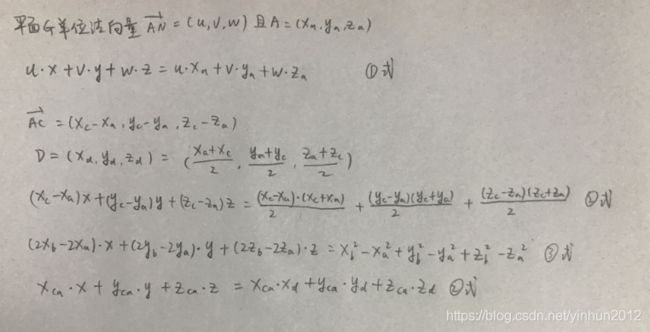几何向量:空间三角形外心和法向量
这次来计算一下世界空间三角形的外心(也就是外接圆的圆心)和外心为起点的平面法向量。
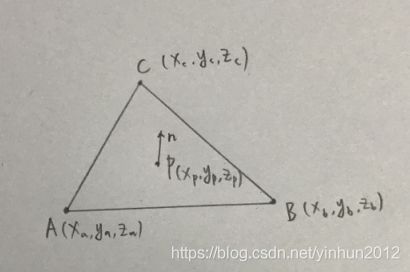
问题:假设我们世界空间中有一个任意三角形,且已知三角形各个顶点ABC的坐标,求三角形的外心P和外心所在的法向量n,如下图:
如果依稀还记得初中几何,就知道一个平面三角形外心计算规则:三角形任意两边的中垂线交点,则为外心。三角形所在平面法向量:以一顶点为端点的逆时针方向两条边的叉积则为平面法向量。
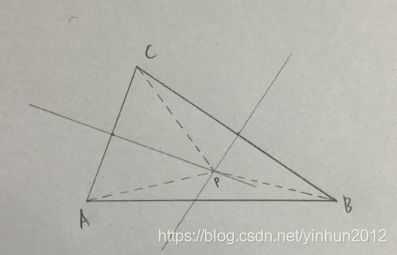
其实一眼就看得出来原理:两条中垂线组成的三角形APC、BPC为等腰三角形,则AP=BP=CP,即P点位外心。
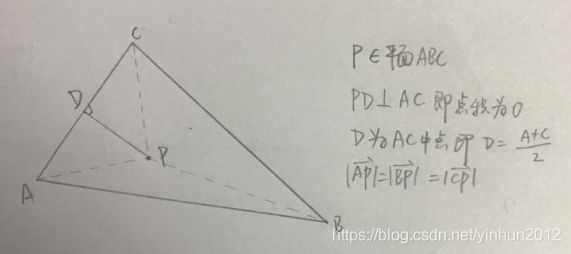
那么我们任意选取三角形一边如AC,计算中垂线DP,根据AP=BP,则可以求出外心P的坐标,如下:
假设△ABC的外心为P(x,y,z),条件整理如下:
1.△ABC各个顶点坐标已知
2.P(x,y,z)在△ABC所处的平面中,可以带入平面方程计算(平面方程理解)
3.PD⊥AC,即dot(PD,AC) = 0
4.D = (A+C)/2
5.AP、BP、CP模长相同
将这些条件用来计算P(x,y,z),我们尝试一下:
我们通过条件整理出①②③三个三元一次方程,接下来我们通过三元一次方程求解,如下:
将①②③带入三元一次方程解:
方程的参数和根巨复杂,我自己推导起来都要不停的返回瞄一下是否参数写错了,小伙伴们可能需要很仔细的查看推导过程。
当然我们还是要用c#代码来实现一下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TriangleVerticeCenter : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform TA;
public Transform TB;
public Transform TC;
public Transform TP;
void Start()
{
}
void Update()
{
Vector3 p = CalculateTriangleOutCircleCenter(TA.position, TB.position, TC.position);
TP.position = p;
//PN法向量
Vector3 PB = TB.position - p;
Vector3 PC = TC.position - p;
Vector3 PN = Vector3.Cross(PB, PC).normalized;
Vector3 n = p + PN;
#if UNITY_EDITOR
Debug.DrawLine(TA.position, TB.position, Color.black);
Debug.DrawLine(TB.position, TC.position, Color.black);
Debug.DrawLine(TC.position, TA.position, Color.black);
Debug.DrawLine(TA.position, p, Color.white);
Debug.DrawLine(TB.position, p, Color.white);
Debug.DrawLine(TC.position, p, Color.white);
Debug.DrawLine(p, n, Color.red);
Debug.LogFormat("AP = {0} BP = {1} CP = {2}", Vector3.Distance(TA.position, p), Vector3.Distance(TB.position, p), Vector3.Distance(TC.position, p));
#endif
}
private Vector3 CalculateTriangleOutCircleCenter(Vector3 A, Vector3 B, Vector3 C)
{
float Xa = A.x;
float Ya = A.y;
float Za = A.z;
float Xb = B.x;
float Yb = B.y;
float Zb = B.z;
float Xc = C.x;
float Yc = C.y;
float Zc = C.z;
Vector3 D = (A + C) / 2;
float Xd = D.x;
float Yd = D.y;
float Zd = D.z;
//单位法向量AN
Vector3 AB = B - A;
Vector3 AC = C - A;
Vector3 AN = Vector3.Cross(AB, AC).normalized;
float u = AN.x;
float v = AN.y;
float w = AN.z;
//构建三元一次方程参数
float a = u;
float b = v;
float c = w;
float d = u * Xa + v * Ya + w * Za;
float e = Xc - Xa;
float f = Yc - Ya;
float g = Zc - Za;
float h = (Xc - Xa) * (Xc + Xa) / 2 + (Yc - Ya) * (Yc + Ya) / 2 + (Zc - Za) * (Zc + Za) / 2;
float k = 2 * Xb - 2 * Xa;
float l = 2 * Yb - 2 * Ya;
float m = 2 * Zb - 2 * Za;
float n = Xb * Xb - Xa * Xa + Yb * Yb - Ya * Ya + Zb * Zb - Za * Za;
float[] equa = CalculateTernaryEquation(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, k, l, m, n);
Vector3 P = new Vector3(equa[0], equa[1], equa[2]);
return P;
}
private float[] CalculateTernaryEquation(float a, float b, float c, float d, float e, float f, float g, float h, float k, float l, float m, float n)
{
float z = ((d * e - a * h) * (f * k - e * l) - (h * k - e * n) * (b * e - a * f)) / ((c * e - a * g) * (f * k - e * l) - (b * e - a * f) * (g * k - e * m));
float y = ((d * e - a * h) * (g * k - e * m) - (h * k - e * n) * (c * e - a * g)) / ((b * e - a * f) * (g * k - e * m) - (f * k - e * l) * (c * e - a * g));
float x = 0;
if (a != 0)
x = (d - b * y - c * z) / a;
else if (e != 0)
x = (h - f * y - g * z) / e;
else if (k != 0)
x = (n - l * y - m * z) / k;
return new float[] { x, y, z };
}
}
效果如下:
可以通过图形标注和打印信息看得出来,外接圆心和法向量计算正确。