ConcurrentHashMap与HashMap的区别,以及怎么简单自己实现ConcurrentHashMap
1.HashMap是线程不安全的,所以效率相对于HashTable较高。HashTable是线程安全的,所以相对于HashMap效率较低。
2.ConcurrentHashMap可以看作是HashMap的线程安全版本,但是内部实现机制与HashTable不同。在不同版本的JDK中有不同的实现。
3. HashMap的键值对允许有null,但是ConCurrentHashMap都不允许。HashTable也是都不允许。
ConcurrentHashMap如何实现线程安全,并且还进行了性能优化
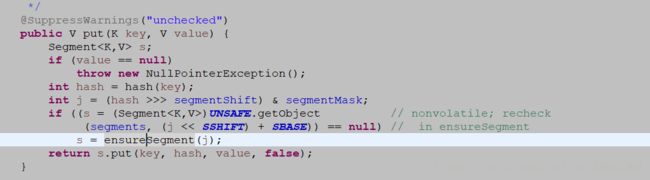
查看ConcurrentHashMap的put方法,与普通的HashMap中put方法不同,多了一部分对Segment的计算。这个Segment就是ConcurrentHashMap为了线程安全又提高效率采用的方法,将整个Map进行分割,分割成多个较小的分区。
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; //根据key进行hash计算,判断该key该落入哪个分区
if ((s = (Segment
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j); //判断并获取Segment
s.put(key, hash, value, false); //调用Segment的方法进行put
最后Put的动作落到了Segment的头上,那么Segment是怎么实现线程安全的呢。已知HashTable是采用syn关键字保证线程安全的,在被操作的HashTable的内容比较大时,可能会导致锁定时间过长。Segment也是这样操作的吗?
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); //采用重入锁,根据返回值判断是否需要继续锁 scanAndLockForPut已经表明这个方法是为了Put占用这个Segment的锁了,最后在finally代码块中也对锁进行了释放。
至此,ConcurrentHashMap的线程安全问题已经明确了,ConcurrentHashMap -- Segment -- lock 保证了线程安全并且获取到了比HashTable的syn更加高效率的操作。
如何自己使用简单代码重现ConcurrentHashMap的功能?
答:直觉方案采用大Map存放小Map的方式解决Segment的问题,就是对Key的Hash算法要进行重写,保证所有的key能落到对应的小map中,线程安全可以复写put等方法,加上syn关键字,简单实现。方案可行性及代码等待后续补充。