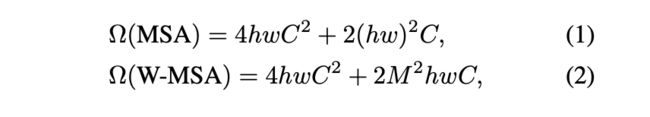Swin Transformer详解
原创:余晓龙
“Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Window”是微软亚洲研究院(MSRA)发表在arXiv上的论文,文中提出了一种新型的Transformer架构,也就是Swin Transformer。本文旨在对Swin Transformer架构进行详细解析。
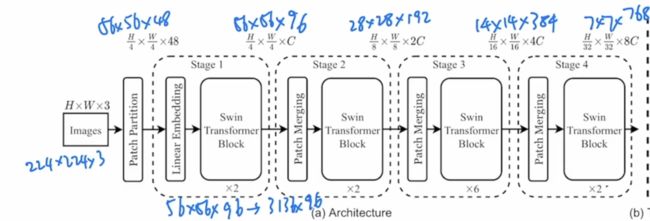
一、Swin Transformer网络架构
整体的网络架构采取层次化的设计,共包含4个stage,每个stage都会缩小输入特征图的分辨率,类似于CNN操作逐层增加感受野。对于一张输入图像224x224x3,首先会像VIT一样,把图片打成patch,这里Swin transformer中使用的patch size大小为 4x4,不同于VIT中使用的大小为16x16。经过Patch Partition,图像的大小会变成56 x 56 x 48, 其中48为 (4x4x3)3 为图片的rgb通道。打完patch之后会经过Linear Embedding,这里的主要目的是为了把向量的维度变成我们预先设定好的值,即可以满足transformer可以输入的值。在Swin-T网络中,这里C的大小为96,得到的网络输出值为56x56x96。之后经过拉直,序列长度变成3136 x 96。其代码如下:
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""
2D Image to Patch Embedding
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_c=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.in_chans = in_c
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
_, _, H, W = x.shape
# padding
# 如果输入图片的H,W不是patch_size的整数倍,需要进行padding
pad_input = (H % self.patch_size[0] != 0) or (W % self.patch_size[1] != 0)
if pad_input:
# to pad the last 3 dimensions,
# (W_left, W_right, H_top,H_bottom, C_front, C_back)
x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1],
0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0],
0, 0))
# 下采样patch_size倍
x = self.proj(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
# flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW]
# transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C]
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, H, W
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn(8, 3, 224, 224)
x, W, H = PatchEmbed()(x)
print(x.size()) # torch.Size([8, 3136, 96])
print(W) # 56
print(H) # 56
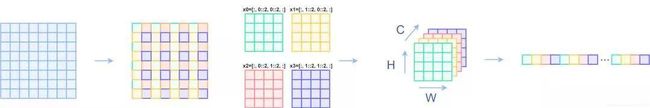
Swin transformer引入了基于窗口的自注意力计算,每个窗口为 7x7=49个patch。如果想要有多尺度的特征信息,就需要构建一个层级式的transformer,类似卷积神经网络里的池化操作,Patch Merging用于缩小分辨率,调整通道数,完成层级式的设计。这里每次的降采样为2,在行和列方向每隔一个点选取元素,之后拼接在一起展开。
相当于在空间上的维度去换到了更多的通道数,维度变成4C,之后在C的维度上利用全连接层,将通道数的大小变成2C,经过上述操作之后网络输出的大小变为28 x 28 x 192。之后经过拉直,序列长度变成784 x 192。后面的stage3、stage4同理。最终的网络输出的大小变为7 x 7 x 768。之后经过拉直,序列长度变成49 x 768。代码如下:
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
r""" Patch Merging Layer.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)
def forward(self, x, H, W):
"""
x: B, H*W, C
"""
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# padding
# 如果输入feature map的H,W不是2的整数倍,需要进行padding
pad_input = (H % 2 == 1) or (W % 2 == 1)
if pad_input:
# to pad the last 3 dimensions, starting from the last dimension and moving forward.
# (C_front, C_back, W_left, W_right, H_top, H_bottom)
# 注意这里的Tensor通道是[B, H, W, C],所以会和官方文档有些不同
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, W % 2, 0, H % 2))
x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C]
x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C]
x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C]
x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C]
x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # [B, H/2, W/2, 4*C]
x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # [B, H/2*W/2, 4*C]
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.reduction(x) # [B, H/2*W/2, 2*C]
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn(8, 3, 224, 224)
x, H, W = PatchEmbed()(x)
# print(x.size()) # torch.Size([8, 3136, 96])
# print(W) # 56
# print(H) # 56
x = PatchMerging(dim=96)(x, H, W)
print(x.size()) # torch.Size([8, 784, 192])
基于窗口/移动窗口的自注意力
由于全局的自注意力计算会导致平方倍的复杂度,因此作者提出了基于窗口的自注意力机制。原来的图片会被平均分成一些没有重叠的窗口,以第一层的输入为例,尺寸大小为56 x 56 x 96。
在每一个小方格中会有7x7=49个patch,因此大的特征图可以分为 56 / 7 x 56 / 7 = 8 x 8 个窗口。
基于窗口的自注意力机制与基于全局的自注意力机制复杂度对比:
以标准的多头自注意力为例, 对于一个输入,自注意力首先会将它变成q, k, v三个向量,之后得到的q, k 相乘得到attention,在有了自注意力之后后和得到的v进行相乘,相当于做了一次加权,最后因为这是使用了多头自注意力机制,还会经过一个projection layer,这个投射层就会把向量的维度投射到我们想要的那个维度,如下图:
公式一 :
3 h w c 2 + ! ( h w ) 2 c + ( h w ) 2 c + h w c 2 3hwc^{2} + ! (hw)^{2}c + (hw)^{2}c + hwc^{2} 3hwc2+!(hw)2c+(hw)2c+hwc2
公式二:基于窗口的自注意力复杂度 一个窗口大小 M x M 代入公式一得
4 M 2 c 2 + 2 M 4 c 4M^{2}c^{2} + 2M^{4}c 4M2c2+2M4c
现在我们一共有 h / M * w / M 个窗口,乘以上式:
4 h w c 2 + 2 M 2 h w c 4hwc^{2} + 2M^{2}hwc 4hwc2+2M2hwc
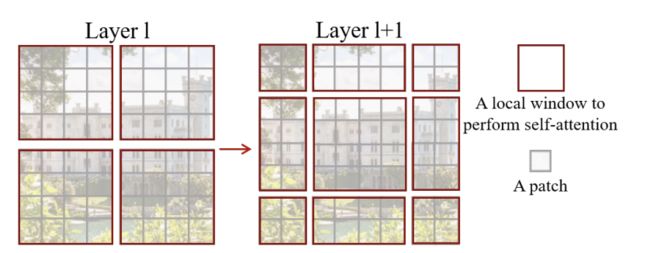
作者通过移动窗口的方法使得窗口之间能够相互通信,使用上下文信息从而得到更好的效果。
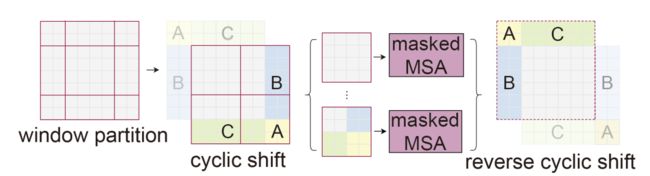
另外W-MSA虽然降低了计算复杂度,但是不重合的window之间缺乏信息交流,于是作者进一步引入shifted window partition来解决不同window的信息交流问题,在两个连续的Swin Transformer Block中交替使用W-MSA和SW-MSA。以上图为例,将前一层Swin Transformer Block的8x8尺寸feature map划分成2x2个patch,每个patch尺寸为4x4,然后将下一层Swin Transformer Block的window位置进行移动,得到3x3个不重合的patch。移动window的划分方式使上一层相邻的不重合window之间引入连接,大大的增加了感受野。
SW-MSA的基本操作流程:
但是shifted window划分方式还引入了另外一个问题,就是会产生更多的windows,并且其中一部分window小于普通的window,比如2x2个patch -> 3x3个patch,windows数量增加了一倍多。于是作者提出了通过沿着左上方向cyclic shift的方式来解决这个问题,移动后,一个batched window由几个特征不相邻的sub-windows组成,因此使用masking mechanism来限制self-attention在sub-window内进行计算。cyclic shift之后,batched window和regular window数量保持一致,极大提高了Swin Transformer的计算效率
- 首先将windows进行半个窗口的循环移位,使用torch.roll实现。
>>> import torch
>>> x=torch.arange(1,17).view(4,4)
>>> x
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]])
>>> y=torch.roll(x,shifts=-1,dims=0)
>>> y
tensor([[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16],
[ 1, 2, 3, 4]])
>>> z=torch.roll(y,shifts=-1,dims=1)
>>> z
tensor([[ 6, 7, 8, 5],
[10, 11, 12, 9],
[14, 15, 16, 13],
[ 2, 3, 4, 1]])
>>>
2.在相同的窗口中计算自注意力,计算结果如下右图所示,window0的结构保存,但是针对window2的计算,其中3与3、6与6的计算生成了attn mask 中window2中的黄色区域,针对windows2中3与6、6与3之间不应该计算自注意力(attn mask中window2的蓝色区域),将蓝色区域mask赋值为-100,经过softmax之后,起作用可以忽略不计。同理window1与window3的计算一致。
代码如下:
import torch
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def window_partition(x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windows
window_size = 7
shift_size = 3
H, W = 14, 14
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, window_size * window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
plt.matshow(img_mask[0, :, :, 0].numpy())
plt.matshow(attn_mask[0].numpy())
plt.matshow(attn_mask[1].numpy())
plt.matshow(attn_mask[2].numpy())
plt.matshow(attn_mask[3].numpy())
plt.show()
在Swin Transformer block里,每次都会先做一次基于窗口的多头自注意力,然后再做一次基于移动窗口的多个自注意力,这样就达到了窗口之间的相互通信。
上图就是一个SwinTransformerBlock的结构,由LayerNorm层、windowAttention层(Window MultiHead self -attention, W-MSA)、MLP层以及shiftWindowAttention层(SW-MSA)组成。
class Mlp(nn.Module):
""" MLP as used in Vision Transformer, MLP-Mixer and related networks
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
return x
def window_partition(x, window_size: int):
"""
将feature map按照window_size划分成一个个没有重叠的window
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size(M)
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
# permute: [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, W//Mh, Mw, Mw, C]
# view: [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B*num_windows, Mh, Mw, C]
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windows
def window_reverse(windows, window_size: int, H: int, W: int):
"""
将一个个window还原成一个feature map
Args:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
window_size (int): Window size(M)
H (int): Height of image
W (int): Width of image
Returns:
x: (B, H, W, C)
"""
B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))
# view: [B*num_windows, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C]
x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
# permute: [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C]
# view: [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] -> [B, H, W, C]
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)
return x
完整的Swin TransformerBlock代码如下:
整体流程如下
(1)先对特征图进行LayerNorm
(2)通过self.shift_size决定是否需要对特征图进行shift
(3)然后将特征图切成一个个窗口
(4)计算Attention,通过self.attn_mask来区分Window Attention还是Shift Window Attention
(5)将各个窗口合并回来
(6)如果之前有做shift操作,此时进行reverse shift,把之前的shift操作恢复
(7)做dropout和残差连接
(8)再通过一层LayerNorm+全连接层,以及dropout和残差连接
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.La
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=(self.window_size, self.window_size), num_heads=n
attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identit
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_la
def forward(self, x, attn_mask):
H, W = self.H, self.W
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# pad feature maps to multiples of window size
# 把feature map给pad到window size的整数倍
pad_l = pad_t = 0
pad_r = (self.window_size - W % self.window_size) % self.window_size
pad_b = (self.window_size - H % self.window_size) % self.window_size
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b))
_, Hp, Wp, _ = x.shape
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_si
else:
shifted_x = x
attn_mask = None
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # [nW*B, Mh
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C)
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_siz
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, Hp, Wp) #
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size
else:
x = shifted_x
if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:
# 把前面pad的数据移除掉
x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous()
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
BasicLayer就是网络结构图中的stage。
每个stage由多个swin Transfomer堆叠以及Patch merging组成。其中Patch Merging在BasicLayer代码中就是Downsample的部分。
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
"""
A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
depth (int): Number of blocks.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Local window size.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: None
use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.depth = depth
self.window_size = window_size
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
self.shift_size = window_size // 2
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(
dim=dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else self.shift_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
if downsample is not None:
self.downsample = downsample(dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
self.downsample = None
def create_mask(self, x, H, W):
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
# 保证Hp和Wp是window_size的整数倍
Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
# 拥有和feature map一样的通道排列顺序,方便后续window_partition
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # [1, Hp, Wp, 1]
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # [nW, Mh, Mw, 1]
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # [nW, Mh*Mw]
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) # [nW, 1, Mh*Mw] - [nW, Mh*Mw, 1]
# [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
def forward(self, x, H, W):
attn_mask = self.create_mask(x, H, W) # [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
for blk in self.blocks:
blk.H, blk.W = H, W
if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, attn_mask)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x, H, W)
H, W = (H + 1) // 2, (W + 1) // 2
return x, H, W
Swin Transform 整体架构
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer
A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
Args:
patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96
depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer.
num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.
window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4
qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
drop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0
attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1
norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.
patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: True
use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24),
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_layers = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.patch_norm = patch_norm
# stage4输出特征矩阵的channels
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1))
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
# build layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
# 注意这里构建的stage和论文图中有些差异
# 这里的stage不包含该stage的patch_merging层,包含的是下个stage的
layers = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
self.layers.append(layers)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward(self, x):
# print('x', x.size()) # x torch.Size([8, 3, 224, 224])
# x: [B, L, C]
x, H, W = self.patch_embed(x) #
# print(x.size()) # torch.Size([8, 3136, 96])
# print(H) # 56
# print(W) # 56
x = self.pos_drop(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x, H, W = layer(x, H, W)
x = self.norm(x) # [B, L, C]
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # [B, C, 1]
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.head(x)
return x
传统的Transformer都是基于全局来计算注意力的,因此计算复杂度十分高。而Swin Transformer则将注意力的计算限制在每个窗口内,进而减少了计算量。
这里主要区别是在原始计算Attention的公式中的Q,K时加入了相对位置编码。
整体流程:
代码如下:
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # [Mh, Mw]
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # [2*Mh-1 * 2*Mw-1, nH]
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w],
# indexing="ij")
))
# [2, Mh, Mw]
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # [2, Mh*Mw]
# [2, Mh*Mw, 1] - [2, 1, Mh*Mw]
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # [2, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw, 2]
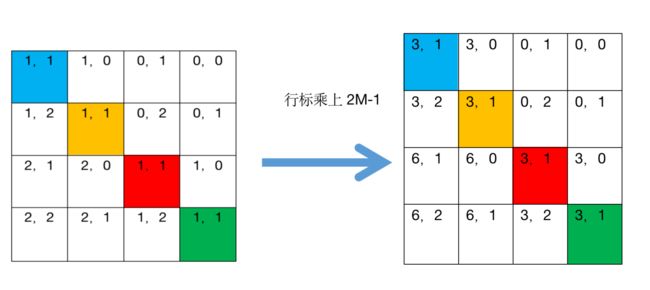
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
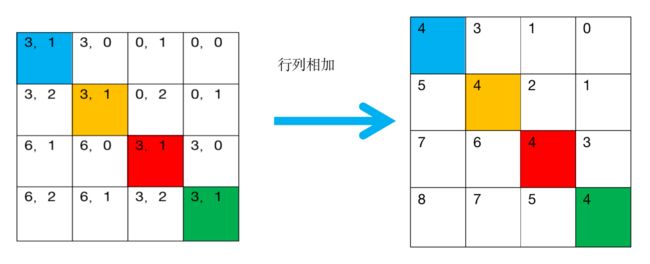
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, Mh*Mw, C)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
# [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim]
B_, N, C = x.shape
# qkv(): -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0) # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, Mh*Mw]
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
# relative_position_bias_table.view: [Mh*Mw*Mh*Mw,nH] -> [Mh*Mw,Mh*Mw,nH]
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # [nH, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
# mask: [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
nW = mask.shape[0] # num_windows
# attn.view: [batch_size, num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
# mask.unsqueeze: [1, nW, 1, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
二、Swin transformer实现图像分类
(1)准备数据
数据格式如下:
(2)模型训练代码实现:
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '2'
import argparse
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision import transforms
from my_dataset import MyDataSet
from model import swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224 as create_model
from utils import read_split_data, train_one_epoch, evaluate
def main(args):
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
if os.path.exists("./weights") is False:
os.makedirs("./weights")
tb_writer = SummaryWriter()
train_images_path, train_images_label, val_images_path, val_images_label = read_split_data(args.data_path)
img_size = 224
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(img_size),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
# 实例化训练数据集
train_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=train_images_path,
images_class=train_images_label,
transform=data_transform["train"])
# 实例化验证数据集
val_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=val_images_path,
images_class=val_images_label,
transform=data_transform["val"])
batch_size = args.batch_size
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 0]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
model = create_model(num_classes=args.num_classes).to(device)
if args.weights != "":
assert os.path.exists(args.weights), "weights file: '{}' not exist.".format(args.weights)
weights_dict = torch.load(args.weights, map_location=device)["model"]
# 删除有关分类类别的权重
for k in list(weights_dict.keys()):
if "head" in k:
del weights_dict[k]
print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False))
if args.freeze_layers:
for name, para in model.named_parameters():
# 除head外,其他权重全部冻结
if "head" not in name:
para.requires_grad_(False)
else:
print("training {}".format(name))
pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.AdamW(pg, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=5E-2)
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# train
train_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
data_loader=train_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
# validate
val_loss, val_acc = evaluate(model=model,
data_loader=val_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
tags = ["train_loss", "train_acc", "val_loss", "val_acc", "learning_rate"]
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[0], train_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[1], train_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[2], val_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[3], val_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[4], optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"], epoch)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./weights/vehicle-model-{}.pth".format(epoch))
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=10)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=20)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=8)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0001)
# 数据集所在根目录
parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str,
default="data/vehicle-10/train")
# 预训练权重路径,如果不想载入就设置为空字符
# https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224.pth
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224.pth',
help='initial weights path')
# 是否冻结权重
parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=False)
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
opt = parser.parse_args()
main(opt)
经过20轮训练在weight文件夹下生成模型文件:
(3)模型预测代码实现:
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '2'
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224 as create_model
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
img_size = 224
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.14)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
# img_path = "data/vehicle-10/val/bus/1b9471eefb6f3951f127beb69ef5a584.jpg"
img_path = "data/vehicle-10/val/jeep/4f7b9fe4f79f9e90ad093f2cf35505f5.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
# print(img)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = create_model(num_classes=10).to(device)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./weights/vehicle-model-19.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
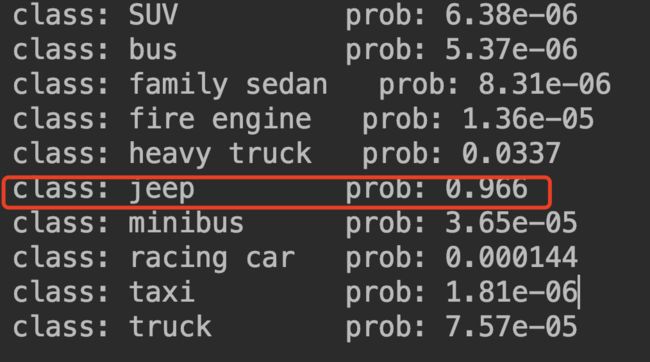
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.savefig('b.png')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
三、Swin transformer实现目标检测
1、安装环境
pip install torch==1.8.0
pip install mmdet==2.4.0
pip uninstall mmcv
pip install mmcv-full==latest+torch1.8.0+cu111 -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/index.html
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex
cd apex
pip install -v --no-cache-dir ./
pip install openmim
# mim install mmdet
mim download mmdet --config faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco --dest .
2、测试图片—检测
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '2'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mmcv
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detector
config_file = 'configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'
# download the checkpoint from model zoo and put it in `checkpoints/`
# url: https://download.openmmlab.com/mmdetection/v2.0/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth
checkpoint_file = 'faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth'
device = 'cuda:0'
# init a detector
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu')
# inference the demo image
result = inference_detector(model, 'demo/demo.jpg')
img = 'demo/demo.jpg'
def show_result_pyplot(model, img, result, score_thr=0.3, fig_size=(15, 10)):
"""Visualize the detection results on the image.
Args:
model (nn.Module): The loaded detector.
img (str or np.ndarray): Image filename or loaded image.
result (tuple[list] or list): The detection result, can be either
(bbox, segm) or just bbox.
score_thr (float): The threshold to visualize the bboxes and masks.
fig_size (tuple): Figure size of the pyplot figure.
"""
if hasattr(model, 'module'):
model = model.module
img = model.show_result(img, result, score_thr=score_thr, show=False)
plt.figure(figsize=fig_size)
plt.imshow(mmcv.bgr2rgb(img))
plt.savefig('demo-result.jpg')
plt.show()
show_result_pyplot(model, img, result)
3、测试图片—分割
4、测试视频
import argparse
import cv2
import mmcv
from mmdet.apis import inference_detector, init_detector
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='MMDetection video demo')
parser.add_argument('video', help='Video file')
parser.add_argument('config', help='Config file')
parser.add_argument('checkpoint', help='Checkpoint file')
parser.add_argument(
'--device', default='cuda:0', help='Device used for inference')
parser.add_argument(
'--score-thr', type=float, default=0.3, help='Bbox score threshold')
parser.add_argument('--out', type=str, help='Output video file')
parser.add_argument('--show', action='store_true', help='Show video')
parser.add_argument(
'--wait-time',
type=float,
default=1,
help='The interval of show (s), 0 is block')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def main():
args = parse_args()
assert args.out or args.show, \
('Please specify at least one operation (save/show the '
'video) with the argument "--out" or "--show"')
model = init_detector(args.config, args.checkpoint, device=args.device)
video_reader = mmcv.VideoReader(args.video)
video_writer = None
if args.out:
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(
args.out, fourcc, video_reader.fps,
(video_reader.width, video_reader.height))
for frame in mmcv.track_iter_progress(video_reader):
result = inference_detector(model, frame)
frame = model.show_result(frame, result, score_thr=args.score_thr)
if args.show:
cv2.namedWindow('video', 0)
mmcv.imshow(frame, 'video', args.wait_time)
if args.out:
video_writer.write(frame)
if video_writer:
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
5、测试摄像头
import argparse
import cv2
import torch
from mmdet.apis import inference_detector, init_detector
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='MMDetection webcam demo')
parser.add_argument('config', help='test config file path')
parser.add_argument('checkpoint', help='checkpoint file')
parser.add_argument(
'--device', type=str, default='cuda:0', help='CPU/CUDA device option')
parser.add_argument(
'--camera-id', type=int, default=0, help='camera device id')
parser.add_argument(
'--score-thr', type=float, default=0.5, help='bbox score threshold')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def main():
args = parse_args()
device = torch.device(args.device)
model = init_detector(args.config, args.checkpoint, device=device)
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(args.camera_id)
print('Press "Esc", "q" or "Q" to exit.')
while True:
ret_val, img = camera.read()
result = inference_detector(model, img)
ch = cv2.waitKey(1)
if ch == 27 or ch == ord('q') or ch == ord('Q'):
break
model.show_result(
img, result, score_thr=args.score_thr, wait_time=1, show=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
6、训练自己的数据集
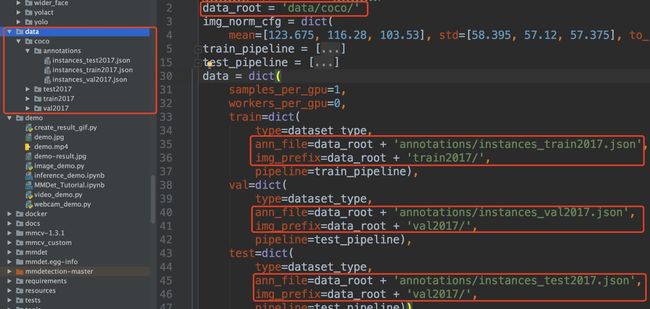
(1)准备coco格式数据
参考链接
MlDl:Swin Transformer in Classificationzhuanlan.zhihu.com
路径格式如下
(2)修改changemaskrcnn.py中num_class
之后会在项目文件中生成模型文件mask_rcnn_swin_3.pth。
(3)修改num_classes=3
(4)修改configs_base_\default_runtime.py加载模型文件
(5)修改mmdet\datasets\coco.py中CLASSES
(6)模型训练
python tools/train.py configs\swin\mask_rcnn_swin_tiny_patch4_window7_mstrain_480-800_adamw_3x_coco.py
经过20轮训练在 work_dirs文件夹下会生成模型文件latest.pth
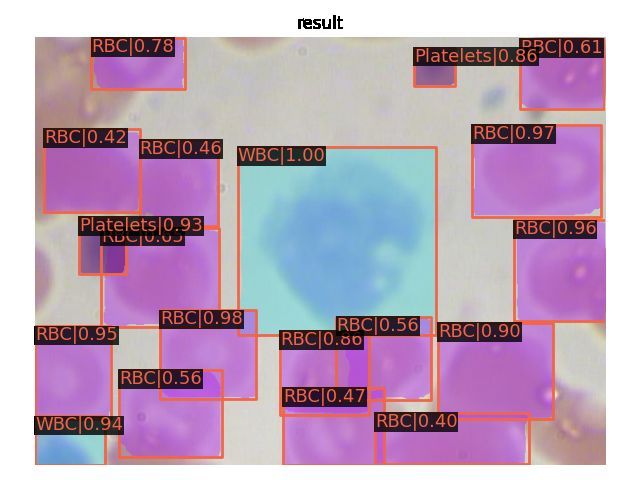
(7)模型测试
python demo/image_demo.py data/coco/test2017/BloodImage_00133_jpg.rf.4f9b4435c673ed96c9deeb985c805d24.jpg configs/swin/mask_rcnn_swin_tiny_patch4_window7_mstrain_480-800_adamw_3x_coco.py work_dirs/mask_rcnn_swin_tiny_patch4_window7_mstrain_480-800_adamw_3x_coco/latest.pth
最后,欢迎大家一起讨论、指正、补充~~