、风格图像中的风格(blog),由此可知:内容代价函数我们需要提取靠近中间的某层的激活值输出,风格代价函数我们需要提取每一层的激活值输出。
- 值得一提的是:我们自定义好的模型之后,一些完全无关的层会被自动剔除,可用
model.summary()验证
- 对于VGG19来说,模型结构如下图所示:
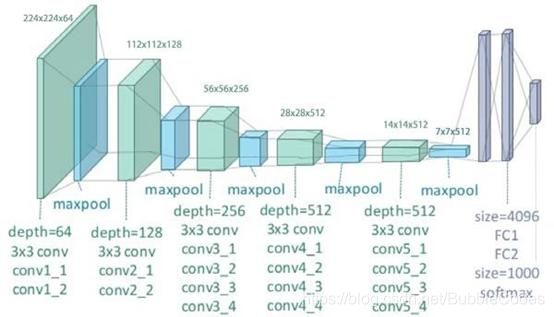
- 需要提取的层的激活值如下所示
content_layers = ['block5_conv2']
style_layers = ['block1_conv1',
'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1',
'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
- 在搞明白以上内容之后,我们可以调用
models.Model(input=, output=)构建我们需要的神经风格迁移模型了。
content_layers = ['block5_conv2']
style_layers = ['block1_conv1',
'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1',
'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
def get_model(content_layers_names, style_layers_names):
"""
:param content_layers_names: content layers names list
:param style_layers_names: style layers name list
:return: neural transfer model
"""
vgg = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.VGG19(include_top=False)
vgg.trainable = False
content_output = [vgg.get_layer(name=layer).output for layer in content_layers_names]
style_output = [vgg.get_layer(name=layer).output for layer in style_layers_names]
model_output = style_output + content_output
neural_transfer_model = models.Model([vgg.input], model_output)
return neural_transfer_model
代价函数
内容代价函数
- 内容直接定义为内容层的激活值,所以内容代价函数定义为激活值的均方差误差MSE
def content_loss_layer(output_layer, target_layer):
"""
:param output_layer:
:param target_layer:
:return: some layer content loss
"""
content_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(output_layer - target_layer))
return content_loss
风格代价函数
- 风格定义为不同通道之间激活值的相关系数,每一层有一个风格矩阵(即为Gram矩阵),风格代价函数定义类似于风格矩阵的均方误差
def gram_matrix(layer):
"""
:param layer: some layer of model
:return: Gram matrix
"""
channels = int(layer.shape[-1])
vector = tf.reshape(layer, [-1, channels])
n = tf.shape(vector)[0]
gram = tf.matmul(vector, vector, transpose_a=True)
return gram / tf.cast(n, tf.float32)
def style_loss_layer(output_layer, target_layer):
"""
:param output_layer:
:param target_layer:
:return:
"""
gram_output = gram_matrix(output_layer)
gram_target = gram_matrix(target_layer)
style_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(gram_target - gram_output))
return style_loss
总代价函数
- 总代价函数由内容代价函数和风格代价函数通过加权和得来
- 为什么在
get_features方法中截取content_feature&style_feature的时候用的layer[0],要解决这个问题必须要理解每一层的激活值到底是什么样的结构!
- 同样的问题:在
neural_transfer_cost方法中对输出图像的输出激活值只去第零维的值
- 源码:
def get_features(neural_transfer_model, content_image, style_image):
"""
:param neural_transfer_model:
:param content_image:
:param style_image:
:return:
"""
content_image = content_image*255.
style_image = style_image*255.
content_image = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(content_image)
style_image = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(style_image)
content_output = neural_transfer_model(content_image)
style_output = neural_transfer_model(style_image)
content_feature = [layer for layer in content_output[number_style:]]
style_feature = [layer for layer in style_output[:number_style]]
return content_feature, style_feature
def neural_transfer_cost(neural_transfer_model, loss_weights, output, target_style_features, target_content_features):
"""
:param neural_transfer_model:
:param loss_weights:
:param output:
:param target_style_features:
:param target_content_features:
:return: model cost
"""
style_weight, content_weight = loss_weights
content_loss = 0
style_loss = 0
output = output*255.
output = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(output)
output_features = neural_transfer_model(output)
output_style_features = output_features[:number_style]
output_content_features = output_features[number_style:]
for i, j in zip(target_style_features, output_style_features):
style_loss += style_loss_layer(i, j)
style_loss *= 1. / number_style
for i, j in zip(target_content_features, output_content_features):
content_loss += content_loss_layer(i, j)
content_loss *= 1. / number_content
total_cost = content_weight * content_loss + style_weight * style_loss
return total_cost
训练模型
- 使用参数字典作为方法参数
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:在context manager中监视计算过程,随后可以调用tape来计算偏导tf.clip_by_value将tensor的值限制在一定范围内var.numpy()是什么意思?
def run_style_transfer(content_image, style_image, epochs=500, content_weight=1e3, style_weight=1e-2):
"""
:param content_image:
:param style_image:
:param epochs:
:param content_weight:
:param style_weight:
:return:
"""
neural_transfer_model = get_model(content_layers_names=content_layers, style_layers_names=style_layers)
target_content_feature, target_style_feature = get_features(neural_transfer_model, content_image, style_image)
output = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(content_image)
output = tf.Variable(output, dtype=tf.float32)
loss_weights = (style_weight, content_weight)
dictionary = {
'neural_transfer_model': neural_transfer_model,
'loss_weights': loss_weights,
'output': output,
'target_style_features': target_style_feature,
'target_content_features': target_content_feature}
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.02, beta_1=0.99, epsilon=1e-1)
start_time = time.time()
start_50_epochs = time.time()
for i in range(epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
model_cost = neural_transfer_cost(**dictionary)
grad = tape.gradient(model_cost, output)
optimizer.apply_gradients([(grad, output)])
clipped = tf.clip_by_value(output, 0, 1)
output.assign(clipped)
if i % 50 == 0:
end_50_epochs = time.time()
print('Epoch:{}, duration:{}s'.format(i, end_50_epochs-start_50_epochs))
print('Total loss: {:.4e}, '.format(model_cost))
print('----------------------------------------------')
start_50_epochs = time.time()
plt.imshow(tensor_to_image(output))
plt.show()
IPython.display.clear_output(wait=True)
end_time = time.time()
print(str(end_time - start_time) + 's')
return output
结果展示
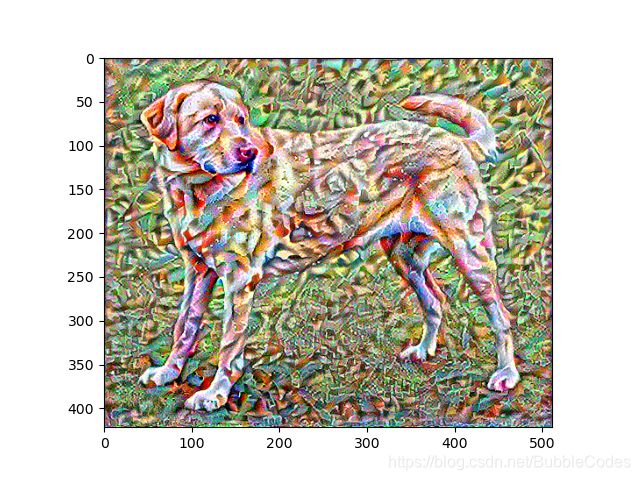
- 第一次用的广州塔的图片和梵高的星空,然后效果不是特别好,可能在参数方面需要调整。图我就不放了,效果不太行,有点丑。
- 然后我就换成了小黄狗,左图迭代10次,右图迭代大概100次,可以看到效果是不错的。

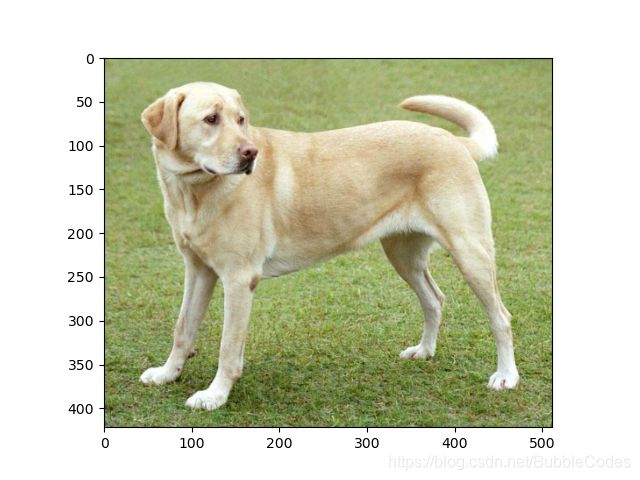

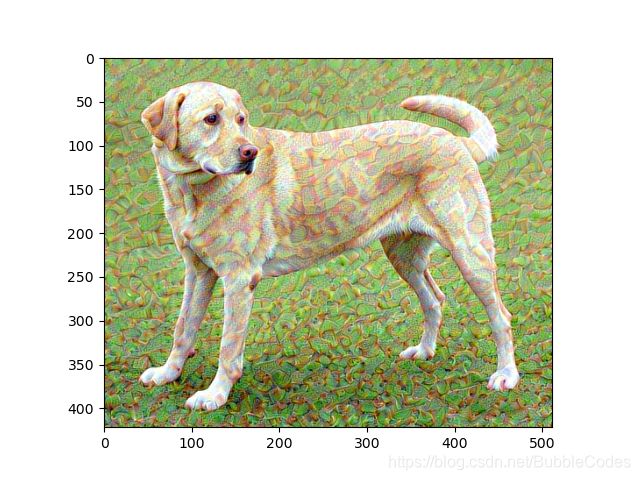
def show_im(img, title=None):
"""
:param img:
:param title:
"""
if len(img.shape) > 3:
image = tf.squeeze(img, axis=0)
plt.imshow(image)
if title:
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
content_path = './input/to.jpg'
style_path = './input/vagao.jpg'
content_image = load_img(content_path)
style_image = load_img(style_path)
show_im(content_image)
show_im(style_image)
content_layers = ['block5_conv2']
style_layers = ['block1_conv1',
'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1',
'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
number_content = len(content_layers)
number_style = len(style_layers)
image_neural_transfer = run_style_transfer(content_image, style_image, epochs=1000)
image_neural_transfer = tensor_to_image(image_neural_transfer)
plt.imshow(image_neural_transfer)
plt.show()
总结
- 主要练习两个内容:如何使用预训练模型、如何搭建神经风格迁移模型
- 在实现过程中遇到了不少麻烦,一直感觉:输出的图像有问题,但是应该不是模型的问题,而是数据类型转换的时候搞错了@.@
- 第二天更新:输出图像怪怪的(指广州塔)。现在解决了一个问题:弄清楚了图像输入的格式、图像显示的格式。
vgg19.preprocess_input()的输入要求0.-255.,输出层的输出0.-1.,计算代价函数的输入0.-1.,所以要特别注意
源码
参考
- kaggle
- VGGpaper
- csdn
- tensorflow
- img_to_array csdn






