Jetson AGX Xavier系列终章--YOLOv5结合ROS小车实现对目标的跟踪
上一篇:jetson agx xavier 完美使用NoMachine远程桌面控制
一、前言
Xavier系列已经到了尾声,前期的相关配置准备了很多,其中包括pytorch的环境、ROS的安装等等。为了更好的体验Xavier的性能,本文利用前文已经完成的内容,实现一个简易的目标跟踪小车。如果还未阅读我之前的文章,可以移步至我的专栏。如果觉得这个专栏有用,还请点个赞评论一下哈。
二、准备
1、硬件:
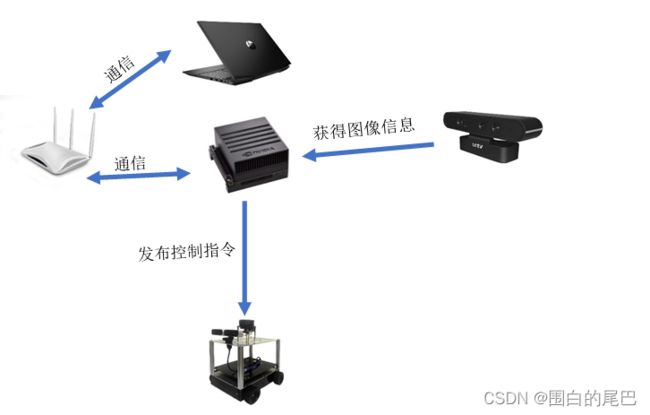
①Jetson AGX Xavier
②ROS小车
小车需搭载有摄像头。
③无线模块
查看文章进行安装。
④信号线
信号线用于Xavier与小车嵌入式底盘进行通信,一般为串口通信。咱信号线最好买好一点的,之前用蓝色的那种方口USB线,经常信号传输失败导致程序卡死。别问我为啥知道!!!
2、软件:
①YOLOv5算法
注意:下文的Follow.py所用的是YOLOv5 v4.0 与 tensorrtx v4.0 !!!, v5.0的版本没有尝试过用于控制小车,有小伙伴完成的可以分享一下。
Xavier能够根据文章实现对YOLOv5模型加速并完成实时检测。
②ROS安装
根据文章安装ROS。能够通过键盘控制ROS小车运动。(由于小车各不相同,大家自行根据小车资料配置,一般都很全面)
③远程控制
根据文章能够实现对Xavier进行远程桌面控制。(小车运动总不好背个显示器啥的)
三、实现
1、整体思路
①本文将人作为小车跟踪对象,将YOLOv5算法获得的人体目标框信息,变成简单的左转、右转或者直行以及原地转圈指令。
②然后该如何将这个指令发给小车呢,我对ROS控制小车方面也很生疏,那我的想法就是:结合ROS现有的键盘控制代码teleop_twist_keyboard.py,把按键信息改为控制指令,就完事了。(当然这个方法是我实在不知道ROS控制小车的代码该如何写时想出来的,精通ROS的大佬就当看个笑话好了哈)。
2、方案实现
①运行roscore
roscore②运行Base_control
这个launch文件用于建立Xavier与小车底盘的通信,负责收发信息。这个地方根据各自小车的资料运行,如果你能通过键盘控制小车运动了,那肯定知道是啥了。
roslaunch ./xxx/Base_control.launch③目标跟踪程序
在tensorrtx/yolov5文件夹下新建Follow.py ,复制以下代码(代码很粗糙,仅作参考)。
注意 libmyplugins.so,yolov5s.engine这两个文件的路径。
"""
An example that uses TensorRT's Python api to make inferences.
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import threading
import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('teleop_twist_keyboard')
import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
import sys, select, termios, tty
import ctypes
import os
import random
import sys
import threading
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
import torch
import torchvision
INPUT_W = 608 #INPUT_W = 640 这里可能要换,如果608跑不通
INPUT_H = 608 #INPUT_W = 640
CONF_THRESH = 0.25
IOU_THRESHOLD = 0.45
msg = ""
x = 0
y = 0
z = 0
th = 0
status = 0
int_box=[0,0,0,0]
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
"""
description: Plots one bounding box on image img,
this function comes from YoLov5 project.
param:
x: a box likes [x1,y1,x2,y2]
img: a opencv image object
color: color to draw rectangle, such as (0,255,0)
label: str
line_thickness: int
return:
no return
"""
tl = (
line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1
) # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(
img,
label,
(c1[0], c1[1] - 2),
0,
tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255],
thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)
class YoLov5TRT(object):
"""
description: A YOLOv5 class that warps TensorRT ops, preprocess and postprocess ops.
"""
def __init__(self, engine_file_path):
# Create a Context on this device,
self.cfx = cuda.Device(0).make_context()
stream = cuda.Stream()
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER)
# Deserialize the engine from file
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
host_inputs = []
cuda_inputs = []
host_outputs = []
cuda_outputs = []
bindings = []
for binding in engine:
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# Allocate host and device buffers
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
# Append the device buffer to device bindings.
bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
host_inputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
else:
host_outputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
# Store
self.stream = stream
self.context = context
self.engine = engine
self.host_inputs = host_inputs
self.cuda_inputs = cuda_inputs
self.host_outputs = host_outputs
self.cuda_outputs = cuda_outputs
self.bindings = bindings
def infer(self, input_image_path):
# threading.Thread.__init__(self)
# Make self the active context, pushing it on top of the context stack.
global int_box,x,y,z,th
self.cfx.push()
# Restore
stream = self.stream
context = self.context
engine = self.engine
host_inputs = self.host_inputs
cuda_inputs = self.cuda_inputs
host_outputs = self.host_outputs
cuda_outputs = self.cuda_outputs
bindings = self.bindings
# Do image preprocess
input_image, image_raw, origin_h, origin_w = self.preprocess_image(
input_image_path
)
# Copy input image to host buffer
np.copyto(host_inputs[0], input_image.ravel())
# Transfer input data to the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(cuda_inputs[0], host_inputs[0], stream)
# Run inference.
context.execute_async(bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(host_outputs[0], cuda_outputs[0], stream)
# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.cfx.pop()
# Here we use the first row of output in that batch_size = 1
output = host_outputs[0]
# Do postprocess
result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid = self.post_process(
output, origin_h, origin_w)
if torch.tensor(0) in result_classid:
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
box = result_boxes[i]
if int(result_classid[i]) == 0 and result_scores[i] >= 0.5:
int_box = list(map(int, box.numpy().tolist())) # tensor变为int
center=int((int_box[0] + int_box[2]) / 2)
print("center:", center)
print('result:', 1)
if center >= 900:
print("right")
x, y, z, th = 1, 0, 0, -1
pass
elif center <= 300:
print("left")
x, y, z, th = 1, 0, 0, 1
pass
else:
print("go")
x,y,z,th = 1,0,0,0
plot_one_box(
box,
image_raw,
label="{}:{:.2f}".format(
categories[int(result_classid[i])], result_scores[i]
),
)
else:
int_box = int_box
pass
return image_raw
else:
prebox = int_box
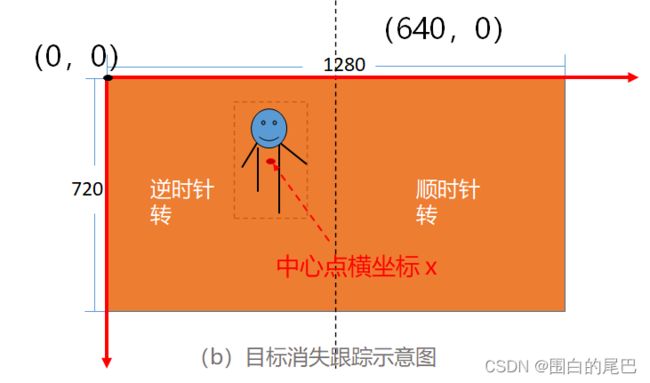
precenter=int((prebox[0] + prebox[2])/2)
print('result:', 2)
if int_box != [0, 0, 0, 0]:
if precenter >= 650:
print("turn right")
x, y, z, th = 0, 0, 0, -1
else:
print("turn left")
x, y, z, th = 0, 0, 0, 1
else:
print("stop!")
x, y, z, th = 0, 0, 0, 0
print("precenter", precenter)
return input_image_path
# parent, filename = os.path.split(input_image_path)
# save_name = os.path.join(parent, "output_" + filename)
# # Save image
# cv2.imwrite(save_name, image_raw)
def destroy(self):
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.cfx.pop()
def preprocess_image(self, input_image_path):
"""
description: Read an image from image path, convert it to RGB,
resize and pad it to target size, normalize to [0,1],
transform to NCHW format.
param:
input_image_path: str, image path
return:
image: the processed image
image_raw: the original image
h: original height
w: original width
"""
image_raw = input_image_path
h, w, c = image_raw.shape
image = cv2.cvtColor(image_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Calculate widht and height and paddings
r_w = INPUT_W / w
r_h = INPUT_H / h
if r_h > r_w:
tw = INPUT_W
th = int(r_w * h)
tx1 = tx2 = 0
ty1 = int((INPUT_H - th) / 2)
ty2 = INPUT_H - th - ty1
else:
tw = int(r_h * w)
th = INPUT_H
tx1 = int((INPUT_W - tw) / 2)
tx2 = INPUT_W - tw - tx1
ty1 = ty2 = 0
# Resize the image with long side while maintaining ratio
image = cv2.resize(image, (tw, th))
# Pad the short side with (128,128,128)
image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
image, ty1, ty2, tx1, tx2, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, (128, 128, 128)
)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
# Normalize to [0,1]
image /= 255.0
# HWC to CHW format:
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
# CHW to NCHW format
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
# Convert the image to row-major order, also known as "C order":
image = np.ascontiguousarray(image)
return image, image_raw, h, w
def xywh2xyxy(self, origin_h, origin_w, x):
"""
description: Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
param:
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
x: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [center_x, center_y, w, h]
return:
y: A boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
"""
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.zeros_like(x)
r_w = INPUT_W / origin_w
r_h = INPUT_H / origin_h
if r_h > r_w:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 - (INPUT_H - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 - (INPUT_H - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y /= r_w
else:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 - (INPUT_W - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 - (INPUT_W - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
y /= r_h
return y
def post_process(self, output, origin_h, origin_w):
"""
description: postprocess the prediction
param:
output: A tensor likes [num_boxes,cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, ...]
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
return:
result_boxes: finally boxes, a boxes tensor, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
result_scores: finally scores, a tensor, each element is the score correspoing to box
result_classid: finally classid, a tensor, each element is the classid correspoing to box
"""
# Get the num of boxes detected
num = int(output[0])
# Reshape to a two dimentional ndarray
pred = np.reshape(output[1:], (-1, 6))[:num, :]
# to a torch Tensor
pred = torch.Tensor(pred).cuda()
# Get the boxes
boxes = pred[:, :4]
# Get the scores
scores = pred[:, 4]
# Get the classid
classid = pred[:, 5]
# Choose those boxes that score > CONF_THRESH
si = scores > CONF_THRESH
boxes = boxes[si, :]
scores = scores[si]
classid = classid[si]
# Trandform bbox from [center_x, center_y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
boxes = self.xywh2xyxy(origin_h, origin_w, boxes)
# Do nms
indices = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_threshold=IOU_THRESHOLD).cpu()
result_boxes = boxes[indices, :].cpu()
result_scores = scores[indices].cpu()
result_classid = classid[indices].cpu()
return result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid
class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, func, args):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.func = func
self.args = args
def run(self):
self.func(*self.args)
class PublishThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, rate):
super(PublishThread, self).__init__()
self.publisher = rospy.Publisher('cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size = 1)
self.x = 0.0
self.y = 0.0
self.z = 0.0
self.th = 0.0
self.speed = 0.0
self.turn = 0.0
self.condition = threading.Condition()
self.done = False
# Set timeout to None if rate is 0 (causes new_message to wait forever
# for new data to publish)
if rate != 0.0:
self.timeout = 1.0 / rate
else:
self.timeout = None
self.start()
def wait_for_subscribers(self):
i = 0
while not rospy.is_shutdown() and self.publisher.get_num_connections() == 0:
if i == 4:
print("Waiting for subscriber to connect to {}".format(self.publisher.name))
rospy.sleep(0.5)
i += 1
i = i % 5
if rospy.is_shutdown():
raise Exception("Got shutdown request before subscribers connected")
def update(self, x, y, z, th, speed, turn):
self.condition.acquire()
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.z = z
self.th = th
self.speed = speed
self.turn = turn
# Notify publish thread that we have a new message.
self.condition.notify()
self.condition.release()
def stop(self):
self.done = True
self.update(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
self.join()
def run(self):
twist = Twist()
while not self.done:
self.condition.acquire()
# Wait for a new message or timeout.
self.condition.wait(self.timeout)
# Copy state into twist message.
twist.linear.x = self.x * self.speed
twist.linear.y = self.y * self.speed
twist.linear.z = self.z * self.speed
twist.angular.x = 0
twist.angular.y = 0
twist.angular.z = self.th * self.turn
self.condition.release()
# Publish.
self.publisher.publish(twist)
# Publish stop message when thread exits.
twist.linear.x = 0
twist.linear.y = 0
twist.linear.z = 0
twist.angular.x = 0
twist.angular.y = 0
twist.angular.z = 0
self.publisher.publish(twist)
def getKey(key_timeout):
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
rlist, _, _ = select.select([sys.stdin], [], [], key_timeout)
if rlist:
key = sys.stdin.read(1)
else:
key = ''
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, settings)
return key
def vels(speed, turn):
return "currently:\tspeed %s\tturn %s " % (speed,turn)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# load custom plugins
PLUGIN_LIBRARY = "build/libmyplugins.so"
ctypes.CDLL(PLUGIN_LIBRARY)
engine_file_path = "build/yolov5s.engine"
settings = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
rospy.init_node('my_code2')
speed = rospy.get_param("~speed", 0.5)
turn = rospy.get_param("~turn", 1.0)
repeat = rospy.get_param("~repeat_rate", 0.0)
# key_timeout = rospy.get_param("~key_timeout", 0.0)
# if key_timeout == 0.0:
# key_timeout = None
pub_thread = PublishThread(repeat)
# load coco labels
categories = ["person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard",
"tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple",
"sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch",
"potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone",
"microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear",
"hair drier", "toothbrush"]
# a YoLov5TRT instance
yolov5_wrapper = YoLov5TRT(engine_file_path)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID') # output video codec
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
save_path = "save/video_out.avi"
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, fourcc, fps, (w, h))
_,image =cap.read()
i=0
try:
pub_thread.wait_for_subscribers()
pub_thread.update(x, y, z, th, speed, turn)
print(msg)
print(vels(speed, turn))
while 1:
_,image =cap.read()
img=yolov5_wrapper.infer(image)
cv2.imshow("result", img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0XFF == ord('q'): # 1 millisecond
break
pub_thread.update(x, y, z, th, speed, turn)
i=i+1
if i<=100:
# vid_writer.write(img)
pass
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
cap.release()
vid_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
yolov5_wrapper.destroy()
pub_thread.stop()
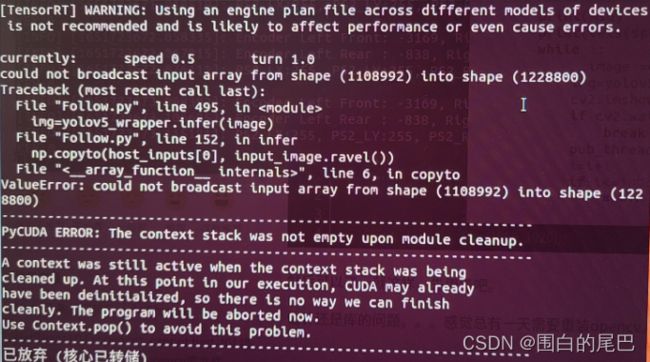
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, settings)【注意】关于报错问题,下面两张图片报错是同一个问题,主要是代码的INPUT_W ,INPUT_H 两个参数,有小伙伴是将这两个参数改为640跑通的。
③执行代码
conda activate yolov5env
python Follow.py3、实现效果
整个控制效果如图,实现了简单的人体跟踪,除了控制有点僵硬,感觉还可以。可惜车上的雷达没有利用好,当时是打算结合雷达做避障功能的,但是由于个人尚未涉及SLAM方面的知识(太菜),所以成品很简单粗糙。对于不同的项目而言,大家可以根据自己的跟踪目标单独训练权重。由于本文直接使用官方权重文件,所以在检测速度上会有所影响。
四、总结
我已经离开之前的学校,不再有设备供我使用,那本文便作为Jetson系列的终章吧。文章去年七月就躺在我的草稿箱里,但是由于各种原因拖到了现在才完成。全文跟踪方案很简单,就是目标检测。没有避障、路径规划的操作,如果感兴趣大家可以作为参考继续做下去。我接触Xavier有大半年时间,这个这巴掌大小的设备竟有小型工作站般的性能,实在令人不可思议,个人很喜欢这个产品 。如果我日后开始工作,资金充沛,那么我会自己入手一个,到时本专栏将继续更新下去。翻过一座山又是一座山,咱们下座山峰见。
五、参考文献
1、GitHub - wang-xinyu/tensorrtx: Implementation of popular deep learning networks with TensorRT network definition API
2、GitHub - ultralytics/yolov5: YOLOv5 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite
3、ROS: Welcome to the ROS Community
4、NVIDIA TensorRT | NVIDIA Developer