数学建模之Python-支持向量回归(SVM)
前言:
本文共介绍了svm的两个重要应用
1.分类问题
2.回归问题
一、支持向量机的分类问题
#程序文件Pex19_1.py
from sklearn import datasets, svm, metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import numpy as np
iris=datasets.load_iris()
print(iris)
x=iris.data; y=iris.target
parameters = {'kernel':('linear','rbf'), 'C':[1,10,15]}
svc=svm.SVC(gamma='scale')
clf=GridSearchCV(svc,parameters,cv=5) #cv为交叉验证参数,为5折
clf.fit(x,y)
print("最佳的参数值:", clf.best_params_)
print("score:",clf.score(x,y))
yh=clf.predict(x); print(yh) #显示分类的结果
print("预测准确率:",metrics.accuracy_score(y,yh))
print("误判的样本点为:",np.where(yh!=y)[0]+1)
from sklearn import datasets, svm
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import numpy as np
iris=datasets.load_iris()
x=iris.data; y=iris.target
clf=svm.LinearSVC(C=1,max_iter=10000)
clf.fit(x,y); yh=clf.predict(x); print(yh)
print("预测的准确率:",clf.score(x,y))
二、支持向量回归分析
#程序文件Pex19_2.py
import numpy as np
import pylab as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVR
np.random.seed(123)
x=np.arange(200).reshape(-1,1)
y=(np.sin(x)+3+np.random.uniform(-1,1,(200,1))).ravel()
model = SVR(gamma='auto'); print(model)
model.fit(x,y); pred_y = model.predict(x)
print("原始数据与预测值前15个值对比:")
for i in range(15): print(y[i],pred_y[i])
plt.rc('font',family='SimHei'); plt.rc('font',size=15)
plt.scatter(x, y, s=5, color="blue", label="原始数据")
plt.plot(x, pred_y, '-r*',lw=1.5, label="预测值")
plt.legend(loc=1)
score=model.score(x,y); print("score:",score)
ss=((y-pred_y)**2).sum() #计算残差平方和
print("残差平方和:", ss)
plt.show()
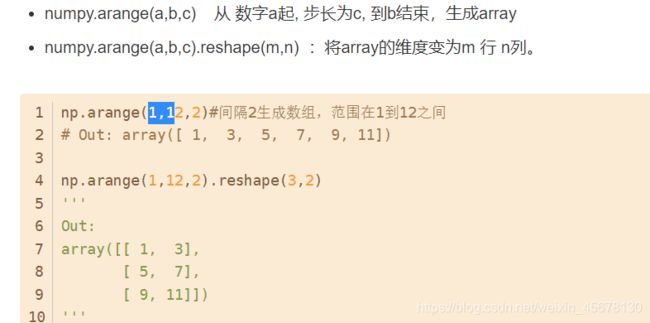
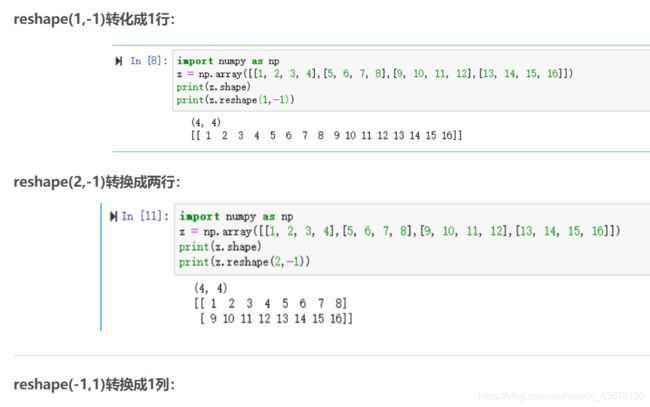
代码补充知识