利用归并排序对大容量文件排序
文章目录
- 前言:
- 问题
- 思路
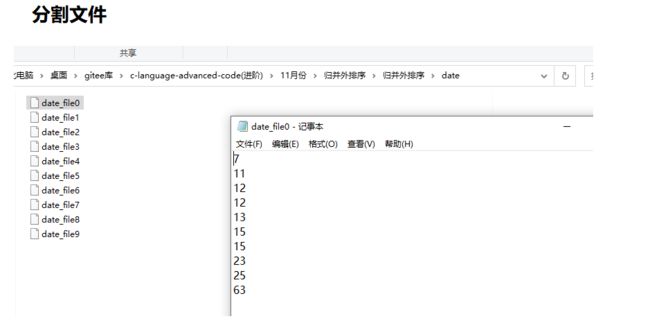
- 分割排序文件
-
- 效果
- 代码
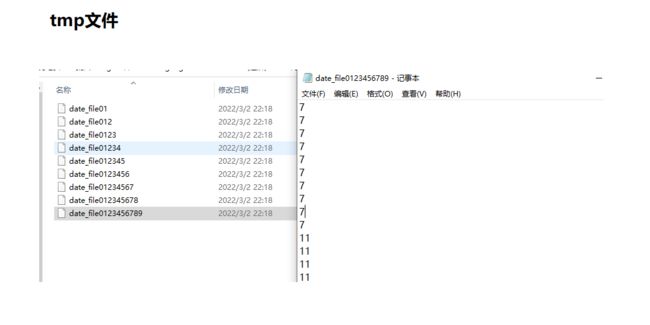
- 归并文件
-
- 效果
- 代码
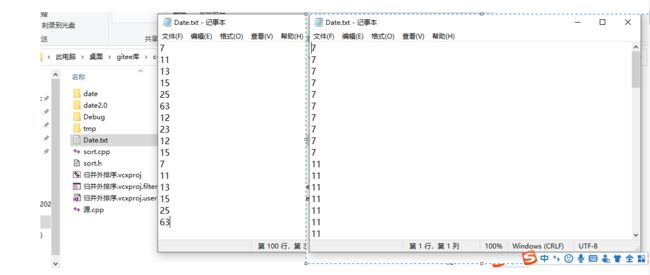
- 赋值文件
-
- 效果
- 代码
- Sort.cpp
- main.cppp
前言:
- 本文介绍,归并排序解决大容量排序问题,声明:是模拟这个过程。
- 本文需要文件一定文件操作知识尤其是 sscanf和sprintf的使用:博客
- 博主收集的资料New Young,连载中。
- 博主收录的问题:New Young
- 转载请标明出处:New Young
问题
如果一个文件有4G大小待排序的数据,而内存大小为1G,请问怎么对文件进行排序。
- 考察的是外排序–归并排序
- 归并排序博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55439426/article/details/123195585?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
思路
分割排序文件
效果
代码
void SortSmallFile(const char* filename, int x, int y)
{
assert(filename);
FILE* PF = fopen(filename, "r+");
assert(PF != NULL);
int n = x/ y;
int* arr = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
assert(arr);
char smallfile[100] = { 0 };
int filei = 0;
int i = 0;
int out = 0;
while (!feof(PF))
{
if (i<n-1)
{
fscanf(PF, "%d\n", &out);
arr[i++] = out;
}
else
{
if (!feof(PF))
{
fscanf(PF, "%d\n", &out);
arr[i++] = out;
}
//排序数组
QuickSort(arr, 0, i - 1);
sprintf(smallfile, "date\\date_file%d", filei++);
//开始拷贝到文件中
FILE* pf = fopen(smallfile, "w");
assert(pf != NULL);
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt < i)
{
fprintf(pf, "%d\n", arr[cnt++]);
}
i = 0;//重置i
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}
}
free(arr);
arr = NULL;
fclose(PF);
PF = NULL;
}
归并文件
效果
代码
void _MergeSortFile(const char* file1, const char* file2, const char* tmpfile)
{
assert(file1);
assert(file2);
assert(tmpfile);
FILE* pf1 = fopen(file1, "r");
assert(pf1 != NULL);
FILE* pf2 = fopen(file2, "r");
assert(pf2 != NULL);
FILE* tmppf = fopen(tmpfile,"w");
assert(tmppf != NULL);
int out1= 0;
int out2 = 0;
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
while (!feof(pf1)&&!feof(pf2))
{
if (out1 <= out2)
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out1);
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
}
else
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out2);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
}
}
while (!feof(pf1))
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out1);
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
}
while (!feof(pf2))
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out2);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
}
fclose(pf1);
pf1 = NULL;
fclose(pf2);
pf2 = NULL;
fclose(tmppf);
tmppf = NULL;
}
char file1[100] = "date\\date_file0";
char file2[100] = "date\\date_file1";
char tmpfile[100] = "date2.0\\date_file01";
int i = 0;
_MergeSortFile(file1, file2, tmpfile);
//这一步要控制好循环。
for (i = 2; i < 10 ;++i)
{
sprintf(file1, "%s", tmpfile);
sprintf(file2, "date\\date_file%d", i);
sprintf(tmpfile, "%s%d", tmpfile, i);
_MergeSortFile(file1, file2, tmpfile);
}
赋值文件
效果
代码
//数据再次存放到文件中中。
FILE* PF = fopen(FileName, "w");
assert(PF);
char fin[100] = { 0 };
sprintf(fin, "%s", tmpfile);
FILE* pf = fopen(fin, "r");
assert(pf);
int cnt = 0;
int out = 0;
while (!feof(pf)&&cnt<M)
{
fscanf(pf, "%d\n", &out);
fprintf(PF, "%d\n", out);
cnt++;
}
fclose(PF);
PF = NULL;
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
Sort.cpp
#include"sort.h"
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)// 插入排序
{
assert(a);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
int x = a[i + 1];
int end = i;
while (end >= 0)
{
if (a[end] > x)
{
a[end + 1] = a[end];
}
else
{
break;
}
end--;
}
a[end + 1] = x;
}
}
int GetMidIndex(int* a, int left, int right)
{
assert(a);
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (a[left] >= a[mid])
{
if (a[mid] >= a[right])
{
return mid;
}
else//a[mid]
{
if (a[right] > a[left])
{
return left;
}
else
{
return right;
}
}
}
else//a[left]
{
if (a[mid] < a[right])
{
return mid;
}
else//a[mid]>=a[right],mid是最大的
{
if (a[right] > a[left])
{
return right;
}
else
{
return left;
}
}
}
}
int PartSort1(int* a, int left, int right)// 快速排序hoare版本
{
assert(a);
//三数取中,是为了解决有序,栈溢出的问题。
//通过取中,打乱有序。
int key = GetMidIndex(a, left, right);
Swap(&a[key], &a[left]);
int keyi = left;
while (left < right)
{
while (right > left && a[right] >= a[keyi])//从右开始,找第一个小于a[key]
{
--right;
}
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])//从左开始,找第一个大于[key]
{
++left;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[keyi], &a[right]);
return left;
}
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
assert(a);
if (left >= right)
{
return;
}
if (right - left < 10)//小区间优化,这可以减少递归的深度。
{
InsertSort(a + left, right - left + 1);
}
else
{
int key = PartSort1(a, left, right);
QuickSort(a, left, key - 1);
QuickSort(a, key + 1, right);
}
}
main.cppp
#include"sort.h"
#define M 100
#define N 10
void SortSmallFile(const char* filename, int x, int y)
{
assert(filename);
FILE* PF = fopen(filename, "r+");
assert(PF != NULL);
int n = x/ y;
int* arr = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
assert(arr);
char smallfile[100] = { 0 };
int filei = 0;
int i = 0;
int out = 0;
while (!feof(PF))
{
if (i<n-1)
{
fscanf(PF, "%d\n", &out);
arr[i++] = out;
}
else
{
if (!feof(PF))
{
fscanf(PF, "%d\n", &out);
arr[i++] = out;
}
//排序数组
QuickSort(arr, 0, i - 1);
sprintf(smallfile, "date\\date_file%d", filei++);
//开始拷贝到文件中
FILE* pf = fopen(smallfile, "w");
assert(pf != NULL);
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt < i)
{
fprintf(pf, "%d\n", arr[cnt++]);
}
i = 0;//重置i
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}
}
free(arr);
arr = NULL;
fclose(PF);
PF = NULL;
}
void _MergeSortFile(const char* file1, const char* file2, const char* tmpfile)
{
assert(file1);
assert(file2);
assert(tmpfile);
FILE* pf1 = fopen(file1, "r");
assert(pf1 != NULL);
FILE* pf2 = fopen(file2, "r");
assert(pf2 != NULL);
FILE* tmppf = fopen(tmpfile,"w");
assert(tmppf != NULL);
int out1= 0;
int out2 = 0;
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
while (!feof(pf1)&&!feof(pf2))
{
if (out1 <= out2)
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out1);
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
}
else
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out2);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
}
}
while (!feof(pf1))
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out1);
fscanf(pf1, "%d\n", &out1);
}
while (!feof(pf2))
{
fprintf(tmppf, "%d\n", out2);
fscanf(pf2, "%d\n", &out2);
}
fclose(pf1);
pf1 = NULL;
fclose(pf2);
pf2 = NULL;
fclose(tmppf);
tmppf = NULL;
}
int main()
{
char FileName[100] = "Date.txt";
//文件分成N份,文件大小为M.并排序这些小文件---先存到数组,对数组排完序后放到文件中就行了。
SortSmallFile(FileName, M, N);
char file1[100] = "date\\date_file0";
char file2[100] = "date\\date_file1";
char tmpfile[100] = "date2.0\\date_file01";
int i = 0;
_MergeSortFile(file1, file2, tmpfile);
//这一步要控制好循环。
for (i = 2; i < 10 ;++i)
{
sprintf(file1, "%s", tmpfile);
sprintf(file2, "date\\date_file%d", i);
sprintf(tmpfile, "%s%d", tmpfile, i);
_MergeSortFile(file1, file2, tmpfile);
}
//数据再次存放到文件中中。
FILE* PF = fopen(FileName, "w");
assert(PF);
char fin[100] = { 0 };
sprintf(fin, "%s", tmpfile);
FILE* pf = fopen(fin, "r");
assert(pf);
int cnt = 0;
int out = 0;
while (!feof(pf)&&cnt<M)
{
fscanf(pf, "%d\n", &out);
fprintf(PF, "%d\n", out);
cnt++;
}
fclose(PF);
PF = NULL;
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
return 0;
}