YOLOv5添加注意力机制
YOLOv5加入注意力机制可分为以下三个步骤:
1.common.py中加入注意力模块
2.yolo.py中增加判断条件
3.yaml文件中添加相应模块
一、CBAM注意力机制添加
(1)在common.py中添加可调用的CBAM模块
1.打开models文件夹中的common.py文件
2.将下面的CBAMC3代码复制粘贴到common.py文件中
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.f1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // ratio, 1, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.f2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // ratio, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
# 写法二,亦可使用顺序容器
# self.sharedMLP = nn.Sequential(
# nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // ratio, 1, bias=False), nn.ReLU(),
# nn.Conv2d(in_planes // rotio, in_planes, 1, bias=False))
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = self.sigmoid(avg_out + max_out)
return torch.mul(x, out)
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
out = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
out = self.sigmoid(self.conv(out))
return torch.mul(x, out)
class CBAMC3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(CBAMC3, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)])
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c2, 16)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(7)
# self.m = nn.Sequential(*[CrossConv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g, 1.0, shortcut) for _ in range(n)])
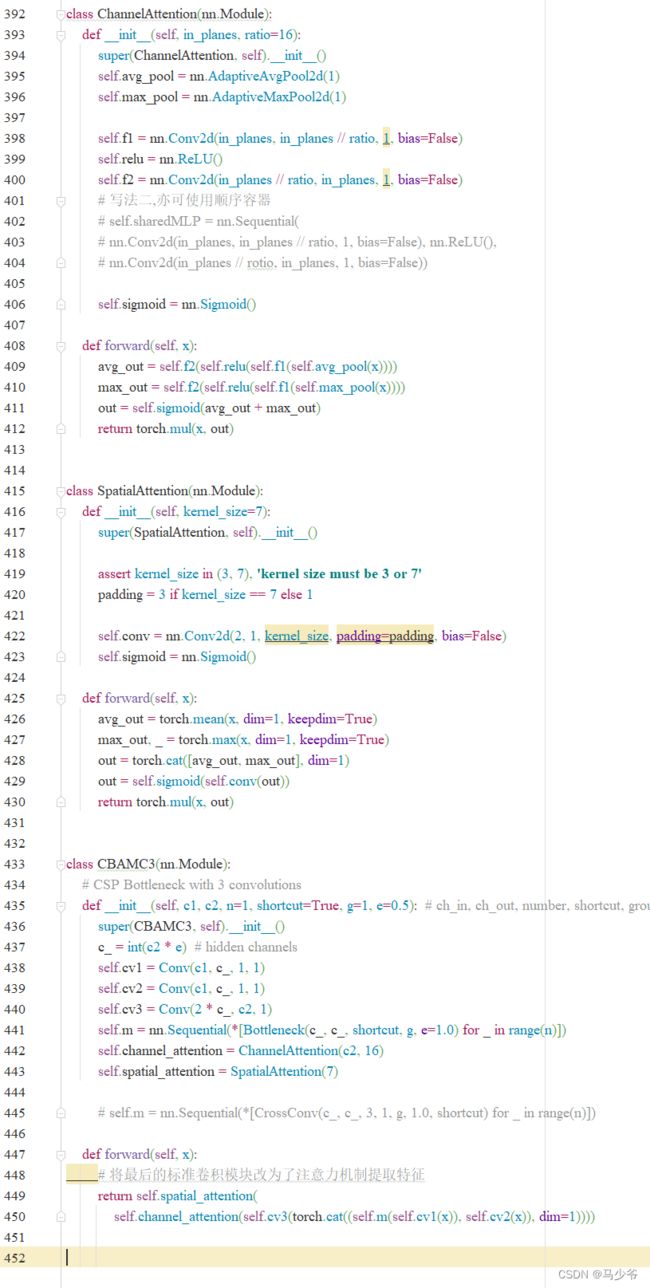
def forward(self, x):
# 将最后的标准卷积模块改为了注意力机制提取特征
return self.spatial_attention(
self.channel_attention(self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))))
如下图所示,本文这里是将其粘贴到了common.py的末尾
(2)向yolo.py文件添加CBAMC3判断语句
1.打开models文件夹中的yolo.py文件
2.分别在239行和245行添加CBAMC3,如下图所示
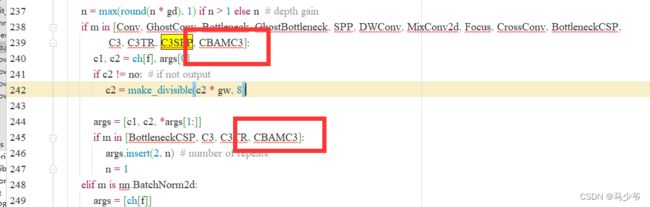
同样改完之后记得点保存
3)修改yaml文件
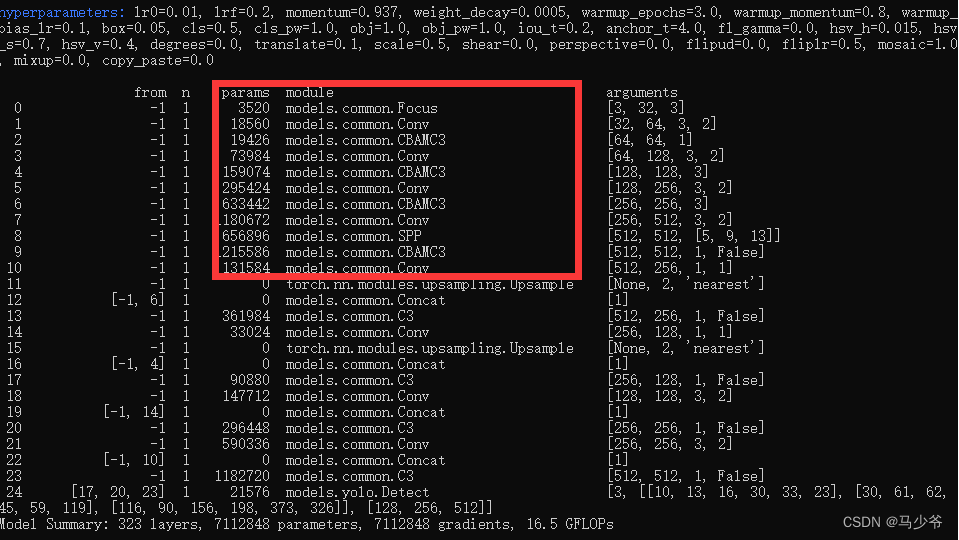
注意力机制可以添加在backbone,Neck,Head等部分,大家可以在yaml文件中修改网络的结构、添加其他模块等等,接下来本文将以向主干网络(backbone)添加CBAM模块为例,本文介绍的只是其中一种添加方式
1.在yolov5-5.0工程文件夹下,找到models文件夹下的yolov5s.yaml文件
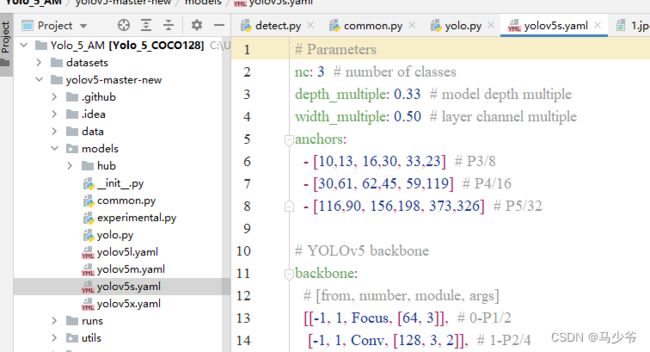
2.backbone主干网络中的4个C3模块改为CBAMC3,如下图所示:
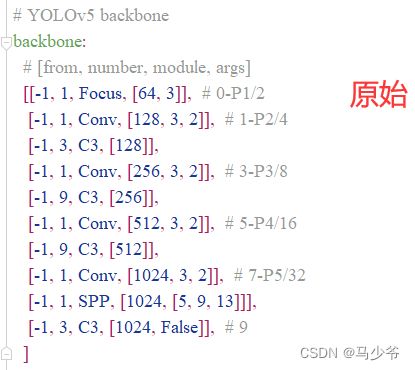

这样我们就在yolov5s主干网络中添加了CBAM注意力机制
接下来开始训练模型,我们就可以看到CBAMC3模块已经成功添加到主干网络中了
二、SE注意力机制添加
(步骤和CBAM相似)
(1)在common.py中添加可调用的SE模块
1.打开models文件夹中的common.py文件
2.将下面的SE代码复制粘贴到common.py文件中
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, r=16):
super(SE, self).__init__()
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.l1 = nn.Linear(c1, c1 // r, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(c1 // r, c1, bias=False)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
print(x.size())
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avgpool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.l1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
y = self.l2(y)
y = self.sig(y)
y = y.view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
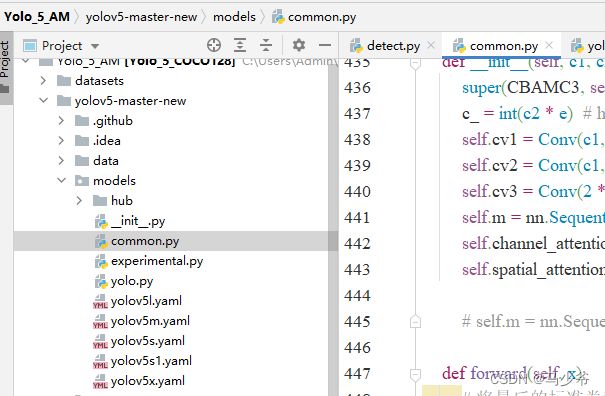
如下图所示,本文这里是将其粘贴到了common.py的末尾

(2)向yolo.py文件添加SE判断语句
1.打开models文件夹中的yolo.py文件
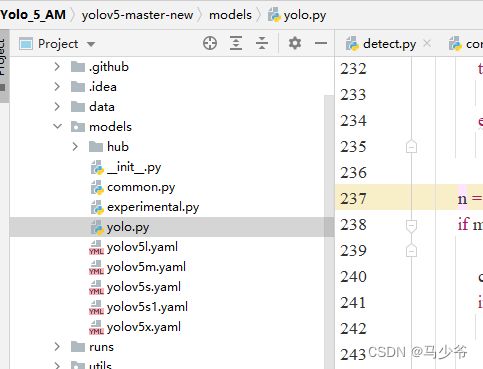
2.分别在238行和245行添加SE,如下图所示
同样改完之后记得点保存
(3)修改yaml文件
注意力机制可以添加在backbone,Neck,Head等部分,大家可以在yaml文件中修改网络的结构、添加其他模块等等。与CBAM的添加过程一样,接下来本文将以向主干网络(backbone)添加SE模块为例,本文介绍的只是其中一种添加方式
1.在yolov5-5.0工程文件夹下,找到models文件夹下的yolov5s.yaml文件
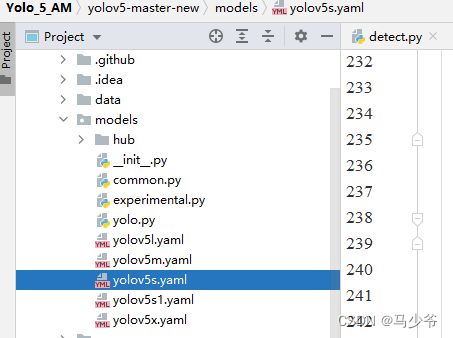
2.backbone主干网络末尾添加下面的代码,如下图所示:
(注意逗号是英文,以及注意对齐)
[-1, 1, SE, [1024, 4]],
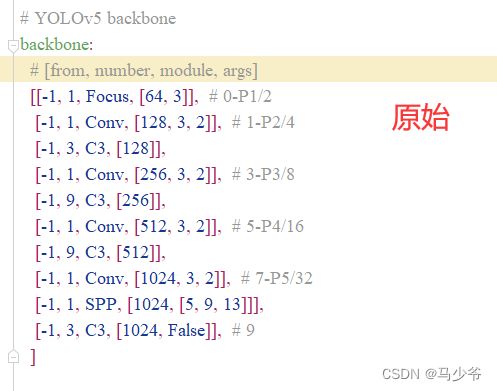

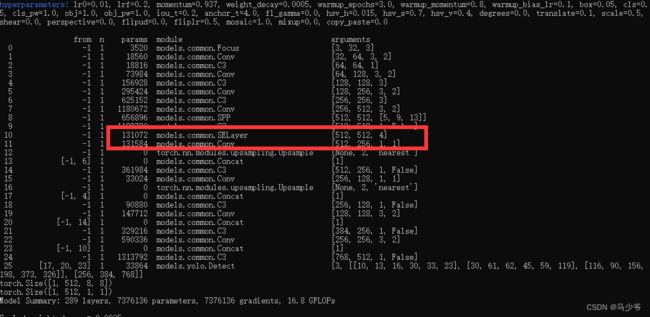
这样我们就在yolov5s主干网络中添加了SE注意力机制
(在服务器上跑代码修改后,记得点击文本编辑器右上角的保存)
接下来开始训练模型,我们就可以看到SE模块已经成功添加到主干网络中了
三、其他几种注意力机制代码
添加过程不再赘述,模仿上方CBAM和SE的添加过程即可
(1)ECA注意力机制代码
class eca_layer(nn.Module):
"""Constructs a ECA module.
Args:
channel: Number of channels of the input feature map
k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size
"""
def __init__(self, channel, k_size=3):
super(eca_layer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
y = self.avg_pool(x)
# Two different branches of ECA module
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
# Multi-scale information fusion
y = self.sigmoid(y)
x=x*y.expand_as(x)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
(2)CA注意力机制代码:
class h_sigmoid(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_sigmoid, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return self.relu(x + 3) / 6
class h_swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_swish, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid = h_sigmoid(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.sigmoid(x)
class CoordAtt(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, reduction=32):
super(CoordAtt, self).__init__()
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, inp // reduction)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inp, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.act = h_swish()
self.conv_h = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_w = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
n, c, h, w = x.size()
x_h = self.pool_h(x)
x_w = self.pool_w(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.act(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
a_h = self.conv_h(x_h).sigmoid()
a_w = self.conv_w(x_w).sigmoid()
out = identity * a_w * a_h
return out
参考文献:https://blog.csdn.net/thy0000/article/details/125016410