【图像重建】基于遗传算法实现二值图像重建附matlab代码
1 内容介绍
图像质量的优劣对人类视觉和各种计算机视觉系统都十分重要,因此图像复原一直是数字图像处理的重要研究内容。作为图像复原的一个分支,超分辨率图像重建问题得到人们越来越多的关注。在视频监控、卫星成像和医学诊断等应用中,由于物理条件的限制,人们获得的图像分辨率较低,无法满足实际需要。超分辨率图像重建技术就是利用这些低分辨率图像序列中各帧图像之间的冗余信息,重构出高分辨率图像。 提出了一种基于遗传算法的图象重建算法,该算法通过构造合适的基因编码方案及个体适应度评价函数,并对遗传算法进行优化,克服了Kuba算法和谷士文AI算法的缺陷,可以成功地解决由带有噪声的二维正交投影重建二维图象的问题,并简化了约束条件.实验结果表明该算法是成功有效的.
2 仿真代码
% Written by Dr. Seyedali Mirjalili
% To watch videos on this algorithm, enrol to my courses with 95% discount using the following links:
% *************************************************************************************************************************************************
% A course on "Optimization Problems and Algorithms: how to understand, formulation, and solve optimization problems":
% https://www.udemy.com/optimisation/?couponCode=MATHWORKSREF
% *************************************************************************************************************************************************
% "Introduction to Genetic Algorithms: Theory and Applications"
% https://www.udemy.com/geneticalgorithm/?couponCode=MATHWORKSREF
% *************************************************************************************************************************************************
function [BestChrom] = GeneticAlgorithm (M , N, MaxGen , Pc, Pm , Er , obj, visuailzation)
load IMG_REF_BINARY;
cgcurve = zeros(1 , MaxGen);
%% Initialization
[ population ] = initialization(M, N);
for i = 1 : M
population.Chromosomes(i).fitness = obj( population.Chromosomes(i).Gene(:), IMG_REF_BINARY);
end
g = 1;
disp(['Generation #' , num2str(g)]);
[max_val , indx] = sort([ population.Chromosomes(:).fitness ] , 'descend');
cgcurve(g) = population.Chromosomes(indx(1)).fitness;
subplot(1,2,2)
%% Main loop
for g = 2 : MaxGen
disp(['Generation #' , num2str(g)]);
for k = 1: 2: M
% Selection
[ parent1, parent2] = selection(population);
% Crossover
[child1 , child2] = crossover(parent1 , parent2, Pc, 'double');
% Mutation
[child1] = mutation(child1, Pm);
[child2] = mutation(child2, Pm);
newPopulation.Chromosomes(k).Gene = child1.Gene;
newPopulation.Chromosomes(k+1).Gene = child2.Gene;
end
% Calcualte the fitness values
for i = 1 : M
newPopulation.Chromosomes(i).fitness = obj( newPopulation.Chromosomes(i).Gene(:), IMG_REF_BINARY);
end
% Elitism
[ newPopulation ] = elitism(population, newPopulation, Er);
cgcurve(g) = newPopulation.Chromosomes(1).fitness;
population = newPopulation; % Replace the previous population with the newly made
BestChrom.Gene = population.Chromosomes(1).Gene;
BestChrom.Fitness = population.Chromosomes(1).fitness;
col_no = size(IMG_REF_BINARY,2);
Recons_IMG = vec2mat(BestChrom.Gene , col_no);
Recons_IMG = Recons_IMG .* 255;
% if rem(g , 100) == 0
subplot(1,2,2)
imshow(Recons_IMG);
title(['Generation #' , num2str(g), ' Error = ' , num2str(-BestChrom.Fitness)])
drawnow
% end
end
if visuailzation == 1
figure
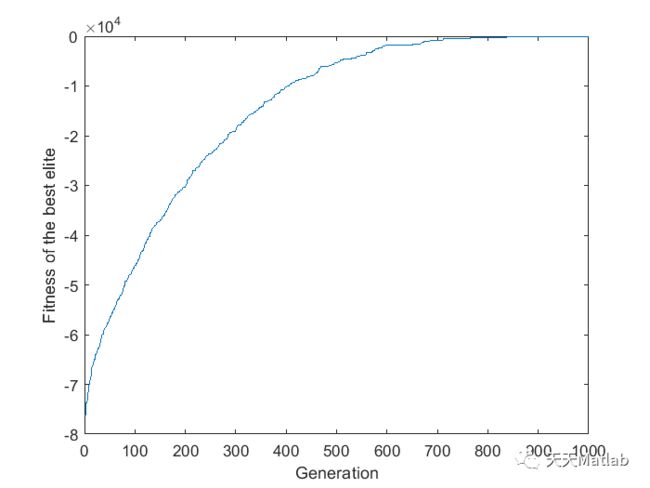
plot( 1 : MaxGen , cgcurve);
xlabel('Generation');
ylabel('Fitness of the best elite')
end
end
3 运行结果
4 参考文献
[1]伍晓平, 谷士文, 费耀平,等. 基于遗传算法的图象重建算法[J]. 计算技术与自动化, 2000, 19(1):4.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。