模型选择、欠拟合和过拟合
1、引入包
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
2、设置阶数、训练测试集的大小、初始化w
# 多项式的最大阶数 确定w向量的维度(1,20)
max_degree = 20
# 训练和测试数据集大小
n_train, n_test = 100, 100
# 分配大量的空间 np.zeros是创建为0的向量
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree)
true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6])
3、生成相应特征,poly_features记录不同阶数的x
# 生成(200,1)的特征
features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1))
# 将生成的特征打乱
np.random.shuffle(features)
# poly_features 生成(200,20)的向量
# np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1)表示x的次数
# poly_features存放的是features经过次方的数据
poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1))4、生成真实labels
# math.gamma()表示的是伽玛函数
# 存储在poly_features中的单项式由gamma函数重新缩放 这里的作用有点不太懂
for i in range(max_degree):
poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1) # gamma(n)=(n-1)!
# labels的维度:(n_train+n_test,)
# np.dot表示矩阵的乘法 poly_features(200,20)true_w(1,20)
labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w)
# 参数scale表示正态分布的标准差,这里相当于来个一个bias
labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape)5、获取相应数据
# 使用pytorch要将numpy的东西转换为tensor的东西
# NumPy ndarray转换为tensor
true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [
# 这种语句的书写自己要学会
torch.tensor(x, dtype=
torch.float32) for x in
[true_w, features, poly_features, labels]
]6、观察获取数据形状
# 观察每个变量的具体形状
true_w.shape,features.shape,poly_features.shape,labels.shape7、观察具体特征类型
features[:2], poly_features[:2, :], labels[:2]8、定义损失函数
def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss): #@save
"""评估给定数据集上模型的损失"""
# d2l.Accumulator(2)创建两个单位,存放总loss和单位数量
# 损失的总和,样本数量
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)
# 传入数据data_iter
for X, y in data_iter:
# out为预测y的值
out = net(X)
# y是真实的y的值
y = y.reshape(out.shape)
# 根据定义的loss函数计算损失
l = loss(out, y)
# l.sum()总损失 l.numel()相等于总共l的数量
metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]9、训练模型
# 传入训练特征,测试特征,训练标签,测试标签,迭代次数
# 最重要的部分
def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,
num_epochs=400):
# 定义loss为nn.MSELoss(reduction='none') 即均方损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
# 输入的形状为train.features的列数
input_shape = train_features.shape[-1]
# 不设置偏置,因为我们已经在多项式中实现了它
# nn.Linear表示定义为线性模型
# 表示一个形状(input_shape,1)
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False))
# 选择小批量大小
batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0])
# d2l.load_array传入相应的数据
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1,1)),
batch_size)
test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1,1)),
batch_size, is_train=False)
# 选择SGD小批量梯度优化器去更新w和b
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
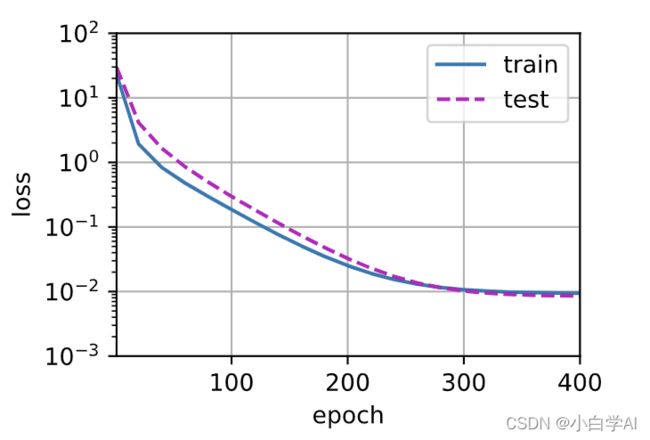
# d2l.Animator动画显示训练和验证集损失情况
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],
legend=['train', 'test'])
# 依次迭代训练,num_epochs=400
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# d2l.train_epoch_ch3表示迭代一次
d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer)
# 每迭代20次画一个图
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
# 默认w的输出方式
print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy())10、取4个维度训练
# 从多项式特征中选择前4个维度,即1,x,x^2/2!,x^3/3!
# n_train为100,一半测试集一半训练集
train(poly_features[:n_train, :4], poly_features[n_train:, :4],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])相对正常情况
11、 取2个维度训练
# 从多项式特征中选择前2个维度,即1和x
train(poly_features[:n_train, :2], poly_features[n_train:, :2],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])12、 取所有维度进行训练
# 从多项式特征中选取所有维度
train(poly_features[:n_train, :], poly_features[n_train:, :],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:], num_epochs=1500)