opencv 学习笔记 (九) 几何变换
几何变换
- 简介
- 一、图像平移
-
- 1.图像平移代码 (不改变图像大小)
- 2.图像平移代码 (改变图像大小)
- 二、图像旋转
-
- 1.图像旋转函数
- 2.仿射变换函数
- 3.代码
- 三、图像缩放
-
- 1.图像缩放函数
- 2.图像缩小代码
- 3.图像放大代码
- 总结
简介
图像的几何变换不改变图像的像素值,而是改变像素所在的几何位置,从变换的性质来分,图像的几何变换有图像的位置变换(平移,镜像,旋转)、图像的形状变换(放大,缩小,错切)等基本变换,以及图像的复合变换等,
一、图像平移
图像平移是将一幅图像中所有的点都按照指定的平移量在水平,垂直方向移动,平移后的图像与原图像相同,平移后的图像上的每一个点都可以在原图像中找到对应的点。图像是由像素组成,假设原来的像素坐标为(x0,y0),经过平移量(△x,△y)坐标变为(x1,y1)
用数学可以表示:x1=x0+△x,y1=y0+△xy
平移变换分为两种,一种是图像大小改变,这样最后的原图像会有一部分不在图像中,另一种是图像大小改变,这样可以保全原图像的内容
1.图像平移代码 (不改变图像大小)
#include效果如下:
2.图像平移代码 (改变图像大小)
代码如下(示例):
int main()
{
Mat img1;
img1 = imread("猫1.jpg");
imshow("原图", img1);
int x0 = 100;
int y0 = 100;
int r = img1.rows + y0;
int c = img1.cols + x0;
Mat img2(r,c, img1.type());
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++)
{
int x = j - x0;
int y = i - y0;
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < c&&y < r)
{
img2.at<Vec3b>(i, j) = img1.ptr<Vec3b>(y)[x];
}
}
}
imshow("改变图像大小", img2);
waitKey(0);
}
效果如下:
二、图像旋转
图像旋转是数字图像处理的一个非常重要的环节,是图像的几何变换的手法之一。一般图像的旋转是图像的位置变换,但旋转后,图像的大小一般会改变。在图像旋转变换中,既可以把转出显示区域的图像截去,也可以扩大图像范围以显示所用的图像。
1.图像旋转函数
opencv提供的getRotationMatrix2D函数来实现图像旋转,用来计算出旋转矩阵。
Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f center, double angle, double scale)
center 旋转中心点
angle 旋转的角度
scale 图像缩放因子
2.仿射变换函数
计算出旋转矩阵后,还需要把旋转应用到仿射变换的输出,仿射变换函数是warpAffine
void warpAffine(InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
InputArray M, Size dsize,
int flags = INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
src 输入
dst 输出
M 变换矩阵
Size 尺寸
flags 插值算法标识符
borderMode 边界像素模式
borderValue 边界取值
3.代码
int main()
{
Mat img1;
img1 = imread("猫1.jpg");
imshow("原图", img1);
Point center(img1.cols / 2, img1.rows / 2);
Mat m = getRotationMatrix2D(center, 30, 0.5);
Mat img2;
warpAffine(img1, img2, m, img1.size());
imshow("旋转", img2);
waitKey(0);
}
三、图像缩放
图像比例缩放是值将给定的图像在x轴方向按比例缩放fx倍,在y轴方向按比例缩放fy倍
1.图像缩放函数
void resize(InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
Size dsize, double fx = 0, double fy = 0,
int interpolation = INTER_LINEAR);
src 输入
dst 输出
dsize 尺寸
fx 在x轴缩放比例
fy 在y轴缩放比例
interpolation 插值方式
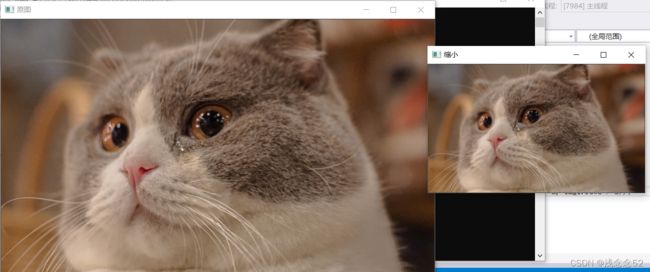
2.图像缩小代码
int main()
{
Mat img1;
img1 = imread("猫1.jpg");
imshow("原图", img1);
Mat img2;
resize(img1, img2, Size(img1.cols / 2, img1.rows / 2));
imshow("缩小", img2);
waitKey(0);
}
3.图像放大代码
int main()
{
Mat img1;
img1 = imread("猫1.jpg");
imshow("原图", img1);
Mat img2;
resize(img1, img2, Size(img1.cols * 2, img1.rows * 2));
imshow("放大", img2);
waitKey(0);
}
效果如下:
总结
本文简单介绍了图像平移,旋转,缩放,这是最基本的调用函数解决,其中还有运用数学公式解决,这里没有介绍,有兴趣的可以去了解了解。