基于LSTM的IMDB电影评论情感分析
基于LSTM的IMDB电影评论情感分析
步骤
- 加载数据 (50K IMDB Movie Review)
- 数据清洗
- 编码“情感”
- 数据集划分(训练集和测试集)
- 对评论进行分词和截断/补零操作
- 构建神经网络模型
- 训练模型并测试
导入相关工具箱
import pandas as pd # to load dataset
import numpy as np # for mathematic equation
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords # to get collection of stopwords
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # for splitting dataset
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer # to encode text to int
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences # to do padding or truncating
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential # the model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, LSTM, Dense,Dropout # layers of the architecture
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint # save model
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model # load saved model
import re
预览数据集
data = pd.read_csv('IMDB Dataset.csv')
print(data)
Stop Word is a commonly used words in a sentence, usually a search engine is programmed to ignore this words (i.e. "the", "a", "an", "of", etc.)
设置停用词,英文中常见的停用词
此处需要下载nltk的stopwords,我选择了百度网盘,直接下载然后放到一个文件夹中D:\nltk_data\corpora
#nltk.download('stopwords')
english_stops = set(stopwords.words('english'))
数据清洗
原始评论数据并不“干净”,存在很多html标签、数字、大写字母、标点符号等等。预处理中需要对评论做预处理,包括去掉html标签,过滤掉停用词,删除标点和数字,将大写字母转成小写
编码正负情感
将正面和负面情感编码成整数,这里0代表负面情感negative,1代表正面情感(positive)
def load_dataset():
df = pd.read_csv('IMDB Dataset.csv')
x_data = df['review'] # Reviews/Input
y_data = df['sentiment'] # Sentiment/Output
# PRE-PROCESS REVIEW
x_data = x_data.replace({'<.*?>': ''}, regex = True) # remove html tag
x_data = x_data.replace({'[^A-Za-z]': ' '}, regex = True) # remove non alphabet
x_data = x_data.apply(lambda review: [w for w in review.split() if w not in english_stops]) # remove stop words
x_data = x_data.apply(lambda review: [w.lower() for w in review]) # lower case
# ENCODE SENTIMENT -> 0 & 1
y_data = y_data.replace('positive', 1)
y_data = y_data.replace('negative', 0)
return x_data, y_data
x_data, y_data = load_dataset()
print('Reviews')
print(x_data, '\n')
print('Sentiment')
print(y_data)
划分数据集
80% 作为训练集
20% 作为测试集
,使用Scikit-Learn中的 train_test_split 方法。
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data, test_size = 0.2)
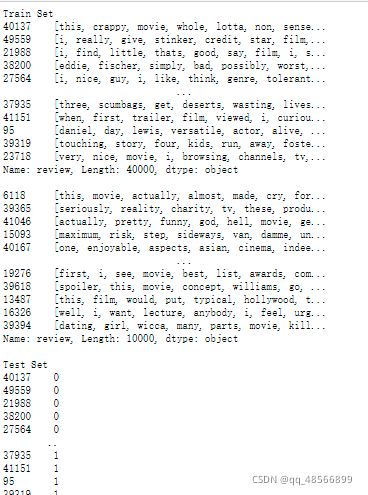
print('Train Set')
print(x_train, '\n')
print(x_test, '\n')
print('Test Set')
print(y_train, '\n')
print(y_test)
该函数能够输出训练集中单条评论最多的词语个数
def get_max_length():
review_length = []
for review in x_train:
review_length.append(len(review))
return int(np.ceil(np.mean(review_length)))
分词以及截断和补零
# ENCODE REVIEW
token = Tokenizer(lower=False) # no need lower, because already lowered the data in load_data()
token.fit_on_texts(x_train)
x_train = token.texts_to_sequences(x_train)
x_test = token.texts_to_sequences(x_test)
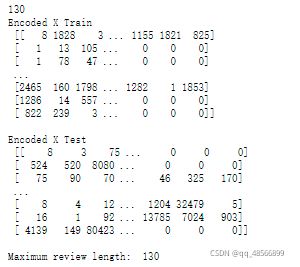
max_length = get_max_length()
print(max_length)
x_train = pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=max_length, padding='post', truncating='post')
x_test = pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen=max_length, padding='post', truncating='post')
total_words = len(token.word_index) + 1 # add 1 because of 0 padding
print('Encoded X Train\n', x_train, '\n')
print('Encoded X Test\n', x_test, '\n')
print('Maximum review length: ', max_length)
构建深度神经网络模型
Embedding Layer
LSTM Layer
Dense Layer
怎么调参:
EMBED_DIM
LSTM_OUT:LSTM输出维度,可以修改
深度可以改变:增减LSTM层,但是数据较少,过于多的层数会出现过拟合的现象,对于该小实验,不用过多的层数
input_length:输入单词的长度,原本为130,可以设的更小一点
epochs可以改为10,到10次迭代的时候可能收敛。
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(128, return_sequences=True)):可以修改为双向的LSTM
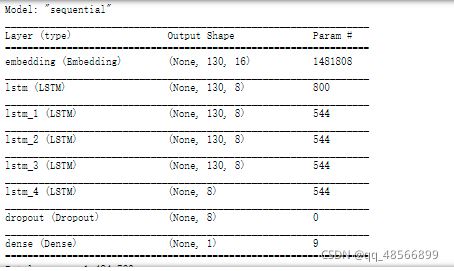
# ARCHITECTURE
EMBED_DIM =16
LSTM_OUT = 8
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(total_words, EMBED_DIM, input_length = max_length))
model.add(LSTM(LSTM_OUT, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(LSTM_OUT, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(LSTM_OUT, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(LSTM_OUT, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(LSTM_OUT))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(optimizer = Adam(1e-3), loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])#metrics分类精度
print(model.summary())
训练模型
batch_size 设置为128 ,epochs设置为5
添加 checkpoint当每个epoch训练完成精度有提升时,就更新保存的模型
epoches5轮训练
batch_size每次送入128个进入模型训练,cpu好就可以设置大一些
checkpoint每轮跑完训练好的模型进行保存,save_best_only=true最后只保存精度最高的模型
文件下有一个目录,模型自动存储在models/LSTM.h5,下次可以不用训练了,每次直接调用模型就可以了。
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(
'models/LSTM.h6',
monitor='accuracy',
save_best_only=True,
verbose=1
)
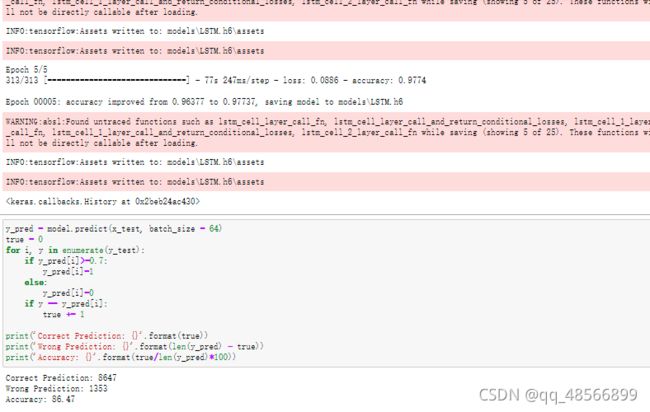
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size = 128, epochs = 5, callbacks=[checkpoint])
y_pred = model.predict(x_test, batch_size = 64)
true = 0
for i, y in enumerate(y_test):
if y_pred[i]>=0.7:
y_pred[i]=1
else:
y_pred[i]=0
if y == y_pred[i]:
true += 1
print('Correct Prediction: {}'.format(true))
print('Wrong Prediction: {}'.format(len(y_pred) - true))
print('Accuracy: {}'.format(true/len(y_pred)*100))
测试模型
测试样本测试,输出精度
y_pred = model.predict(x_test, batch_size = 64)
y_pred
y_pred = model.predict(x_test, batch_size = 128)
y_pred=np.argmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
true = 0
for i, y in enumerate(y_test):
if y == y_pred[i]:
true += 1
print('Correct Prediction: {}'.format(true))
print('Wrong Prediction: {}'.format(len(y_pred) - true))
print('Accuracy: {}'.format(true/len(y_pred)*100))
加载已训练好的模型
用已经训练好的深度模型去预测一条新的电影评论的情感
loaded_model = load_model('models/LSTM.h5')
自行输入一条评论(用英文)
review = str(input('Movie Review: '))
预测之前这条新的评论也需要进行预处理
# Pre-process input
regex = re.compile(r'[^a-zA-Z\s]')
review = regex.sub('', review)
print('Cleaned: ', review)
words = review.split(' ')
filtered = [w for w in words if w not in english_stops]
filtered = ' '.join(filtered)
filtered = [filtered.lower()]
print('Filtered: ', filtered)
对这条新评论进行分词和编码
tokenize_words = token.texts_to_sequences(filtered)
tokenize_words = pad_sequences(tokenize_words, maxlen=max_length, padding='post', truncating='post')
print(tokenize_words)
结果显示了预测的置信度分数 confidence score
result = loaded_model.predict(tokenize_words)
print(result)
若置信度分数接近0则评论为负面 negative. 若置信度分数接近1则评论为正面 positive. 这里选择 0.7 作为置信度阈值,如果分数大于0.7判定为正面,如果分数小于0.7则判定为负面
if result >= 0.7:
print('positive')
else:
print('negative')