语义分割图像增强新方法
最近在日常挖坑中发现了另一种简单有效数据扩充方法,将其分享使用。 之前都是利用opencv自己编写代码进行图像的翻转、旋转角度,裁剪、亮度变化等等操作。
对于语义分割任务来说,一种有效的提升性能的办法就是对现有数据进行增强,扩充现有数据的多样性。
在图像的深度学习中,为了丰富图像训练集,更好的提取图像特征,泛化模型(防止模型过拟合),一般都会对数据图像进行数据增强。数据增强,常用的方式,就是旋转图像,剪切图像,改变图像色差,扭曲图像特征,改变图像尺寸大小,增强图像噪音(一般使用高斯噪音,盐椒噪音)等。但是需要注意,不要加入其他图像轮廓的噪音.
本文介绍一种比较好用的数据增强工具:Augmentor
对于本人常用方法代码:
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
2 """数据增强
3 1. 翻转变换 flip
4 2. 随机修剪 random crop
5 3. 色彩抖动 color jittering
6 4. 平移变换 shift
7 5. 尺度变换 scale
8 6. 对比度变换 contrast
9 7. 噪声扰动 noise
10 8. 旋转变换/反射变换 Rotation/reflection
11 author: NiuXueRui
12 date:2020-10-29
13 """
14
15 from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance, ImageOps, ImageFile
16 import numpy as np
17 import random
18 import threading, os, time
19 import logging
20
21 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
22 ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True
23
24
25 class DataAugmentation:
26 """
27 包含数据增强的八种方式
28 """
29
30
31 def __init__(self):
32 pass
33
34 @staticmethod
35 def openImage(image):
36 return Image.open(image, mode="r")
37
38 @staticmethod
39 def randomRotation(image, mode=Image.BICUBIC):
40 """
41 对图像进行随机任意角度(0~360度)旋转
42 :param mode 邻近插值,双线性插值,双三次B样条插值(default)
43 :param image PIL的图像image
44 :return: 旋转转之后的图像
45 """
46 random_angle = np.random.randint(1, 360)
47 return image.rotate(random_angle, mode)
48
49 @staticmethod
50 def randomCrop(image):
51 """
52 对图像随意剪切,考虑到图像大小范围(68,68),使用一个一个大于(36*36)的窗口进行截图
53 :param image: PIL的图像image
54 :return: 剪切之后的图像
55
56 """
57 image_width = image.size[0]
58 image_height = image.size[1]
59 crop_win_size = np.random.randint(40, 68)
60 random_region = (
61 (image_width - crop_win_size) >> 1, (image_height - crop_win_size) >> 1, (image_width + crop_win_size) >> 1,
62 (image_height + crop_win_size) >> 1)
63 return image.crop(random_region)
64
65 @staticmethod
66 def randomColor(image):
67 """
68 对图像进行颜色抖动
69 :param image: PIL的图像image
70 :return: 有颜色色差的图像image
71 """
72 random_factor = np.random.randint(0, 31) / 10. # 随机因子
73 color_image = ImageEnhance.Color(image).enhance(random_factor) # 调整图像的饱和度
74 random_factor = np.random.randint(10, 21) / 10. # 随机因子
75 brightness_image = ImageEnhance.Brightness(color_image).enhance(random_factor) # 调整图像的亮度
76 random_factor = np.random.randint(10, 21) / 10. # 随机因1子
77 contrast_image = ImageEnhance.Contrast(brightness_image).enhance(random_factor) # 调整图像对比度
78 random_factor = np.random.randint(0, 31) / 10. # 随机因子
79 return ImageEnhance.Sharpness(contrast_image).enhance(random_factor) # 调整图像锐度
80
81 @staticmethod
82 def randomGaussian(image, mean=0.2, sigma=0.3):
83 """
84 对图像进行高斯噪声处理
85 :param image:
86 :return:
87 """
88
89 def gaussianNoisy(im, mean=0.2, sigma=0.3):
90 """
91 对图像做高斯噪音处理
92 :param im: 单通道图像
93 :param mean: 偏移量
94 :param sigma: 标准差
95 :return:
96 """
97 for _i in range(len(im)):
98 im[_i] += random.gauss(mean, sigma)
99 return im
100
101 # 将图像转化成数组
102 img = np.asarray(image)
103 img.flags.writeable = True # 将数组改为读写模式
104 width, height = img.shape[:2]
105 img_r = gaussianNoisy(img[:, :, 0].flatten(), mean, sigma)
106 img_g = gaussianNoisy(img[:, :, 1].flatten(), mean, sigma)
107 img_b = gaussianNoisy(img[:, :, 2].flatten(), mean, sigma)
108 img[:, :, 0] = img_r.reshape([width, height])
109 img[:, :, 1] = img_g.reshape([width, height])
110 img[:, :, 2] = img_b.reshape([width, height])
111 return Image.fromarray(np.uint8(img))
112
113 @staticmethod
114 def saveImage(image, path):
115 image.save(path)
116
117
118 def makeDir(path):
119 try:
120 if not os.path.exists(path):
121 if not os.path.isfile(path):
122 # os.mkdir(path)
123 os.makedirs(path)
124 return 0
125 else:
126 return 1
127 except Exception, e:
128 print str(e)
129 return -2
130
131
132 def imageOps(func_name, image, des_path, file_name, times=5):
133 funcMap = {"randomRotation": DataAugmentation.randomRotation,
134 "randomCrop": DataAugmentation.randomCrop,
135 "randomColor": DataAugmentation.randomColor,
136 "randomGaussian": DataAugmentation.randomGaussian
137 }
138 if funcMap.get(func_name) is None:
139 logger.error("%s is not exist", func_name)
140 return -1
141
142 for _i in range(0, times, 1):
143 new_image = funcMap[func_name](image)
144 DataAugmentation.saveImage(new_image, os.path.join(des_path, func_name + str(_i) + file_name))
145
146
147 opsList = {"randomRotation", "randomCrop", "randomColor", "randomGaussian"}
148
149
150 def threadOPS(path, new_path):
151 """
152 多线程处理事务
153 :param src_path: 资源文件
154 :param des_path: 目的地文件
155 :return:
156 """
157 if os.path.isdir(path):
158 img_names = os.listdir(path)
159 else:
160 img_names = [path]
161 for img_name in img_names:
162 print img_name
163 tmp_img_name = os.path.join(path, img_name)
164 if os.path.isdir(tmp_img_name):
165 if makeDir(os.path.join(new_path, img_name)) != -1:
166 threadOPS(tmp_img_name, os.path.join(new_path, img_name))
167 else:
168 print 'create new dir failure'
169 return -1
170 # os.removedirs(tmp_img_name)
171 elif tmp_img_name.split('.')[1] != "DS_Store":
172 # 读取文件并进行操作
173 image = DataAugmentation.openImage(tmp_img_name)
174 threadImage = [0] * 5
175 _index = 0
176 for ops_name in opsList:
177 threadImage[_index] = threading.Thread(target=imageOps,
178 args=(ops_name, image, new_path, img_name,))
179 threadImage[_index].start()
180 _index += 1
181 time.sleep(0.2)
182
183
184 if __name__ == '__main__':
185 threadOPS("/home/pic-image/train/12306train",
186 "/home/pic-image/train/12306train3")
最近发现的方法:
(1)安装 Augmentor
在终端中输入命令:pip install Augmentor
即可完成安装。
(2)数据增强
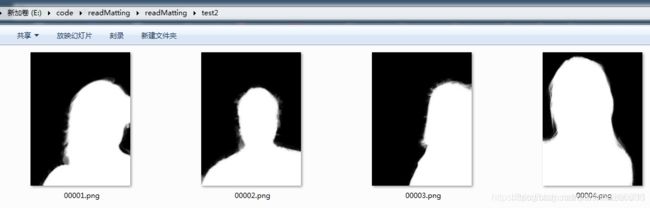
语义分割任务需要同时对原始图和掩码图(mask)进行增强,因此,很多现有的深度学习框架中自带的图像增强工具都不能直接使用。但是通过Augmentor可以很方便的实现该功能。下面举例说明。假设有四张图像以及它们对应的掩码图,分别放在test1文件夹以及test2文件夹中,如下图所示:
————————————————

可以使用下面的python代码进行数据增强:
#导入数据增强工具
import Augmentor
#确定原始图像存储路径以及掩码文件存储路径
p = Augmentor.Pipeline("test1")
p.ground_truth("test2")
#图像旋转: 按照概率0.8执行,最大左旋角度10,最大右旋角度10
p.rotate(probability=0.8, max_left_rotation=10, max_right_rotation=10)
#图像左右互换: 按照概率0.5执行
p.flip_left_right(probability=0.5)
#图像放大缩小: 按照概率0.8执行,面积为原始图0.85倍
p.zoom_random(probability=0.3, percentage_area=0.85)
#最终扩充的数据样本数
p.sample(20)
执行后,最终在test1文件目录下会生成一个output文件夹,该文件夹中即为增强过后的图片,如下图所示:
