Multi-Head Attention 原理与代码实现
1.Multi-Head Attention 结构
2.Multi-Head Attention 计算
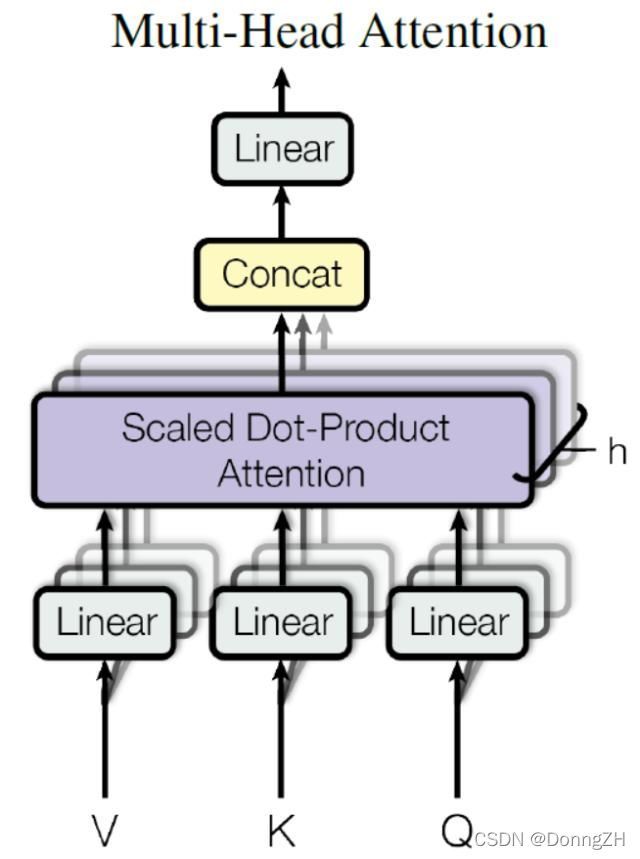
Multi-Head Attention 是由多个 Self-Attention 组合形成的。对于同一个文本,一个Attention获得一个表示空间,如果多个Attention,则可以获得多个不同的表示空间。基于这种想法,就有了Multi-Head Attention。换句话说,Multi-Head Attention为Attention提供了多个“representation subspaces”。因为在每个Attention中,采用不同的Query / Key / Value权重矩阵,每个矩阵都是随机初始化生成的。然后通过训练,将词嵌入投影到不同的“representation subspaces(表示子空间)”中。
将模型分为多个头,形成多个子空间,可以让模型去关注不同方面的信息。上图中Multi-Head Attention 就是将 Scaled Dot-Product Attention 过程做了8次,再把输出合并起来。
3.Multi-Head Attention 代码实现
from math import sqrt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MultiHeadSelfAttention(nn.Module):
dim_in: int # input dimension
dim_k: int # key and query dimension
dim_v: int # value dimension
num_heads: int # number of heads, for each head, dim_* = dim_* // num_heads
def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_k, dim_v, num_heads=8):
super(MultiHeadSelfAttention, self).__init__()
#维度必须能被num_head 整除
assert dim_k % num_heads == 0 and dim_v % num_heads == 0, "dim_k and dim_v must be multiple of num_heads"
self.dim_in = dim_in
self.dim_k = dim_k
self.dim_v = dim_v
self.num_heads = num_heads
#定义线性变换矩阵
self.linear_q = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_k, bias=False)
self.linear_k = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_k, bias=False)
self.linear_v = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_v, bias=False)
self._norm_fact = 1 / sqrt(dim_k // num_heads)
def forward(self, x):
# x: tensor of shape (batch, n, dim_in)
batch, n, dim_in = x.shape
assert dim_in == self.dim_in
nh = self.num_heads
dk = self.dim_k // nh # dim_k of each head
dv = self.dim_v // nh # dim_v of each head
q = self.linear_q(x).reshape(batch, n, nh, dk).transpose(1, 2) # (batch, nh, n, dk)
k = self.linear_k(x).reshape(batch, n, nh, dk).transpose(1, 2) # (batch, nh, n, dk)
v = self.linear_v(x).reshape(batch, n, nh, dv).transpose(1, 2) # (batch, nh, n, dv)
dist = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(2, 3)) * self._norm_fact # batch, nh, n, n
dist = torch.softmax(dist, dim=-1) # batch, nh, n, n
att = torch.matmul(dist, v) # batch, nh, n, dv
att = att.transpose(1, 2).reshape(batch, n, self.dim_v) # batch, n, dim_v
return att