【负荷预测】布谷鸟(CS)算法优化BP神经网络的负荷及天气预测附Matlab代码
✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机
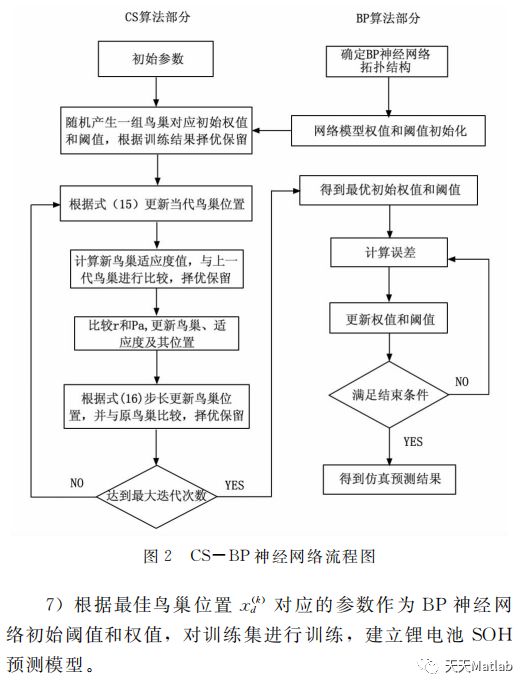
⛄ 内容介绍
锂电池健康状态(SOH)的预测是电动汽车锂电池管理系统的最重要的关键技术之一;传统的误差逆向传播(BP)神经网络容易使权值和阈值陷入局部最优,从而导致预测结果不精确;结合布谷鸟搜索算法(CS)的全局优化能力,提出一种基于CS算法优化BP神经网络的锂电池SOH预测方法,该方法的核心在于优化BP神经网络的初始权值和阈值,从而减小算法对初始值的依赖。
⛄ 部分代码
function [bestnest,fmin]=cuckoo_search(n,inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn) %n为鸟巢数目
if nargin<1, % nargin是用来判断输入变量个数的函数
% Number of nests (or different solutions)
n=25;
end
% Discovery rate of alien eggs/solutions
pa=0.25;
%% Change this if you want to get better results
% Tolerance
Tol=1.0e-5; %为最大迭代次数限制
%% Simple bounds of the search domain
% Lower bounds
nd=22;
Lb=-5*ones(1,nd);
% Upper bounds
Ub=5*ones(1,nd);
%随机产生初始解
% Random initial solutions
for i=1:n,
nest(i,:)=Lb+(Ub-Lb).*rand(size(Lb));
end
%得到当前的最优解
s=nest(j,:);
% This is a simple way of implementing Levy flights
% For standard random walks, use step=1;
%% Levy flights by Mantegna's algorithm
u=randn(size(s))*sigma;
v=randn(size(s));
step=u./abs(v).^(1/beta);
% In the next equation, the difference factor (s-best) means that
% when the solution is the best solution, it remains unchanged.
stepsize=0.01*step.*(s-best);
% Here the factor 0.01 comes from the fact that L/100 should the typical
% step size of walks/flights where L is the typical lenghtscale;
% otherwise, Levy flights may become too aggresive/efficient,
% which makes new solutions (even) jump out side of the design domain
% (and thus wasting evaluations).
% Now the actual random walks or flights
s=s+stepsize.*randn(size(s));
% Apply simple bounds/limits
nest(j,:)=simplebounds(s,Lb,Ub);
end
%% Find the current best nest
function [fmin,best,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,newnest,fitness,inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn)
% Evaluating all new solutions
for j=1:size(nest,1),
fnew=fobj(newnest(j,:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
if fnew<=fitness(j),
fitness(j)=fnew;
nest(j,:)=newnest(j,:);
end
end
% Find the current best
[fmin,K]=min(fitness) ;
best=nest(K,:);
%% Replace some nests by constructing new solutions/nests
function new_nest=empty_nests(nest,Lb,Ub,pa)
% A fraction of worse nests are discovered with a probability pa
n=size(nest,1);
% Discovered or not -- a status vector
K=rand(size(nest))>pa;
% In the real world, if a cuckoo's egg is very similar to a host's eggs, then
% this cuckoo's egg is less likely to be discovered, thus the fitness should
% be related to the difference in solutions. Therefore, it is a good idea
% to do a random walk in a biased way with some random step sizes.
%% New solution by biased/selective random walks
stepsize=rand*(nest(randperm(n),:)-nest(randperm(n),:));
new_nest=nest+stepsize.*K;
% Application of simple constraints
function s=simplebounds(s,Lb,Ub)
% Apply the lower bound
ns_tmp=s;
I=ns_tmp ns_tmp(I)=Lb(I); % Apply the upper bounds J=ns_tmp>Ub; ns_tmp(J)=Ub(J); % Update this new move s=ns_tmp; [1]孙晨, 李阳, 李晓戈, et al. 基于布谷鸟算法优化BP神经网络模型的股价预测[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2016, 33(2):4. ❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料 ❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献