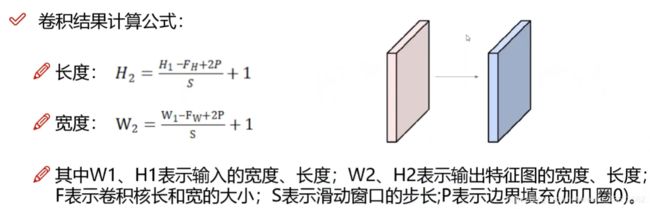
卷积神经网络初解
卷积神经网络入门
这是个初学卷积神经网络的小白
卷积神经网络用于特征提取,卷积是特征提取的一种方法。
输入的是三维的h,w,c的矩阵。
- 输入层
- 卷积层
- 池化层
- 全连接层
输入的是三维的h,w,c的矩阵。
卷积
卷积核即是权重参数矩阵w
计算的是内积,对应位置相乘再相加。rgb三通道单独计算,计算完再加。最后再加上一个偏置b。经过步长移动得到特征矩阵。
卷积核的通道和输入图像通道相同。
一层网络的卷积核可以有多个,得到的特征矩阵维数增加。
- 步长越短,提取的特征越多,加计算越复杂
- 卷积核尺寸
- 边缘填充 越往边界的点利用的次数越少,在矩阵四周加上一圈0,使得原来边界的点利用的多一点
池化
对卷积的结果进行压缩
全连接层
把最后一次池化的结果转化为一维的向量,与输出结果对应
层数只看卷积层和全连接层
一些网络模型
- vgg池化后使特征图翻倍,弥补池化的损失
-残差网络 resnet。层数越高,若损失高,则舍弃这层网络。
感受野
附上minst的卷积神经网络案例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# In[1]:
import tensorflow as tf
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
# In[2]:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=True)
#  # In[3]:
tf.reset_default_graph()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 28,28,1]) #shape in CNNs is always None x height x width x color channels
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 10]) #shape is always None x number of classes
#
# In[3]:
tf.reset_default_graph()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 28,28,1]) #shape in CNNs is always None x height x width x color channels
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 10]) #shape is always None x number of classes
#  # In[4]:
W_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 32], stddev=0.1))#shape is filter x filter x input channels x output channels
#5*5的卷积核心,1通道,32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [32])) #shape of the bias just has to match output channels of the filter
#
# In[4]:
W_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 32], stddev=0.1))#shape is filter x filter x input channels x output channels
#5*5的卷积核心,1通道,32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [32])) #shape of the bias just has to match output channels of the filter
#  # In[8]:
#卷积操作,strides第一个和最后一个都是1,中间两个为左右上下移动的步长
h_conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input=x, filter=W_conv1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + b_conv1
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(h_conv1)
#池化操作
h_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# In[9]:
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(input=x, filter=W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# In[10]:
#Second Conv and Pool Layers
W_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 32, 64], stddev=0.1))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [64]))
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
#First Fully Connected Layer
W_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([7 * 7 * 64, 1024], stddev=0.1))
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) #拉成一条
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
#Dropout Layer 防止过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float") #保留率
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) #当前结果
#Second Fully Connected Layer
W_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1024, 10], stddev=0.1))
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [10]))
#Final Layer
y = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2
# In[11]:
crossEntropyLoss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels = y_, logits = y))
trainStep = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(crossEntropyLoss)#自适应的优化器
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
# In[12]:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
batchSize = 50
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batchSize)
trainingInputs = batch[0].reshape([batchSize,28,28,1])
trainingLabels = batch[1]
if i%100 == 0:
trainAccuracy = accuracy.eval(session=sess, feed_dict={x:trainingInputs, y_: trainingLabels, keep_prob: 1.0})
print ("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, trainAccuracy))
trainStep.run(session=sess, feed_dict={x: trainingInputs, y_: trainingLabels, keep_prob: 0.5})
# In[8]:
#卷积操作,strides第一个和最后一个都是1,中间两个为左右上下移动的步长
h_conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input=x, filter=W_conv1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + b_conv1
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(h_conv1)
#池化操作
h_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# In[9]:
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(input=x, filter=W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# In[10]:
#Second Conv and Pool Layers
W_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 32, 64], stddev=0.1))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [64]))
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
#First Fully Connected Layer
W_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([7 * 7 * 64, 1024], stddev=0.1))
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) #拉成一条
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
#Dropout Layer 防止过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float") #保留率
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) #当前结果
#Second Fully Connected Layer
W_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1024, 10], stddev=0.1))
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(.1, shape = [10]))
#Final Layer
y = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2
# In[11]:
crossEntropyLoss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels = y_, logits = y))
trainStep = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(crossEntropyLoss)#自适应的优化器
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
# In[12]:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
batchSize = 50
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batchSize)
trainingInputs = batch[0].reshape([batchSize,28,28,1])
trainingLabels = batch[1]
if i%100 == 0:
trainAccuracy = accuracy.eval(session=sess, feed_dict={x:trainingInputs, y_: trainingLabels, keep_prob: 1.0})
print ("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, trainAccuracy))
trainStep.run(session=sess, feed_dict={x: trainingInputs, y_: trainingLabels, keep_prob: 0.5})