Leetcode刷题04-字符串
字符串
基础知识
简介
1.介绍
字符串:简称为串,是由零个或多个字符组成的有限序列。一般记为s = “a1a2…an”
- 字符串名称:字符串定义中的s就是字符串的名称
- 字符串的值:"a1a2…an"组成的字符序列就是字符串的值,一般用双引号括起来
- 字符变量:字符串每一个位置上的元素都是一个字符变量。字符ai可以是字母、数字或者其他字符。i是该字符在字符串中的位置。
- 字符串的长度:字符串中字符的数目n称为字符串的长度
- 空串:零个字符构成的串也称为空字符串,它的长度为0,可以表示为""
- 子串:字符串中任意个连续的字符组成的子序列称为该字符串的子串。并且有两种特殊子串,为前缀和后缀
- 主串:包含子串的字符串相应的称为主串
根据字符串的特点,可以将字符串问题分为以下几种:
- 字符串匹配问题
- 子串相关问题
- 前缀/后缀相关问题
- 回文串相关问题
- 子序列相关问题
2.字符串的比较
字符串之间的比较是通过组成字符串的字符之间的字符编码来决定的,而字符编码指的是字符在对应字符集中的序号。
def strcmp(str1, str2):
index1, index2 = 0, 0
while index1 < len(str1) and index2 < len(str2):
if ord(str1[index1]) == ord(str2[index2]):
index1 += 1
index2 += 2
elif ord(str1[index1]) < ord(str2[index2]):
return -1
else:
return 1
if len(str1) < len(str2):
return -1
elif len(str1) > len(str2):
return 1
else:
return 0
字符编码:计算机中常用字符使用的是ASCII码,但是只能解决以英文为主的语言。为了解决中文编码,我国制定了GB2312、GBK、GB18030等中文编码标准,为了解决全世界语言问题,出现了Unicode编码,常见的Unicode编码是UTF-8,把一个Unicode字符根据不同的数字大小编码成1-6个字节,常用的英文字母被编码成1个字节,汉字通常是3个字节。
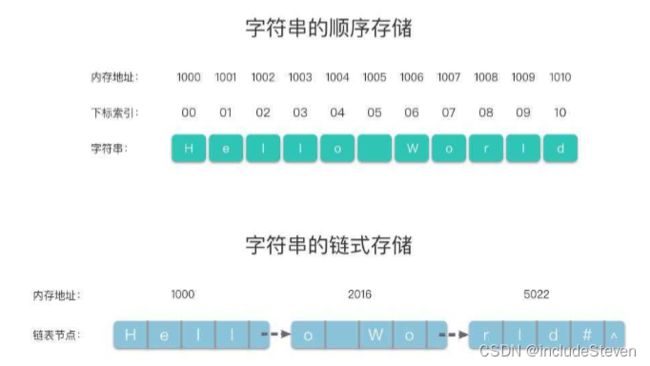
3.字符串的存储结构
字符串的存储结构跟线性表相同,分为顺序存储结构和链式存储结构
字符串匹配问题
字符串匹配:又称模式匹配。可以简单理解为,给定字符串T和p,在主串T中寻找子串p。主串T被称为文本串,子串p称为模式串。
根据模式串的个数,字符串匹配问题分为单模式串匹配问题和多模式串匹配问题。
1.单模式串匹配问题
定义:给定一个文本串T=t1t2…tn,再给定一个特定模式串p=p1p2…pn.要求从文本串T找出特定模式串p的所有出现位置。
-
基于前缀搜索方法:在搜索窗口内从前向后逐个读入文本字符,搜索窗口中文本和模式串的最长公共前缀。
- 著名的KMP算法和更快的Shift-Or算法使用的就是这种方法。
-
基于后缀搜索方法:在搜索窗口内从后向前(沿着文本的反向)逐个读入文本字符,搜索窗口中文本和模式串的最长公共后缀。使用这种搜索算法可以跳过一些文本字符,从而具有亚线性的平均时间复杂度。
- 著名的BM算法、Horspool算法、Sunday算法都是用了这种方法
-
基于子串搜索方法:在搜索窗口从后向前逐个读入文本字符,搜索满足既是窗口中文本的后缀,也是模式串的子串的最长字符串。该方法也具有亚线性的平均时间复杂度。主要缺点在于需要识别模式串的所有子串,这是一个非常复杂的问题。
- Rabin-Karp算法、BDM算法、BNDM算法和BOM算法使用的是这种思想,其中Rabin-Karp算法使用了基于散列的子串搜索算法。
2.多模式串匹配问题
多模式匹配算法大多使用了一种基本的数据结构:字典树(Trie)。著名的AC自动机就是在KMP算法的基础上,与字典树结构相结合诞生的。而AC自动机算法也是多模式串匹配算法中最有效的算法之一。
所以学习多模式匹配算法,重点是掌握字典树和AC自动机算法。
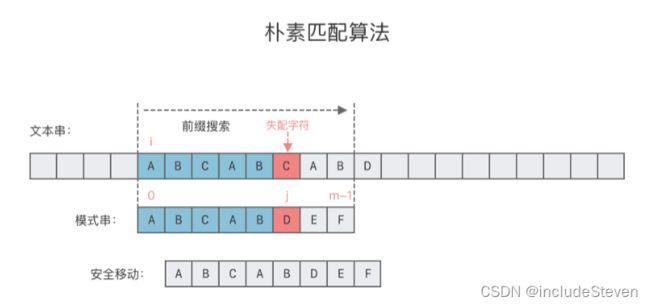
3.单模式串朴素匹配算法
Brute Force算法:暴力匹配算法,也可以叫做朴素匹配算法。
BF算法思想:
def bruteForce(T: str, p: str) -> int:
n, m = len(T), len(p)
i, j = 0, 0
while i < n and j < m:
if T[i] == p[j]:
i += 1
j += 1
else:
i = i - (j - 1)
j = 0
if j == m:
return i - j
return -1
最坏时间复杂度为O(m * n),最理想时间复杂度为O(m),平均时间复杂度O(n + m)
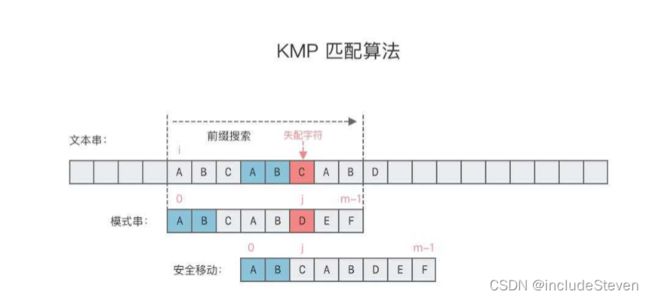
4.单模式串KMP匹配算法
KMP算法思想:对于给定文本串T与模式串p,当发现文本串T的某个字符与模式串p不匹配的时候,可以利用匹配失败后的信息,尽量减少模式串与文本串的匹配次数,避免文本串位置的回退,以达到快速匹配的目的。
朴素匹配算法的缺陷:当文本串与模式串某个字符不匹配时,指向文本串的指针i需要回退到之前匹配开始位置的下一个位置。
KMP算法的改进:利用了每一次匹配失败的信息,主串的某个子串等于模式串的某一个前缀。也就是T[i: i + j] == p[0: j]
KMP算法利用了匹配失败的信息,对模式串p进行了预处理,计算出一个部分匹配表,用一个数组next记录。在每次匹配失败时,不回退文本串的指针i,而是根据next数组中匹配失败j的前一个位置的值,即next[j - 1]来决定模式串可以向右移动的位数。
比如上述示例中模式串p在j=5匹配失败,则说明文本中子串T[i: i + 5]和模式串p[0: 5]字符一致,根据部分匹配表中next[4] = 2,所以不用回退i,而是将j移动到下标为2的位置,让T[i + 5]对准p[2]继续比对。
def generateNext(p: str):
m = len(p)
next = [0 for _ in range(m)]
left = 0
for right in range(1, m):
while left > 0 and p[left] != p[right]:
left = next[left - 1]
if p[left] == p[right]:
left += 1
next[right] = left
return next
def kmp(T: str, p: str) -> int:
n, m = len(T), len(p)
next = generateNext(p)
j = 0
for i in range(n):
while j > 0 and T[i] != p[j]:
j = next[j - 1]
if T[i] == p[j]:
j += 1
if j == m:
return i - j + 1
return -1
时间复杂度为O(n + m)
题目解析
验证回文串
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解析思路及代码
思路:有两种方法:
- 对字符串进行预处理,去掉空格,将字母都变成小写,然后将字符串翻转判断与原字符串是否相等。
- 使用双指针直接判断,i指向字符串第一个位置,j指向字符串最后一个位置,如果不是字母或数字就跳过,然后判断i和j指向字符的小写是否相等,不相等返回false,否则继续判断,直到i == j返回true。
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
StringBuffer sgood = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++ ) {
if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(i))) {
sgood.append(Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(i)));
}
}
int l = 0, r = sgood.length() - 1;
while (l < r) {
if (sgood.charAt(l) != sgood.charAt(r)) return false;
l ++;
r --;
}
return true;
}
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
n = len(s)
l, r = 0, n - 1
while l < r:
while l < r and not s[l].isalnum():
l += 1
while l < r and not s[r].isalnum():
r -= 1
if l < r:
if s[l].lower() != s[r].lower():
return False
else:
l += 1
r -= 1
return True
翻转字符串里的单词
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
思路:
- 利用语言特定:分割字符串、翻转字符串、join等
- 自己编写函数实现
public String reverseWords(String s) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList(s.split("\\s+"));
Collections.reverse(words);
return String.join(" ", words);
}
public String reverseWords(String s) {
int l = 0, r = s.length() - 1;
while (l <= r && s.charAt(l) == ' ') l ++ ;
while (l <= r && s.charAt(r) == ' ') r -- ;
List<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (l <= r) {
if (s.charAt(l) != ' ') {
sb.append(s.charAt(l));
} else {
if (sb.length() > 0) {
words.add(sb.toString());
}
sb = new StringBuilder();
}
l ++ ;
}
if (sb.length() > 0) words.add(sb.toString());
// reverse
l = 0;
r = words.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
String tmp = words.get(l);
words.set(l, words.get(r));
words.set(r, tmp);
l ++ ;
r -- ;
}
return String.join(" ", words);
}
class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
return " ".join(reversed(s.split()))
验证回文字符串 Ⅱ
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
带贪心的双指针:双指针分别指向字符串第一个位置和最后一个位置,然后判断对应字符是否相等,如果不相等,则分为两种情况,一种是删除左边指针字符,一种是删除右边指针字符,然后判断是否是回文串返回即可。
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
int l = 0, r = s.length() - 1;
while (l < r) {
char c1 = s.charAt(l), c2 = s.charAt(r);
if (c1 == c2) {
l ++ ;
r -- ;
} else {
return validPalindrome(s, l, r - 1) || validPalindrome(s, l + 1, r);
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean validPalindrome(String s, int low, int high) {
for (int i = low, j = high; i < j; i ++ , j -- ) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) return false;
}
return true;
}
class Solution:
def validPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
def check(low, high):
i, j = low, high
while i < j:
if s[i] != s[j]:
return False
i += 1
j -= 1
return True
l, r = 0, len(s) - 1
while l < r:
if s[l] == s[r]:
l += 1
r -= 1
else:
return check(l + 1, r) or check(l, r - 1)
return True
Excel表列名称
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
思想:本质上就是26进制的问题。需要注意在取模时需要先减去1保证当columnNumber为26时返回26,而不是0
public String convertToTitle(int columnNumber) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (columnNumber > 0) {
int c = (columnNumber - 1) % 26 + 1;
sb.insert(0, (char)(c - 1 + 'A'));
columnNumber = (columnNumber - c) / 26;
}
return sb.toString();
}
class Solution:
def convertToTitle(self, columnNumber: int) -> str:
ans = list()
while columnNumber > 0:
a0 = (columnNumber - 1) % 26 + 1
ans.append(chr(a0 - 1 + ord('A')))
columnNumber = (columnNumber - a0) // 26
return "".join(ans[::-1])
字符串解码
1.题目描述
题目链接
2.解题思路及代码
思路:处理顺序是先处理最里面括号的字母,再处理外面的字母,因此使用递归处理。如果遇到数字位,接下来一定是括号,然后递归解析下面的内容。
也可以使用栈实现。
class Solution {
String src;
int ptr;
public String decodeString(String s) {
src = s;
ptr = 0;
return getString();
}
public String getString() {
if (ptr == src.length() || src.charAt(ptr) == ']') {
return "";
}
char cur = src.charAt(ptr);
int repTime = 1;
String res = "";
if (Character.isDigit(cur)) {
repTime = getDigits();
ptr ++ ;
String str = getString();
ptr ++ ;
while (repTime-- > 0) {
res += str;
}
} else if (Character.isLetter(cur)) {
res = String.valueOf(src.charAt(ptr ++ ));
}
return res + getString();
}
public int getDigits() {
int res = 0;
while (ptr < src.length() && Character.isDigit(src.charAt(ptr))) {
res = res * 10 + src.charAt(ptr ++ ) - '0';
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
NUM = "0123456789"
stack, num, str_ = [], '', ''
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] in NUM:
num += s[i]
if s[i + 1] not in NUM:
stack.append(int(num))
num = ''
elif s[i] == ']':
str_ = ''
while stack[-1] != '[':
str_ = stack.pop() + str_
stack.pop()
stack.append(str_ * stack.pop())
else:
stack.append(s[i])
return "".join(stack)