一.索引作用
提供了类似于书中目录的作用,目的是为了优化查询
二.索引的种类
B树索引 Hash索引 R树索引 Full text GIS
三.B树基于不同的查找算法分类介绍
B-tree
B+tree 在范围查询方面提供了更好的性能 (> < >= <=)
B*tree
四.在功能上的分类
4.1辅助索引(s)怎么构建B树结构的?
1) 索引是基于表中,列(索引建)的值生成的B树结构
2)首先提取此列的所有值,进行自动排序
3)将排好序的值,均匀分布到索引树的叶子节点中(16k)
4)然后生成此索引的键值所对应的后端数据页的指针
5)生成枝节点和根节点,根据数据量级和索引键长度,生成合适的索引树高度
问题: 基于索引键做where查询,对于id列是顺序IO,但是对于其他列的查询,可能是随机IO.
4.2聚集索引(C)
4.2.1前提
1)表中设置了主键,主键列就会自动被作为聚集索引
2)如果没有主键,会选择唯一键作为聚集索引
3)聚集索引必须在建表时才有意义,一般是表的无关列(ID)
4)聚集索引在叶子节点上是整行的数据(辅助索引仅是提取列的值进行排序)
4.2.2辅助索引(s)怎么构建B树结构的
1)在建表时,设置了主键列(ID)
2)在将来录入数据时,就会按照ID列的顺序存储到磁盘上(又称之为聚集索引组织表)
3)将排好序的整行数据,生成叶子节点,可以理解为,磁盘的数据页就是叶子节点
(因为聚集索引是在创建表的时候就将每一行的内容进行了排序生成了叶子节点。因此在将来存储的时候就会按照这个顺序进行存储。而辅助索引只是某一列的值进行排列。)
五.辅助索引细分
1.普通的单列辅助索引
2.覆盖索引(联合索引):多个列作为索引条件,生成索引树,理论上设计的好的,可以减少大量的回表查询
3.唯一索引 : 索引列的值都是唯一的
六.索引树的高度受什么影响
1.数据量级,解决方法:分表,分库,分布式
2.索引列值过长,解决方法:前缀索引
3.数据类型
变长长度的字符串,使用了char,解决方案:边长字符串使用varchar
enum类型的使用 ('山东','河北','黑龙江','吉林','辽宁','陕西'......) 1 2 3
七.索引的基本管理
7.1索引的建立前
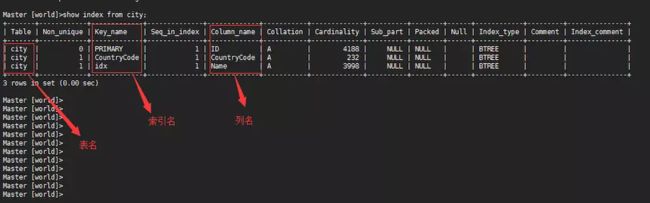
db01 [world]>desc city;
+-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
Field :列名字
key :有没有索引,索引类型
PRI: 主键索引
UNI: 唯一索引
MUL: 辅助索引(单列,联和,前缀)
7.1.单列普通辅助索引
7.1.1创建索引
alter table 表 add index 索引名(列名)
例: alter table city add index idx_name(name);
show index from city;(查看表的索引名)
注:同一个表中,索引名不能同名。同时在生产操作中,不建议在一个列上建多个索引
7.1.2删除索引:
alter table 表名 drop index 索引名
例:alter table city drop index idx_name1;
7.2覆盖索引(联合索引)
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名,列名)
例:alter table city add index idx_co_po(countrycode,population);
7.3前缀索引
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名(前几个字符))
例:alter table city add index idx_di(district(5));
7.4 唯一索引
db01 [world]>alter table city add unique index idx_uni1(name);
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'San Jose' for key 'idx_uni1'
统计city表中,以省的名字为分组,统计组的个数
select district,count(id) from city group by district;
需求: 找到world下,city表中 name列有重复值的行,最后删掉重复的行
db01 [world]>select name,count(id) as cid from city group by name having cid>1 order by cid desc;
db01 [world]>select * from city where name='suzhou';
===============================================
八. 执行计划获取及分析
8.0 介绍
(1)
获取到的是优化器选择完成的,他认为代价最小的执行计划.
作用: 语句执行前,先看执行计划信息,可以有效的防止性能较差的语句带来的性能问题.
如果业务中出现了慢语句,我们也需要借助此命令进行语句的评估,分析优化方案。
(2) select 获取数据的方法
1. 全表扫描(应当尽量避免,因为性能低)
2. 索引扫描
3. 获取不到数据
8.1 执行计划获取
获取优化器选择后的执行计划
8.2 执行计划分析
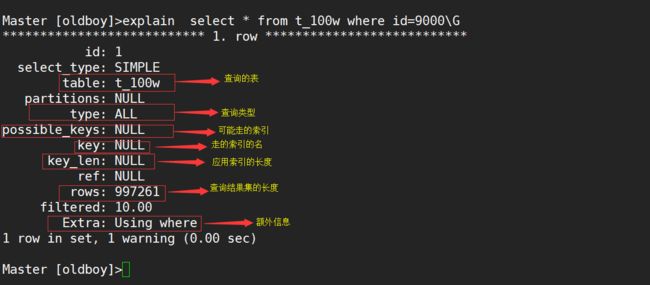
8.2.0 重点关注的信息
table: city ---->查询操作的表 **
possible_keys: CountryCode,idx_co_po ---->可能会走的索引 **
key: CountryCode ---->真正走的索引 ***
type: ref ---->索引类型 *****
Extra: Using index condition ---->额外信息 *****
8.2.1 type详解
从左到右性能依次变好.
ALL,index,range,ref,eq_ref,system(const),NULL(*****)
(1) ALL: 代表的是全表扫描
desc select * from city;
desc select * from city where name like '%C%';
desc select * from city where name != 'CHN';
desc select * from city where countrycode not in ('CHN','USA');
注意:生产中几乎是没有这种需求的。尽量避免
(2) index: 全索引扫描
需要扫描整个索引树,获取到想要数据,比ALL性能好,顺序IO,可以减少回表查询
db01 [world]>desc select name from city;
(3) range : 索引范围查询
> < >= <=
in
or
like 'CH%'
between and
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where id<10;
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where countrycode like 'CH%';
B+树额外优化:
> < >= <=
between and
like 'CH%'
in or无法享受B+树的额外优化,可以用union all来替代
例:查看中国和美国的城市信息
SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode='CHN' OR countrycode='USA';
或者:
SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode='CHN'
UNION ALL
SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode='USA'
(4) ref: 辅助索引的等值查询
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where countrycode = 'CHN';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | city | NULL | ref | CountryCode,idx_co_po | CountryCode | 3 | const | 363 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN'
-> union all
-> select * from city where countrycode='USA';
(5) eq_ref :多表连接的表,On的条件是主键或唯一键
desc select city.name,country.name
from city
join country
on city.countrycode=country.code
where city.population<100\G
(6) system 或 const :主键或唯一键的等值查询
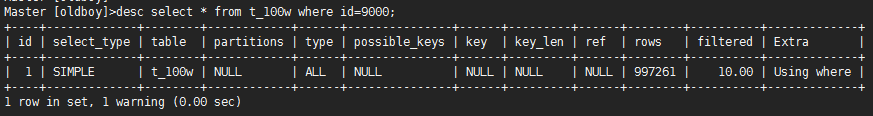
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where id=10;
(7) NULL , 索引中扫描不到这个数据
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where id=5000;
结论:在索引扫描类型方面,至少保证在range以上级别。
============================
8.2.2 其他字段解释
Extra:
Using filesort(关注)
意思是在查询过程中又一次启用了排序的功能*因为索引在构造B+树的时候本身就进行了一次排列,数据已经是有序的了。如果出现 Using filesort 则说名 索引是有问题的。
**** 统一优化方法 把该列与前面where 条件的列进行一个联合索引。
desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN' order by population desc limit 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | city | ref | CountryCode | CountryCode | 3 | const | 363 | Using index condition; Using where; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------
db01 [world]>alter table city add index idx_po(countrycode,population);
db01 [world]>desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN' order by population limit 10;
解决思路:
索引可以减少排序,可以很大程度减少CPU时间
辅助索引 应用顺序(优化器选择的)
如果查询条件:符合覆盖索引的顺序时,优先选择覆盖索引
不符合顺序,优先会走where条件的索引
优化方法,将where列和order列建立联合索引
alter table city add index idx_co_po(countrycode,population);
6.2.3 explain(desc)使用场景(面试题)
SQL语句有问题,
题目意思: 我们公司业务慢,请你从数据库的角度分析原因
1.mysql出现性能问题,我总结有两种情况:
(1)应急性的慢:突然夯住
应急情况:数据库hang(卡了,资源耗尽)
处理过程:
1.show full processlist; 获取到导致数据库hang的语句
额外关注一个time ,语句执行时间。通常有问题的SQL语句执行时间都会很长
2. explain 分析SQL的执行计划,有没有走索引,索引的类型情况
3. 建索引,改语句
(2)一段时间慢(持续性的):
(1)记录慢日志slowlog,分析slowlog
(2)explain 分析SQL的执行计划,有没有走索引,索引的类型情况
(3)建索引,改语句
九. 索引效果压力测试
===========压力测试===========
1、模拟数据库数据
drop database if exists oldboy;
create database oldboy charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin;
use oldboy;
create table t_100w (id int,num int,k1 char(2),k2 char(4),dt timestamp);
delimiter //
create procedure rand_data(in num int)
begin
declare str char(62) default 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789';
declare str2 char(2);
declare str4 char(4);
declare i int default 0;
while i set str2=concat(substring(str,1+floor(rand()*61),1),substring(str,1+floor(rand()*61),1)); set str4=concat(substring(str,1+floor(rand()*61),2),substring(str,1+floor(rand()*61),2)); set i=i+1; insert into t_100w values (i,floor(rand()*num),str2,str4,now()); end while; end; // delimiter ; 插入100w条数据: call rand_data(1000000); commit; 2、检查数据可用性 mysql -uroot -p select count(*) from oldboy. t_100w; 3、在没有优化之前我们使用mysqlslap来进行压力测试 mysqlslap --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf \ --concurrency=100 --iterations=1 --create-schema='oldboy' \ --query="select * from oldboy.t1 where stuname='alexsb_100'" engine=innodb \ --number-of-queries=2000 -uroot -p123 -verbose ========================================================== 压力测试工具: tpcc sysbench ================================================= 十. 索引应用规范 业务: 1.产品的功能 2.用户的行为 "热"查询语句 "热"数据 为了使索引的使用效率更高,在创建索引时,必须考虑在哪些字段上创建索引和创建什么类型的索引。那么索引设计原则又是怎样的? 10.1.1 (必须的) 建表时一定要有主键,一般是个无关列 10.1.2 选择唯一性索引 唯一性索引的值是唯一的,可以更快速的通过该索引来确定某条记录。 例如,学生表中学号是具有唯一性的字段。为该字段建立唯一性索引可以很快的确定某个学生的信息。 如果使用姓名的话,可能存在同名现象,从而降低查询速度。 优化方案: (1) 如果非得使用重复值较多的列作为查询条件(例如:男女),可以将表逻辑拆分 (2) 可以将此列和其他的查询类,做联和索引 select count(*) from world.city; select count(distinct countrycode) from world.city; select count(distinct countrycode,population ) from world.city; 10.1.3(必须的) 为经常需要where 、ORDER BY、GROUP BY,join on等操作的字段, 排序操作会浪费很多时间。 where A B C ----》 A B C in 如果where A group by B order by C 联合索引需要的顺序为 A,B,C 如果为其建立索引,优化查询 注:如果经常作为条件的列,重复值特别多,可以建立联合索引。 10.1.4 尽量使用前缀来索引 如果索引字段的值很长,最好使用值的前缀来索引。 ------------------------以上的是重点关注的,以下是能保证则保证的-------------------- 10.1.5 限制索引的数目 索引的数目不是越多越好。 可能会产生的问题: (1) 每个索引都需要占用磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。 (2) 修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦。越多的索引,会使更新表变得很浪费时间。 (3) 优化器的负担会很重,有可能会影响到优化器的选择. percona-toolkit中有个工具,专门分析索引是否有用 10.1.6 删除不再使用或者很少使用的索引(percona toolkit) 表中的数据被大量更新,或者数据的使用方式被改变后,原有的一些索引可能不再需要。数据库管理 员应当定期找出这些索引,将它们删除,从而减少索引对更新操作的影响。 10.1.7 大表加索引,要在业务不繁忙期间操作 10.1.8 尽量少在经常更新值的列上建索引 10.1.9 建索引原则 (1) 必须要有主键,如果没有可以做为主键条件的列,创建无关列 (2) 经常做为where条件列 order by group by join on, distinct 的条件(业务:产品功能+用户行为) (3) 最好使用唯一值多的列作为索引,如果索引列重复值较多,可以考虑使用联合索引 (4) 列值长度较长的索引列,我们建议使用前缀索引. (5) 降低索引条目,一方面不要创建没用索引,不常使用的索引清理,percona toolkit(xxxxx) (6) 索引维护要避开业务繁忙期 =============================================== select * from tab; 全表扫描。 select * from tab where 1=1; 在业务数据库中,特别是数据量比较大的表。 是没有全表扫描这种需求。 1、对用户查看是非常痛苦的。 2、对服务器来讲毁灭性的。 (1)select * from tab; SQL改写成以下语句: select * from tab order by price limit 10 ; 需要在price列上建立索引 (2) select * from tab where name='zhangsan' name列没有索引 改: 1、换成有索引的列作为查询条件 2、将name列建立索引 查询的结果集,超过了总数行数25%,优化器觉得就没有必要走索引了。 假如:tab表 id,name id:1-100w ,id列有(辅助)索引 select * from tab where id>500000; 如果业务允许,可以使用limit控制。 怎么改写 ? 结合业务判断,有没有更好的方式。如果没有更好的改写方案 尽量不要在mysql存放这个数据了。放到redis里面。 索引有自我维护的能力。 对于表内容变化比较频繁的情况下,有可能会出现索引失效。 一般是删除重建 例子: 错误的例子:select * from test where id-1=9; 正确的例子:select * from test where id=10; 算术运算 函数运算 子查询 这样会导致索引失效. 错误的例子: mysql> alter table tab add index inx_tel(telnum); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> mysql> desc tab; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | telnum | varchar(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from tab where telnum='1333333'; +------+------+---------+ | id | name | telnum | +------+------+---------+ | 1 | a | 1333333 | +------+------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from tab where telnum=1333333; +------+------+---------+ | id | name | telnum | +------+------+---------+ | 1 | a | 1333333 | +------+------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum='1333333'; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | inx_tel | inx_tel | 63 | const | 1 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum=1333333; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ALL | inx_tel | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum=1555555; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ALL | inx_tel | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum='1555555'; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | inx_tel | inx_tel | 63 | const | 1 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> --------------------------------------- 10.2.6 <> ,not in 不走索引(辅助索引) EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum <> '110'; EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum NOT IN ('110','119'); ------------ mysql> select * from tab where telnum <> '1555555'; +------+------+---------+ | id | name | telnum | +------+------+---------+ | 1 | a | 1333333 | +------+------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum <> '1555555'; ----- 单独的>,<,in 有可能走,也有可能不走,和结果集有关,尽量结合业务添加limit or或in 尽量改成union EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum IN ('110','119'); 改写成: EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum='110' UNION ALL SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum='119' ----------------------------------- 10.2.7 like "%_" 百分号在最前面不走 EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum LIKE '31%' 走range索引扫描 EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum LIKE '%110' 不走索引 %linux%类的搜索需求,可以使用elasticsearch+mongodb 专门做搜索服务的数据库产品 作者:wwwoldguocom 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/3621e36cf0af 来源: 著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。10.1 建立索引的原则(DBA运维规范)
10.1.0 说明
10.2 不走索引的情况(开发规范)
10.2.1 没有查询条件,或者查询条件没有建立索引
10.2.2 查询结果集是原表中的大部分数据,应该是25%以上。
10.2.3 索引本身失效,统计数据不真实
10.2.4 查询条件使用函数在索引列上,或者对索引列进行运算,运算包括(+,-,*,/,! 等)
10.2.5 隐式转换导致索引失效.这一点应当引起重视.也是开发中经常会犯的错误.