数据结构与算法(五):哈希表
如有理解不对,欢迎评论留言。
文章目录
- 1.概述
- 2.哈希函数
-
- 2.1 字符串转数字
- 3.基本过程
- 4. 封装哈希表
在此之前,先简单概述下整个基本过程(深入链地址法为例):
插入:输入键值对,根据键key通过哈希函数生成对应的HashCode,将HashCode哈希化生成索引,在数组对应索引处的位置生成数组(链表)添加数组单元,存储键和值。
删除:同理key转换为对应索引,直接往索引处查找
1.概述
哈希表在数据结构中有着非常重要的地位,因为它有着非常高的查找、插入、删除效率,这也是我们经常使用它的原因。
哈希表存储的是一个个键值对,即key,value
哈希表是基于数组进行实现的,因为数组它具有一个优点,就是可以直接通过数据的索引直接进行查找,这样是非常高效的。
但是数组它的插入和删除就略显笨拙了,它需要对整个数组进行遍历,找到对应的位置进行插入或删除,然后还会影响之后的所有元素产生移动。如
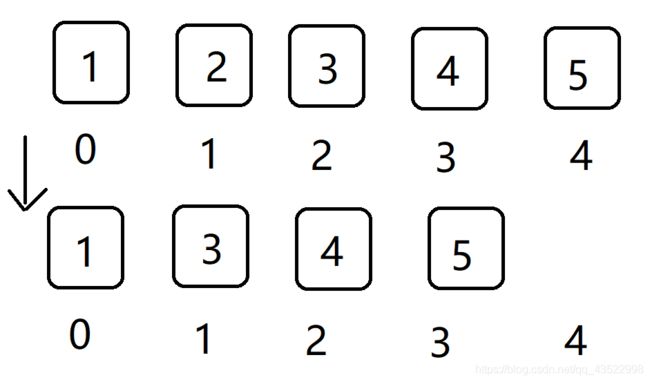
原数组删除第二个元素2时,后面所有的元素都需往前移。也就是arr[n]=a[n+1],这样效率非常低。
所以哈希表对此做出了改变,接着看。
2.哈希函数
数组每次删除或者添加元素都会影响其他元素其实就是因为有序的下标,一个元素的删除和添加会造成其他元素的下标不有序,从而向有序发生变化。
所以哈希表保留了按照索引快速查找的方法,但是去除了索引的有序性。
还是会有疑问,比如那索引怎么产生的,冲突了怎么办…
2.1 字符串转数字
哈希表里保存的是键值对,而键key也不一定是数字,怎么做下标? 这就要通过一个函数将其转为数字,也就是我们常说的哈希函数。
先来封装一个哈希函数
function hashFunction(str, range) {
// 1.定义哈希变量
let hashCode = 0;
// 2.霍纳算法,计算hashCode值
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i)
}
// 3.取余操作
let index = hashCode % range;
return index;
}
这个哈希函数的功能就是将输入的字符串str,按照一定的转换转为0-range内的数字。那怎么实现的呢?
如输入的str为 ‘hello’,一堆字母组成的一串字符串,字母和数字挂钩的话就可以想到用字符编码来进行转换,这里用的Unicode编码,即charCodeAt。
如hello可以得到 104 101 108 108 111.
方案
得到了这些数字那怎么联合呢。
方案一:简单的方法,加起来。104+101+108+108+111=532;
方案二:幂的连乘。即104*10^4 + 101 *10^3 +108 * 10^2 +108 * 10 + 111 * 10^0
方案一太简单了,直接相加取得的数值不大,很容易造成重复,唯一性不大
所以选第二种方案,
第二种方案这里写了霍纳算法,霍纳算法是什么,为什么需要?
霍纳算法
其实就是提公因式,将多次乘法转化为更少次的乘法
如x^4 + x^3 + x^2 +x^1=x(x(x(x+1)+1)+1)
可以看到这里将6(3+2+1)次乘法转为了3次乘法。
因为在计算机中,乘法的运算更加消耗性能,所以用霍纳算法可以优化性能。
但是第二种方案也有问题,就是数值太大,虽然唯一性高但是这么大的内存太占内存,所以需要对其进行哈希化
哈希化
哈希化就是对其进行压缩,压缩到想要的大小范围内,也就是上述给定的range内。这里用到的是取余运算。
这里的range一般取质数,因为质数可以让取余后的数处于均匀分布。取余后的数即为插入或查找的索引
3.基本过程
冲突
上述说完就可以生成对应存储的索引,但是肯定会产生冲突,因为取余后的索引肯定会重复,那怎么添加呢。
有两种方法:
1.深入链地址法
2.深入开放地址法
深入开放地址法简单的来说就是索引遇到冲突了然后就给索引+1或+2,但是也比较局限,只能放少量数据,数据一多就需要频繁扩容。
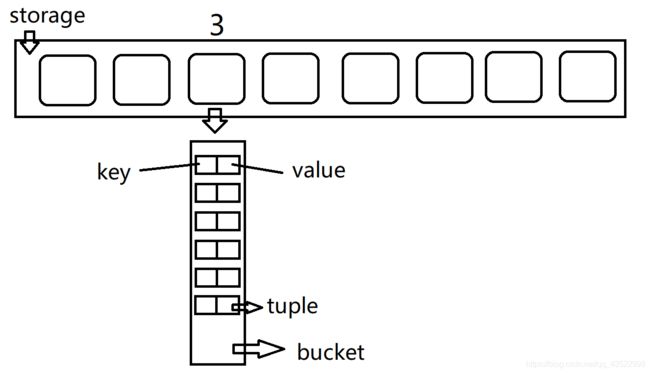
具体以深入链地址法为例
如上,当生成同索引为3时,这时在数组storage 中3的位置创建一个数组(链表)bucket,用来装这些索引都为三的键值对,而键和值又分别存在bucket内的子数组tuble中,这里bucket可以用数组,也可以用链表,因为如果都是从上往下遍历的话效率是差不多的。
4. 封装哈希表
这里以bucket为数组为例
<script>
function HashTable() {
this.storage = [];
this.count = 0;
this.limit = 7;
// 1.哈希函数
HashTable.prototype.hashFun = function (str, range) {
// 定义hashCode
let hashCode = 0;
// 霍纳算法,计算hashCode
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = hashCode * 37 + str.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 3.取余操作
let index = hashCode % range;
return index;
}
// 2.插入修改操作
HashTable.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
// 1.获取index
let index = this.hashFun(key, this.limit);
// 2.根据index找bucket
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// 3.判断bucket是否为空,为空则创建新数组
if (bucket == null) {
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
// 4.判断是否修改
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i]
if (tuple[0] === key) {
tuple[1] = value;
return
}
}
// 5.插入操作
bucket.push([key, value]);
this.count += 1;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (this.count > this.limit * 0.7) {
let newLimit = this.isPrime(this.limit * 2)
this.resize(newLimit)
}
}
// 3.查找
HashTable.prototype.get = function (key) {
let index = this.hashFun(key, this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// 数组为空,直接返回
if (bucket === undefined) return undefined;
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] === key)
return tuple[1];
}
// 未找到
return null;
}
// 4.删除
HashTable.prototype.remove = function (key) {
let index = this.hashFun(key, this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// 数组为空,直接返回
if (bucket === undefined) return undefined;
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] === key) {
bucket.splice(i, 1);
this.count -= 1;
// 判断是否需要缩容
if (this.limit >= 7 && this.count < this.limit * 0.25) {
let newLimit = isPrime(Math.floor(this.limit / 2))
this.resize(newLimit)
}
return tuple[1];
}
}
// 未找到
return null;
}
// 5.size
HashTable.prototype.size = function () {
return this.count;
}
// 6.isEmpty
HashTable.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.count === 0;
}
// 7.修改容量
HashTable.prototype.resize = function (newlimit) {
// 创建老数组指向当前数组
let oldStorage = this.storage;
// 当前数组指向空
this.storage = [];
// 重置属性
this.count = 0;
this.limit = newlimit;
for (let i = 0; i < oldStorage.length; i++) {
let bucket = oldStorage[i];
if (bucket == null) {
continue;
}
else {
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i];
this.put(tuple[0], tuple[1])
}
}
}
}
// 8.判断是否是质数
HashTable.prototype.isPrime = function (num) {
if (num < 2) return false;
if (num === 2) return true;
let temp = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(num))
for (let i = 2; i < temp; i++) {
if (num % i === 0)
return isPrime(num + 1);
}
return num;
}
}
</script>